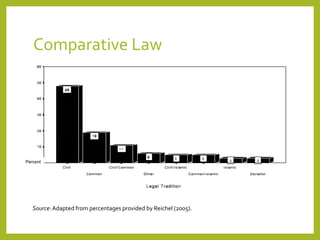
This document provides an overview of comparative law and different legal traditions around the world. It discusses the importance of understanding legal systems other than one's own and describes some key features of the major legal traditions: common law, civil law, socialist law, and Islamic law. For each tradition, it examines historical origins, basic structural features like use of written codes versus precedent, adversarial versus inquisitorial procedures, and role of judicial review. Specific examples are given of legal systems from different countries and cultures to illustrate variations within the overarching traditions.