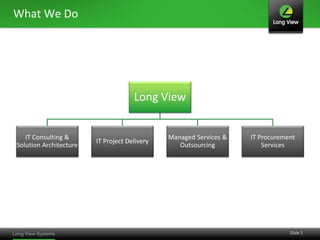
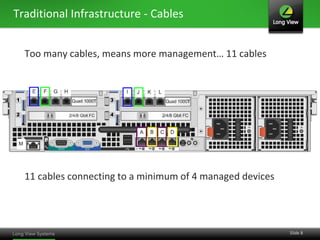
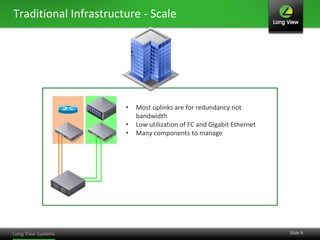
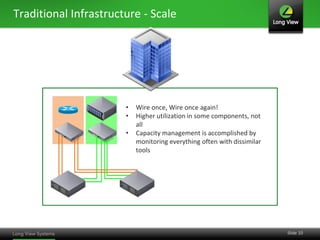
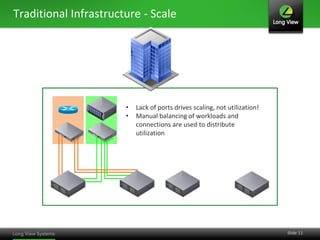
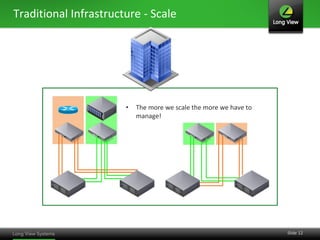
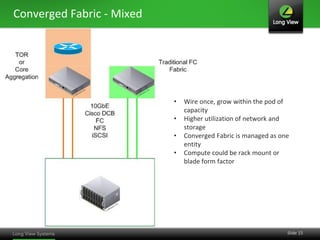
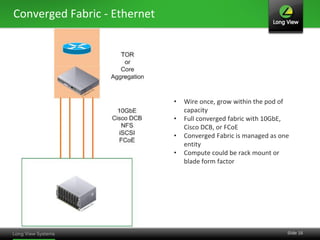
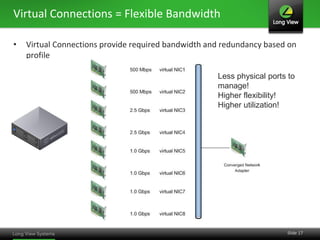
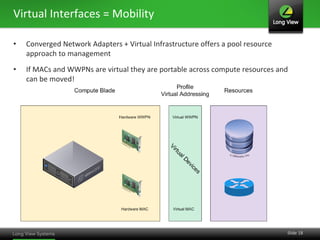
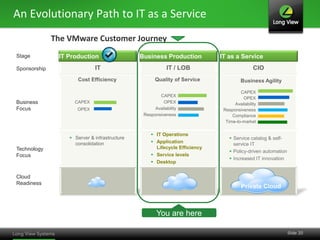
The document discusses the transition from traditional IT infrastructure to converged infrastructure as an effective data center strategy. It outlines the benefits of converged infrastructure, such as increased resource utilization, streamlined management, and improved agility, emphasizing the importance of adopting new technologies and methodologies. The content also highlights the timing for making this transition and offers steps for assessing hardware and network topologies to support this change.