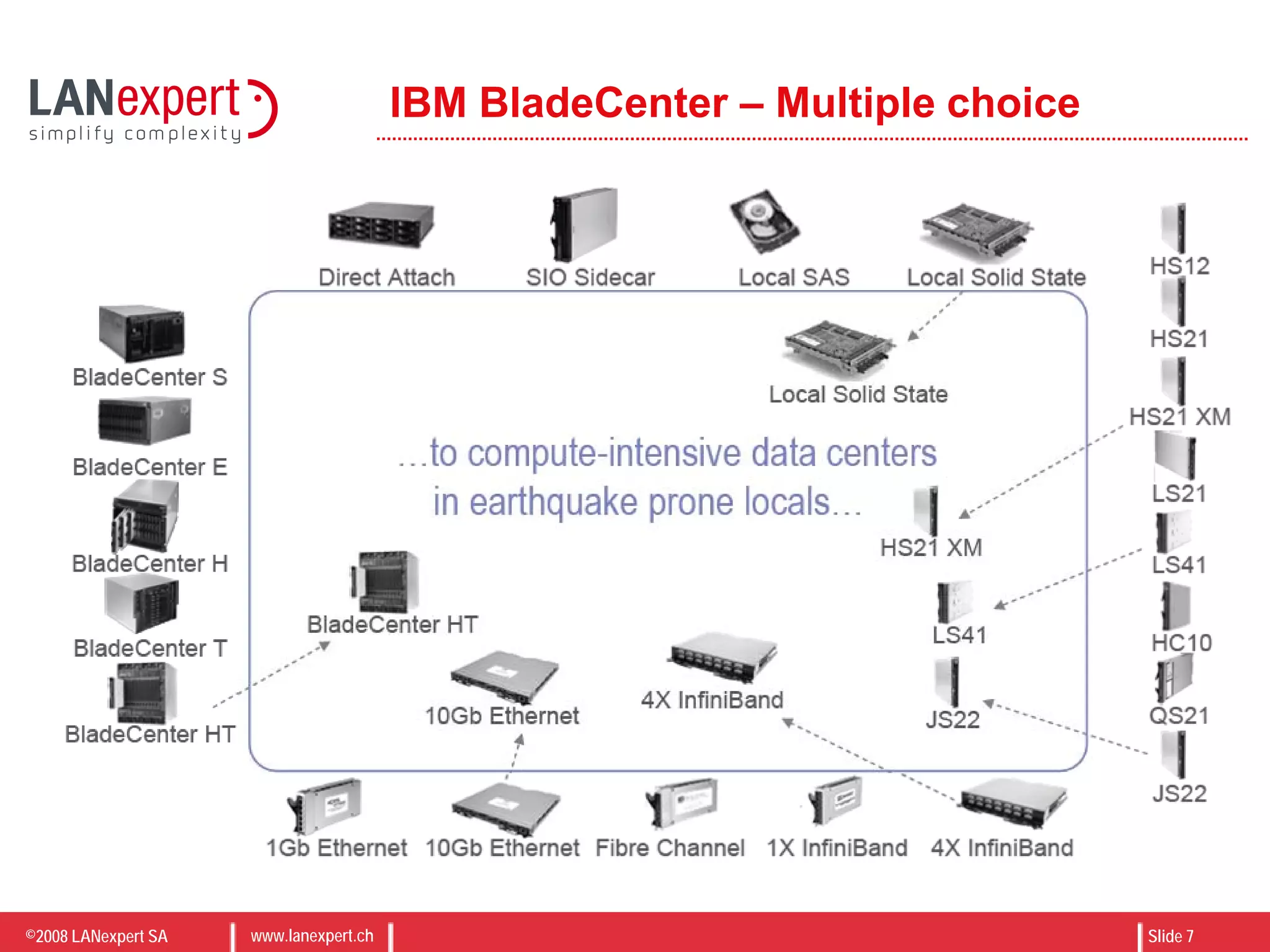
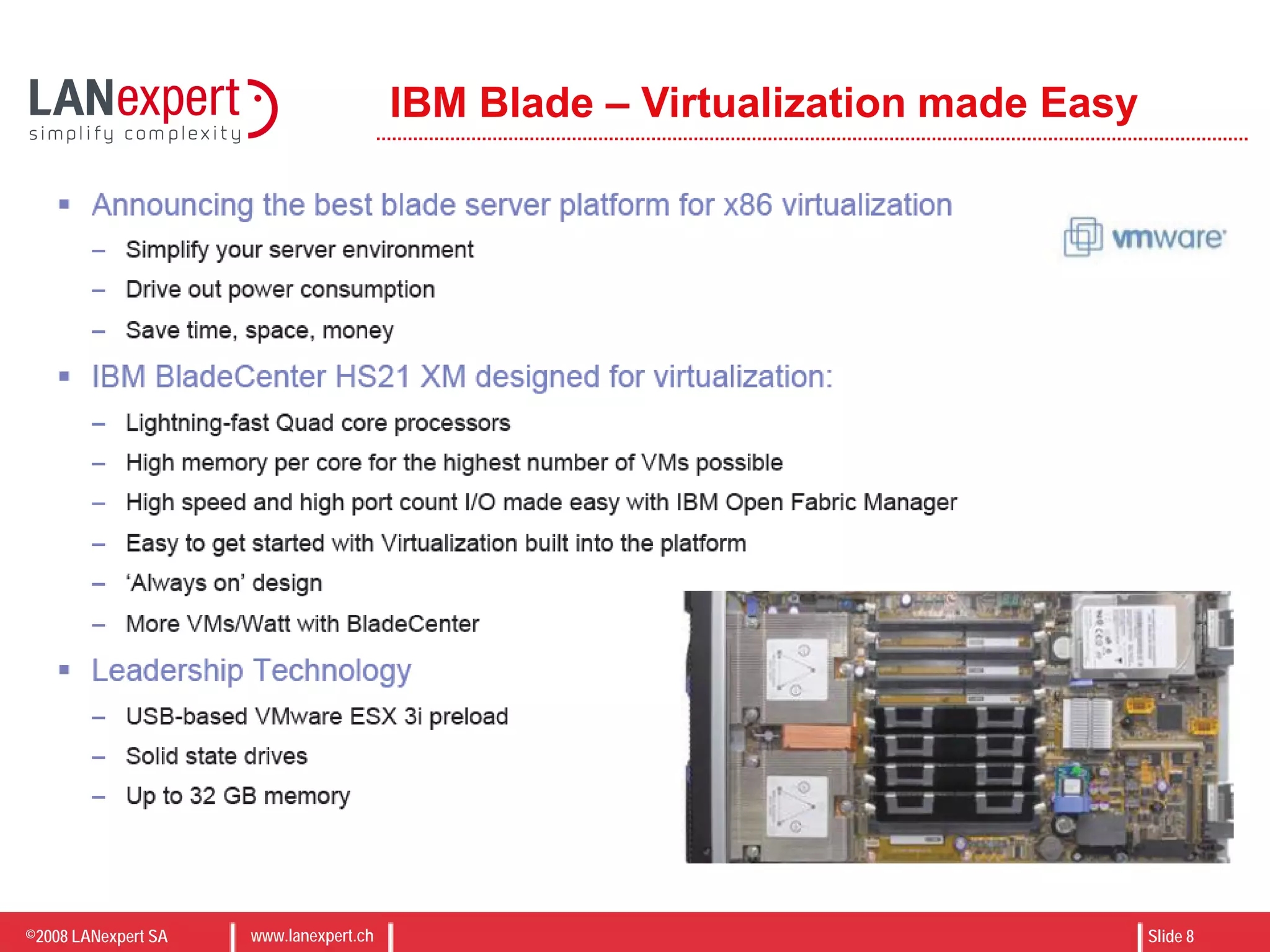
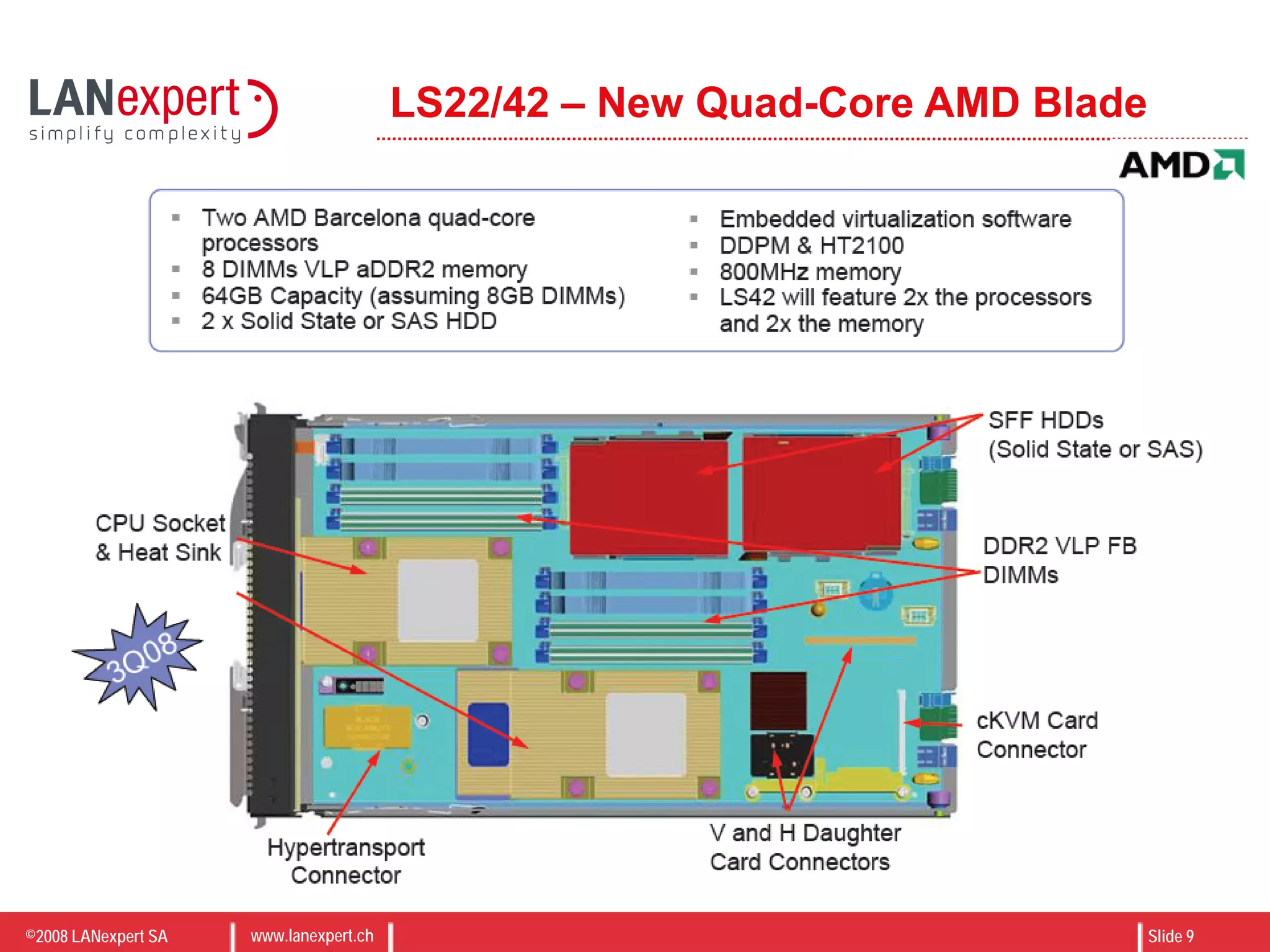
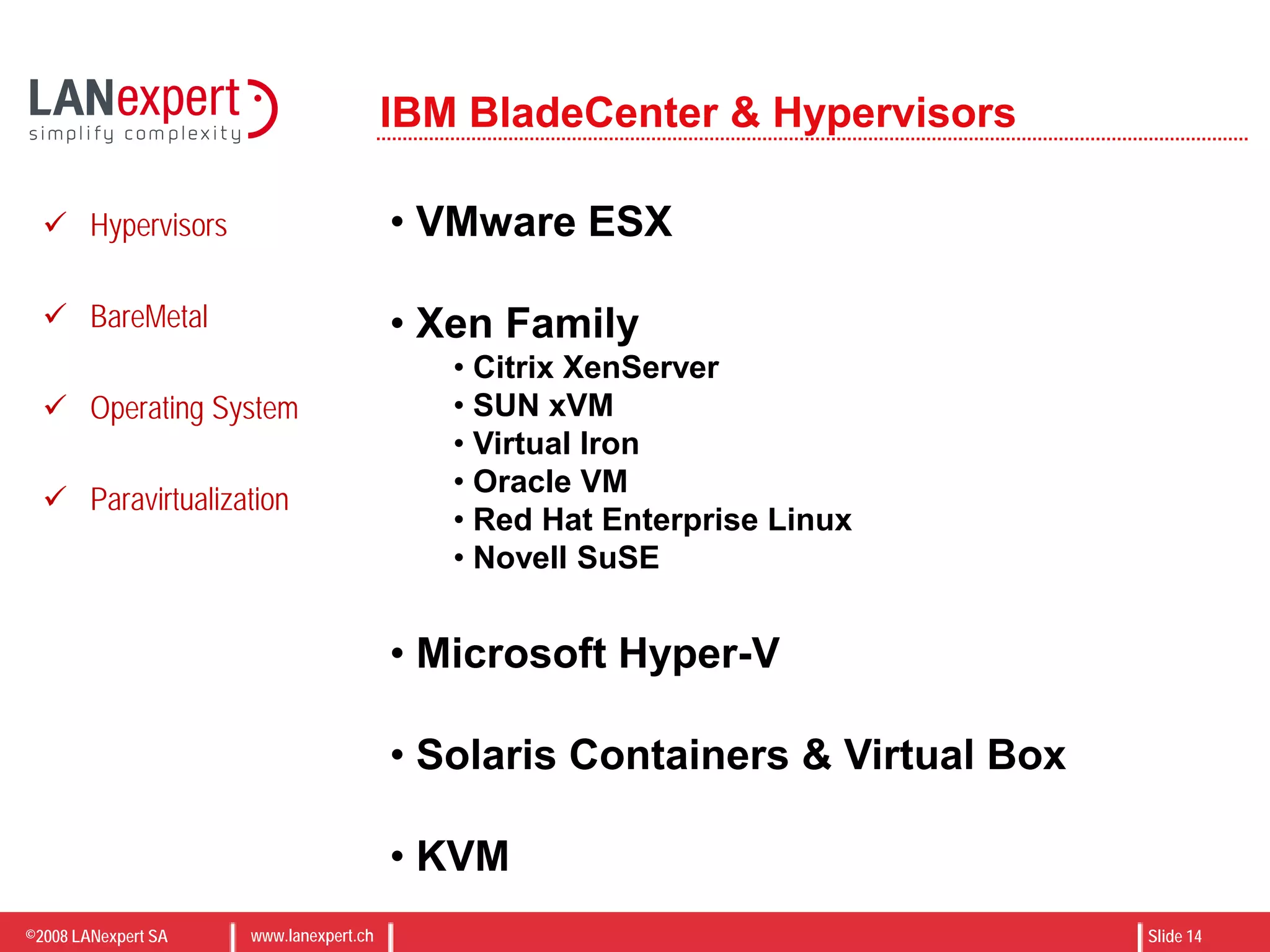
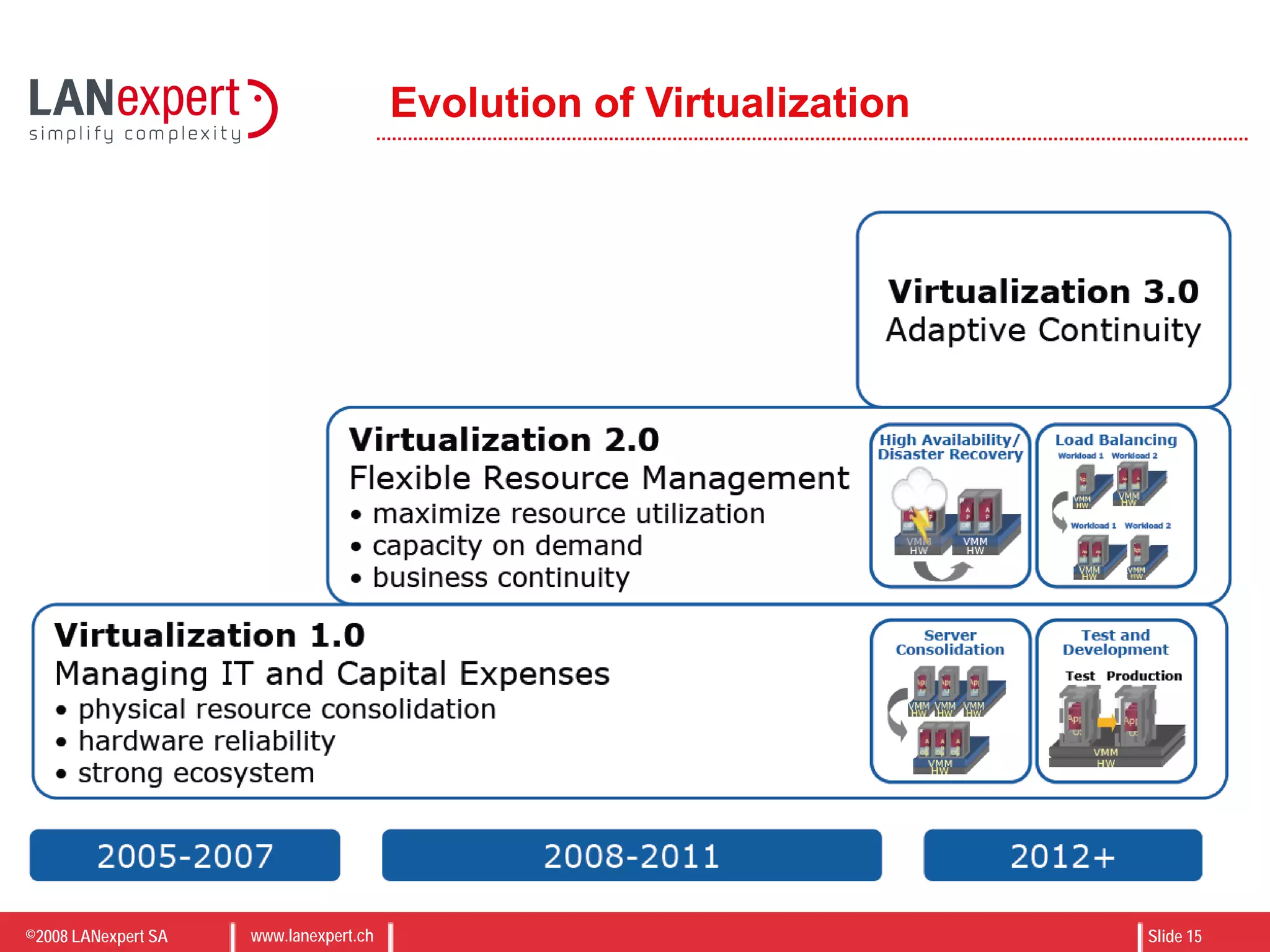
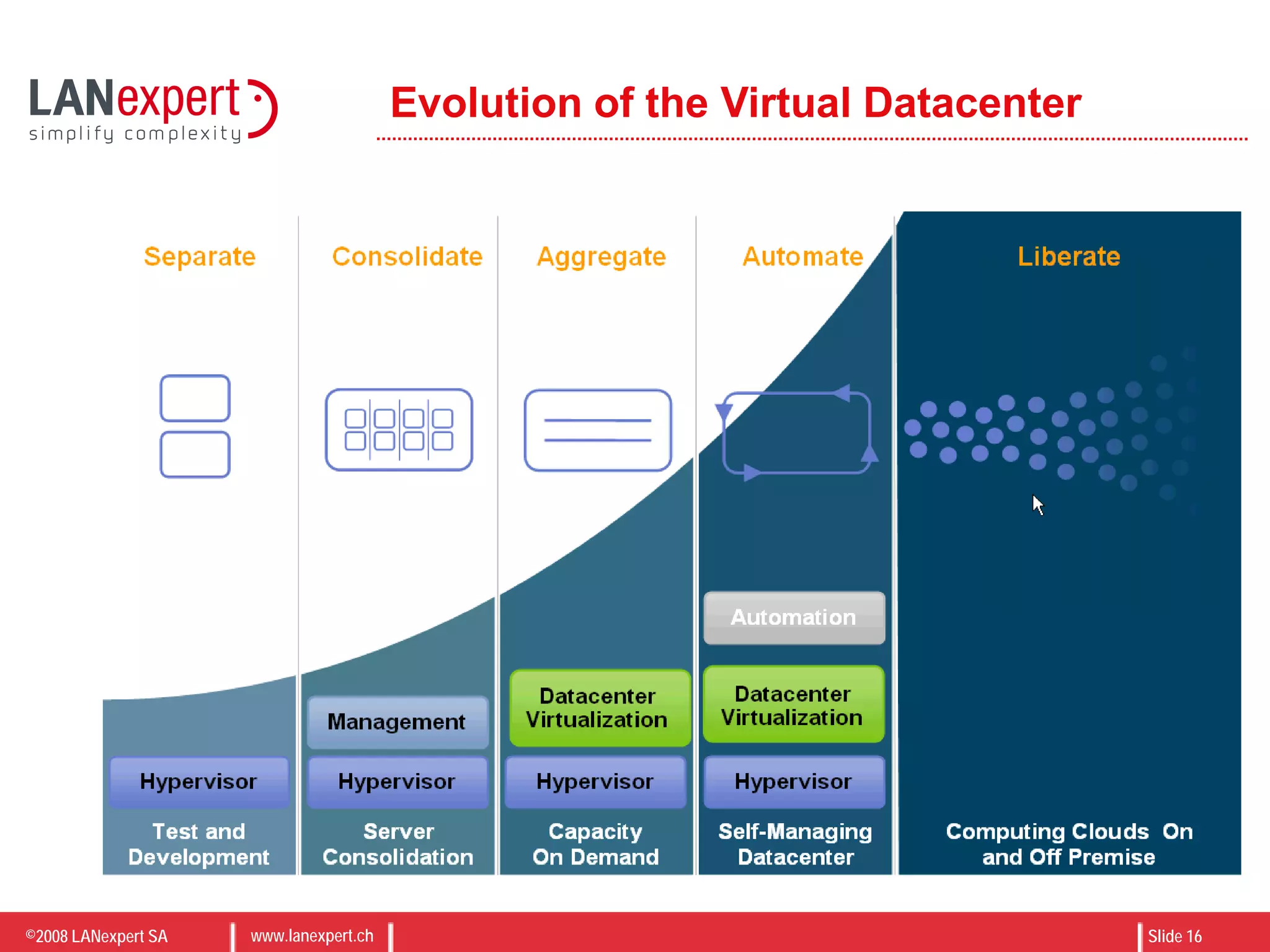
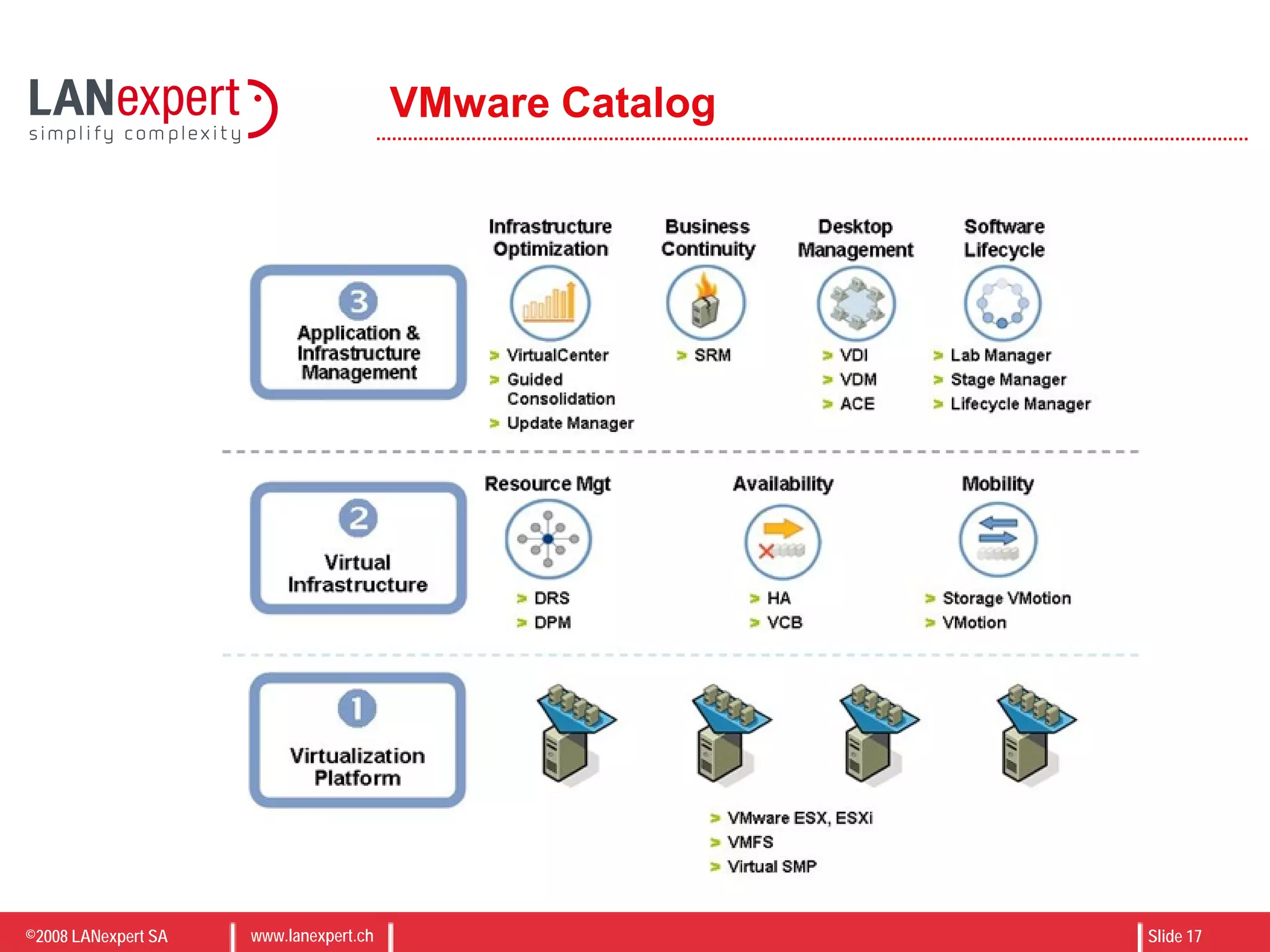
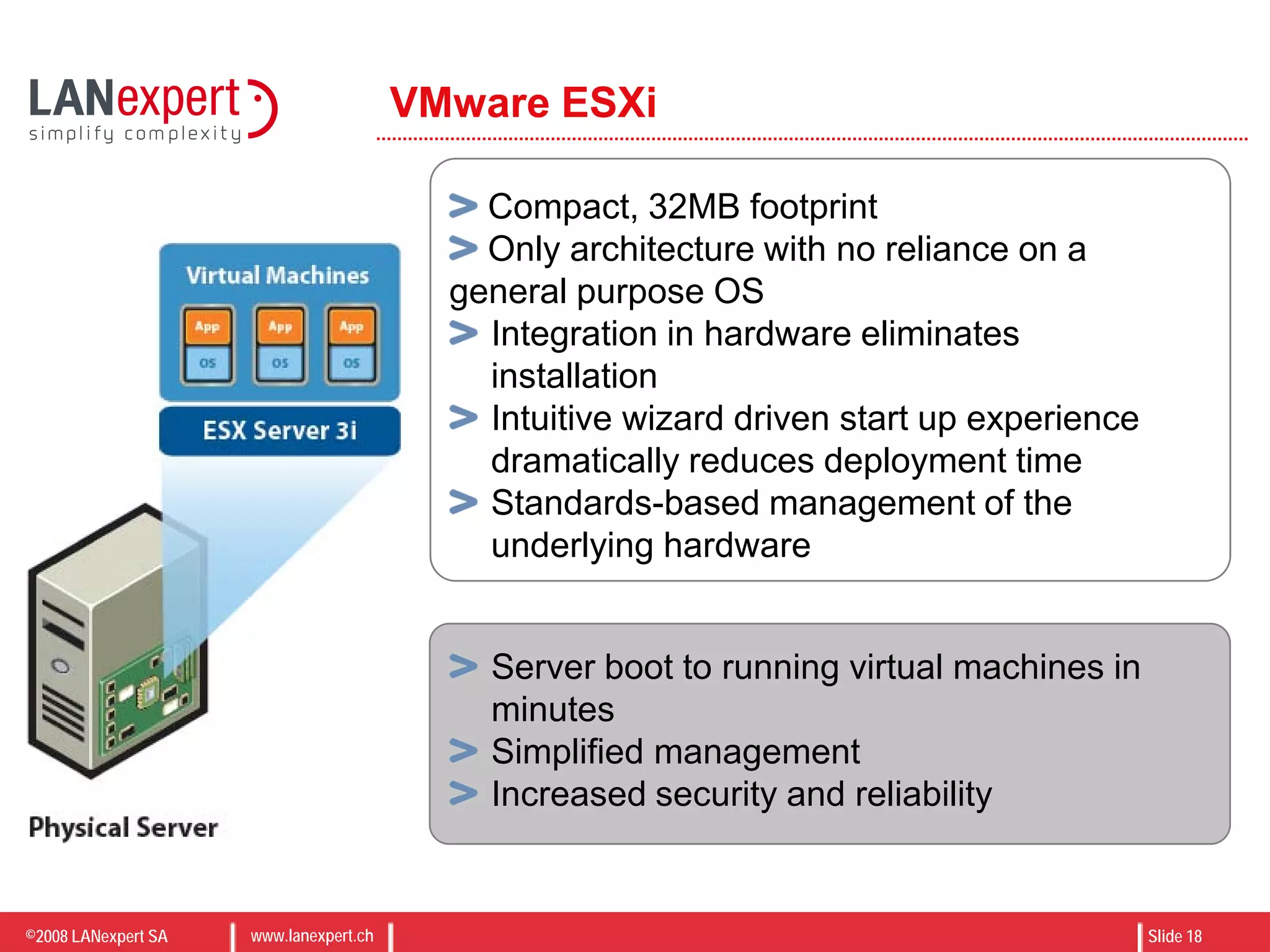
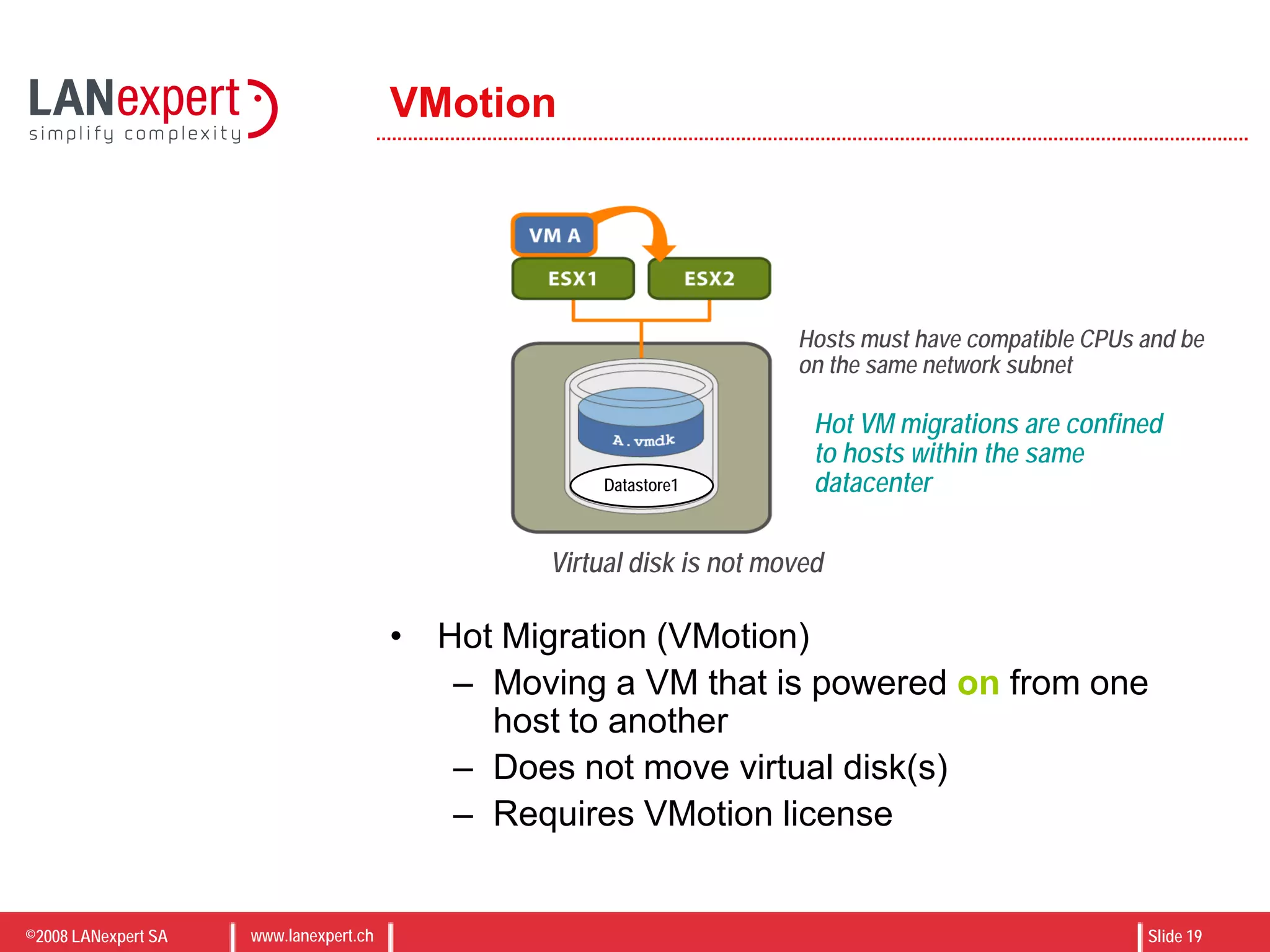
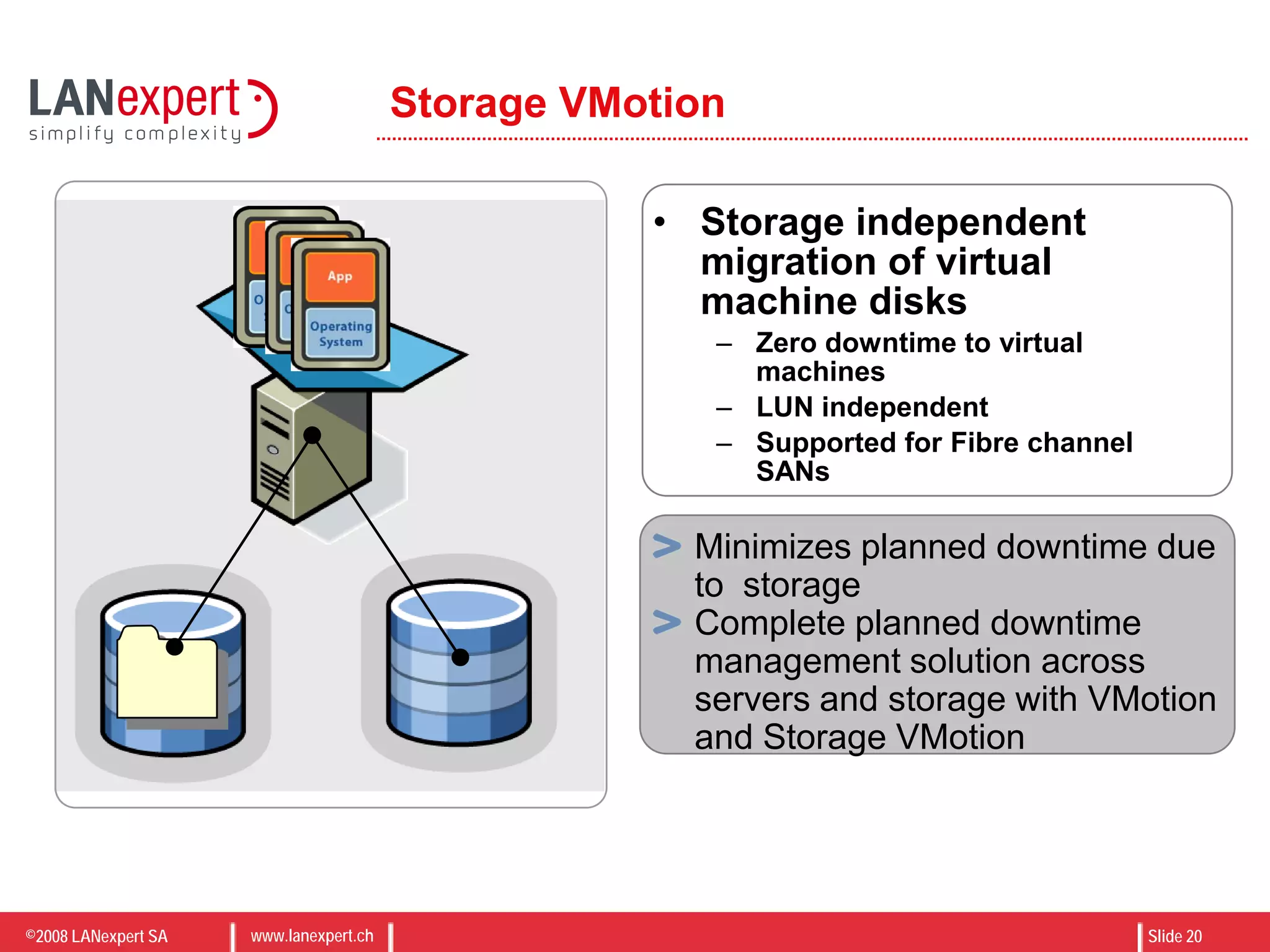
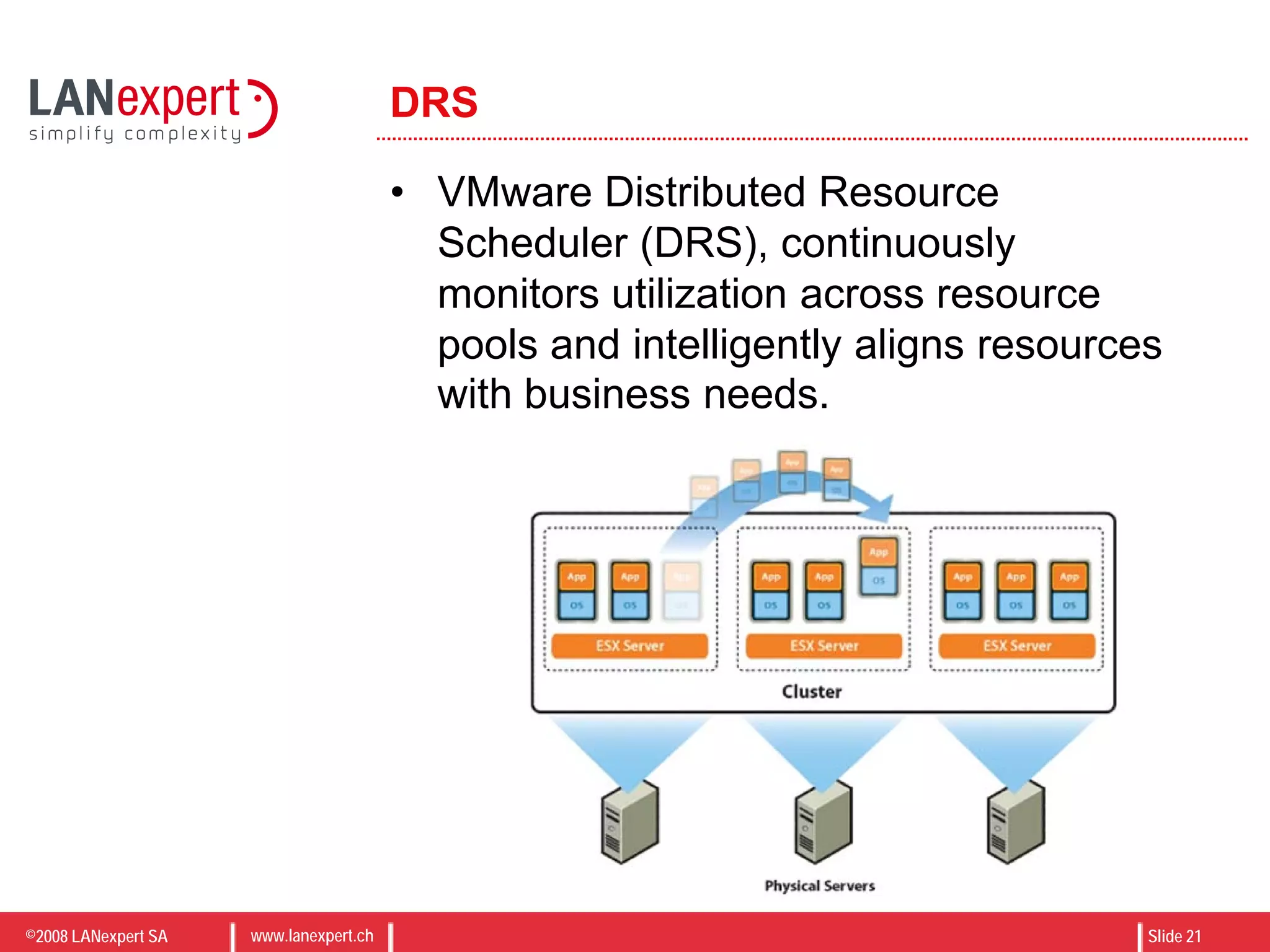
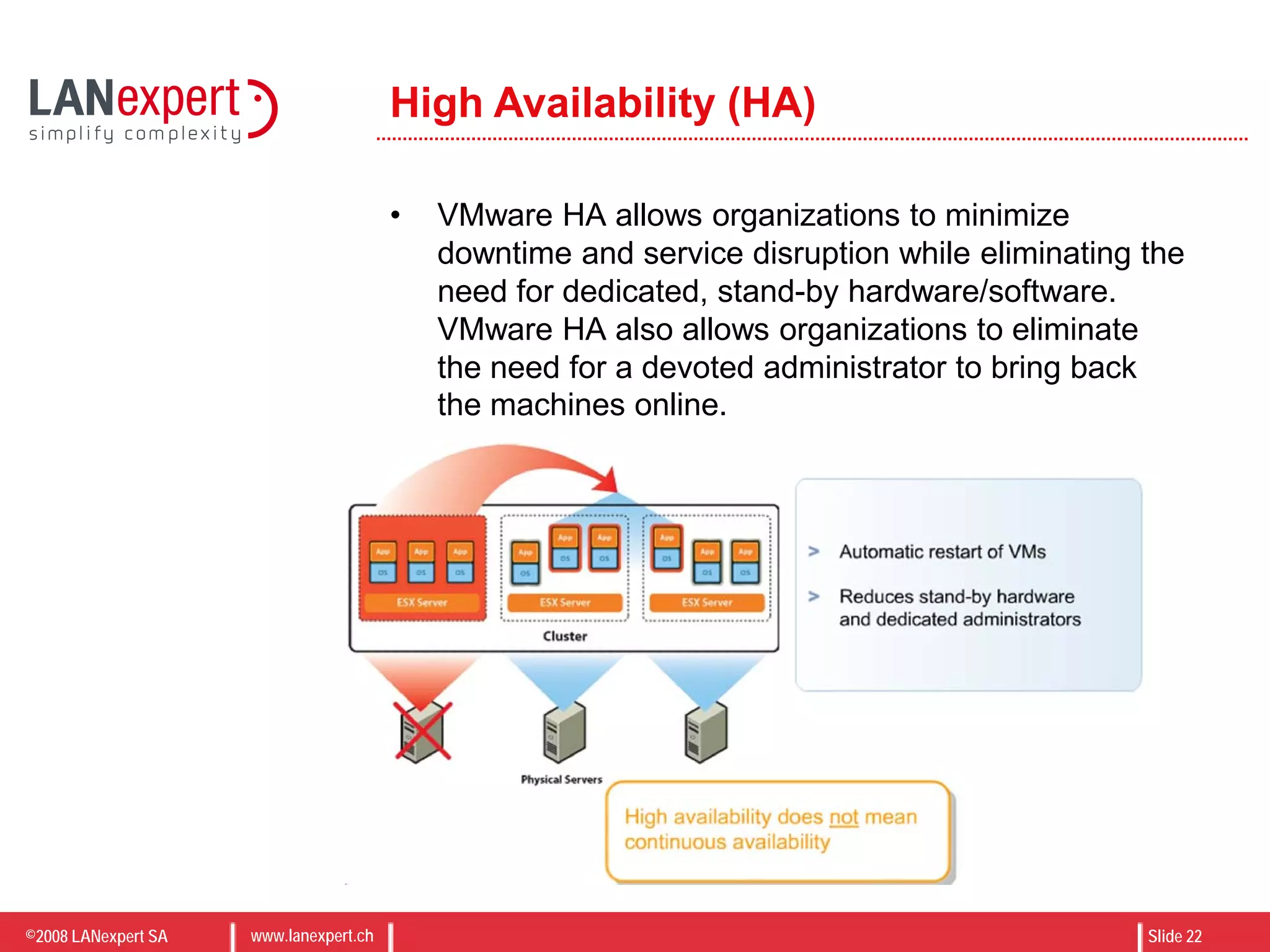
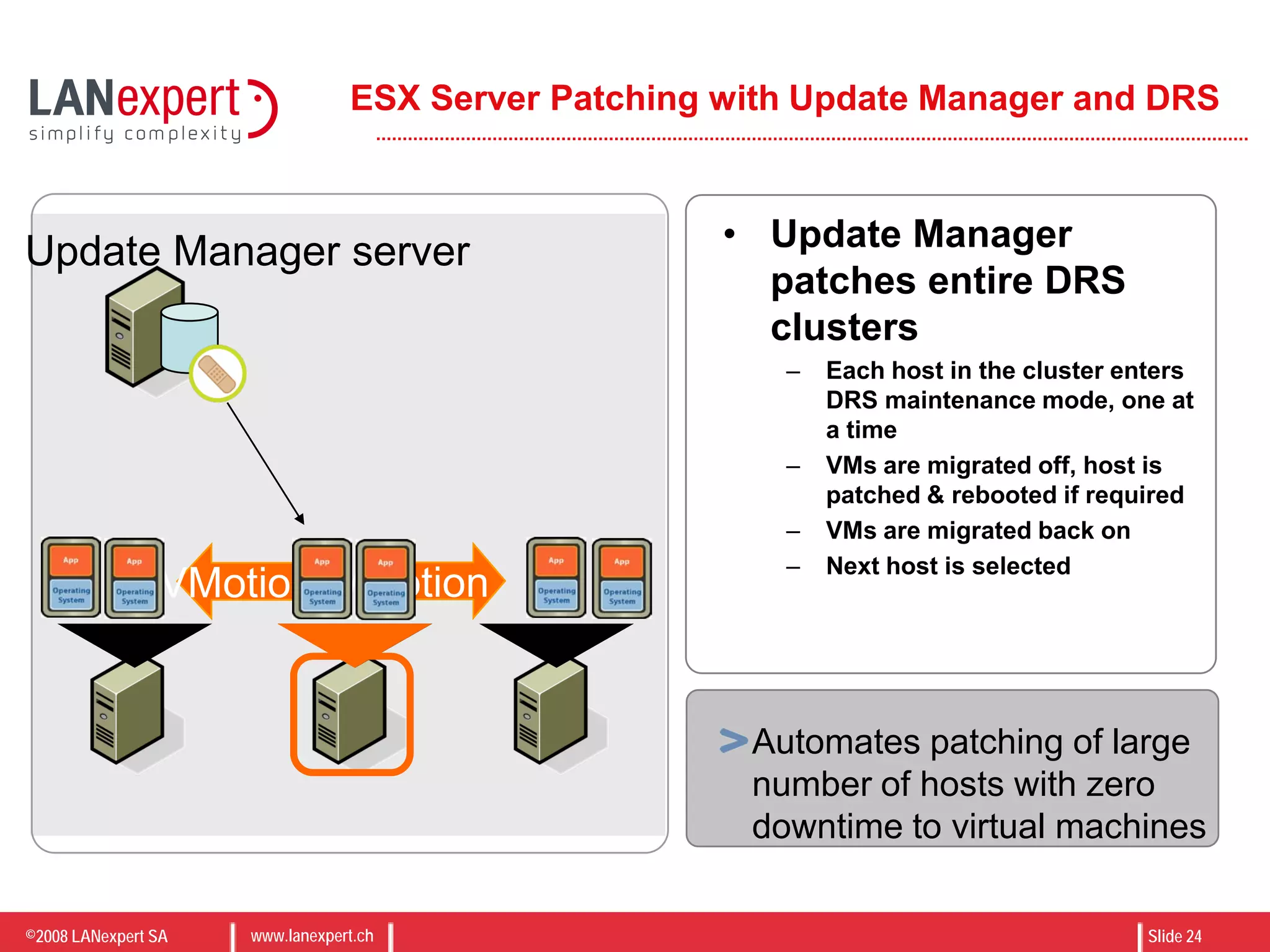
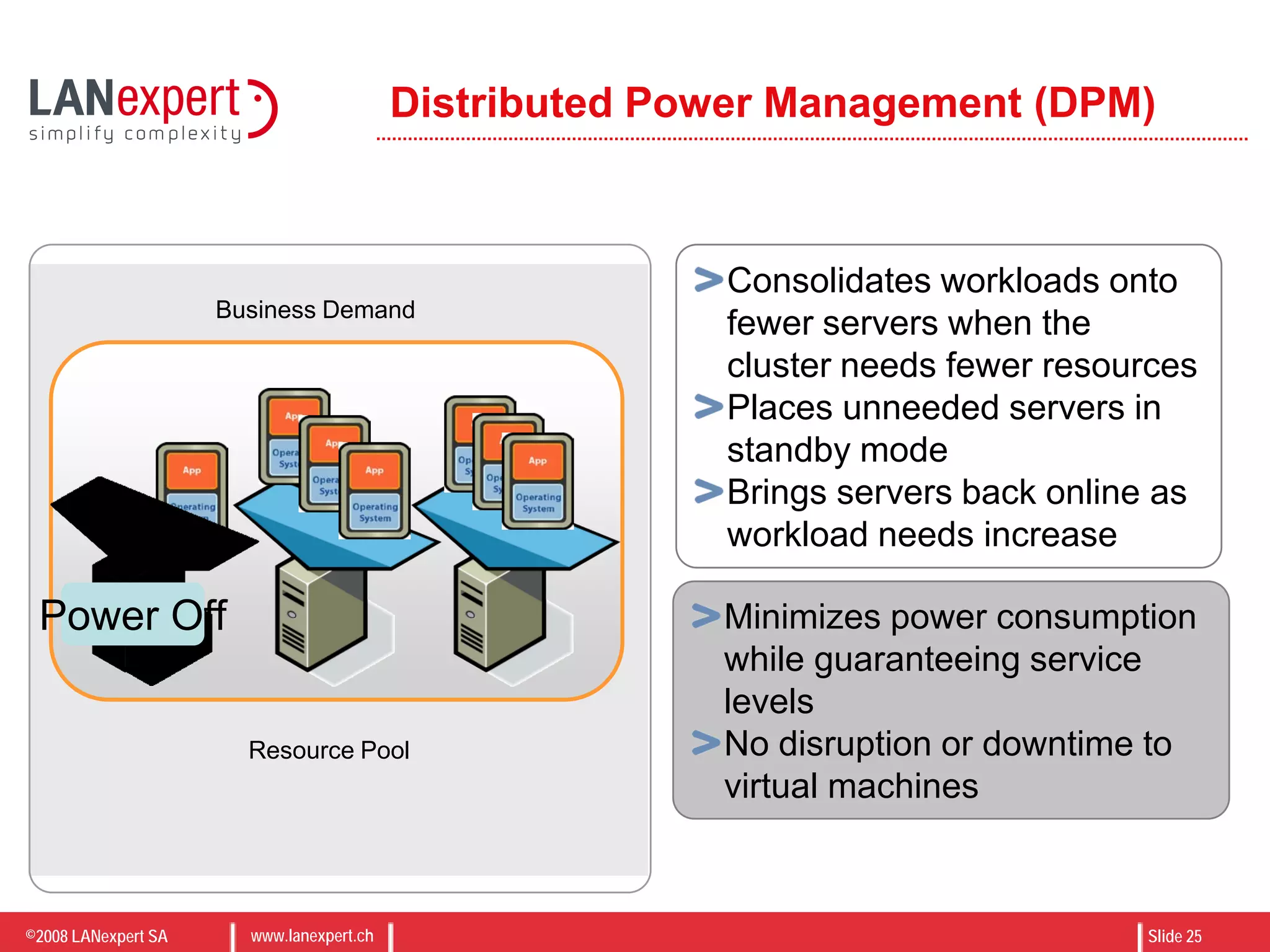
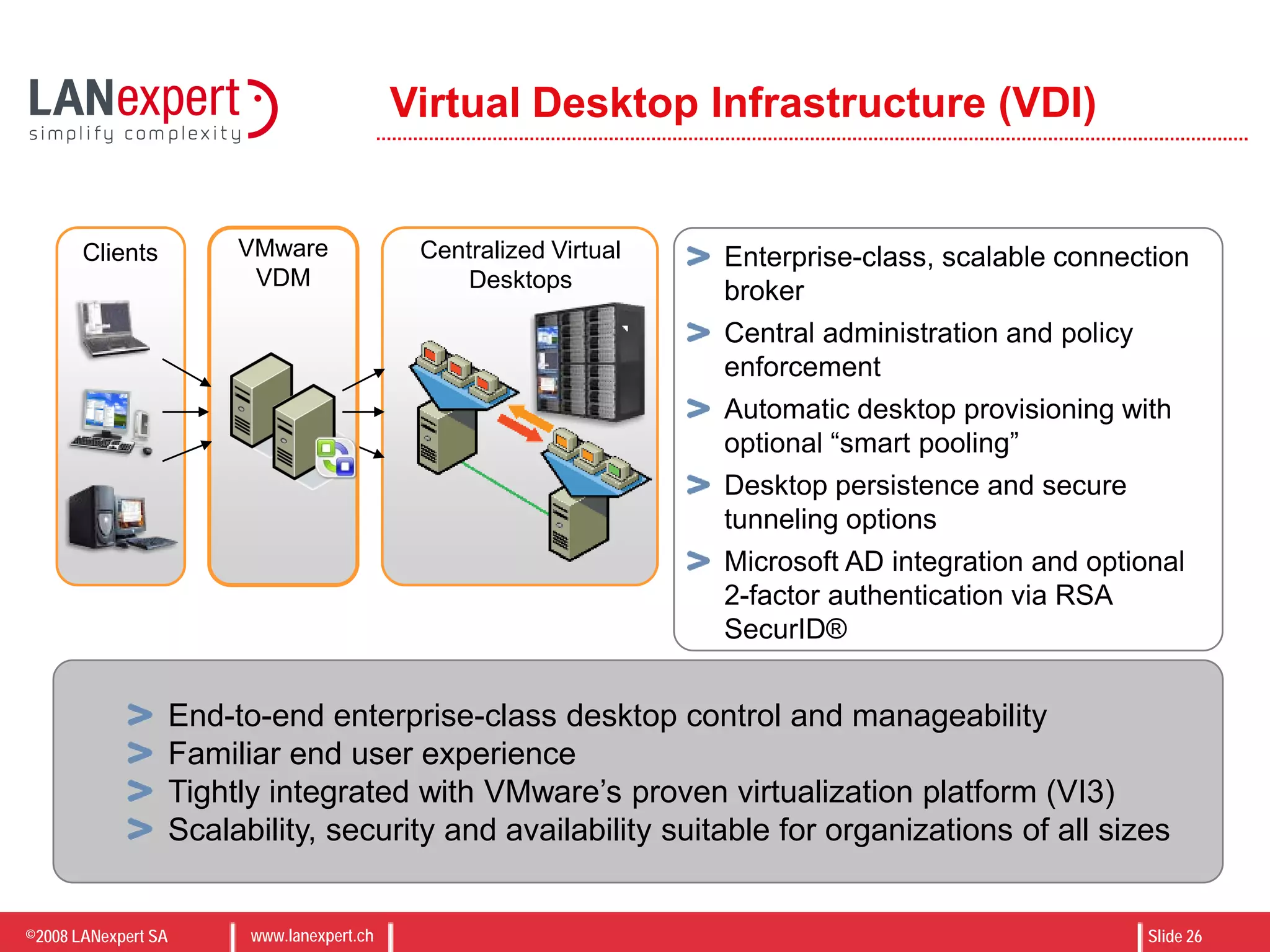
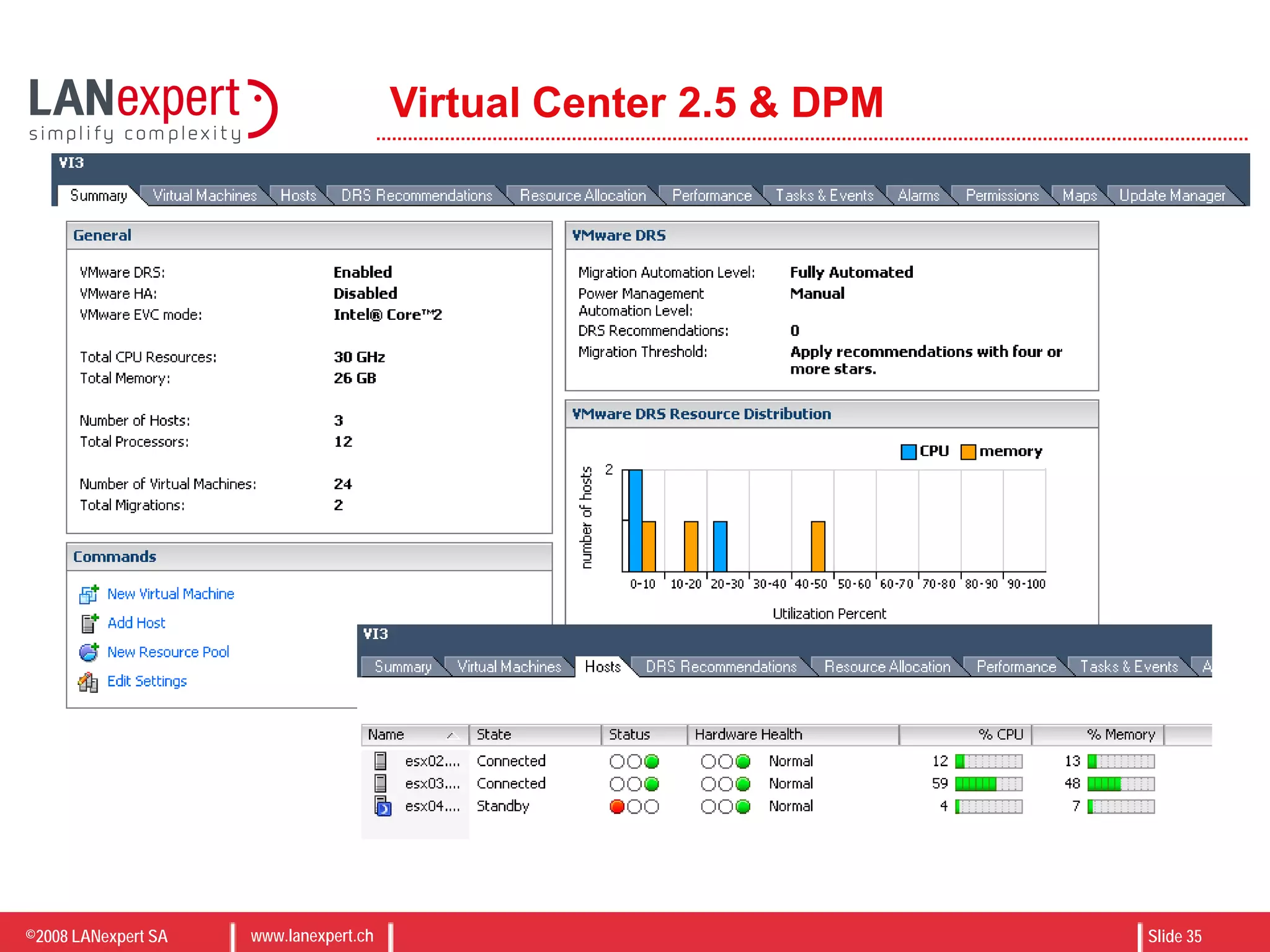
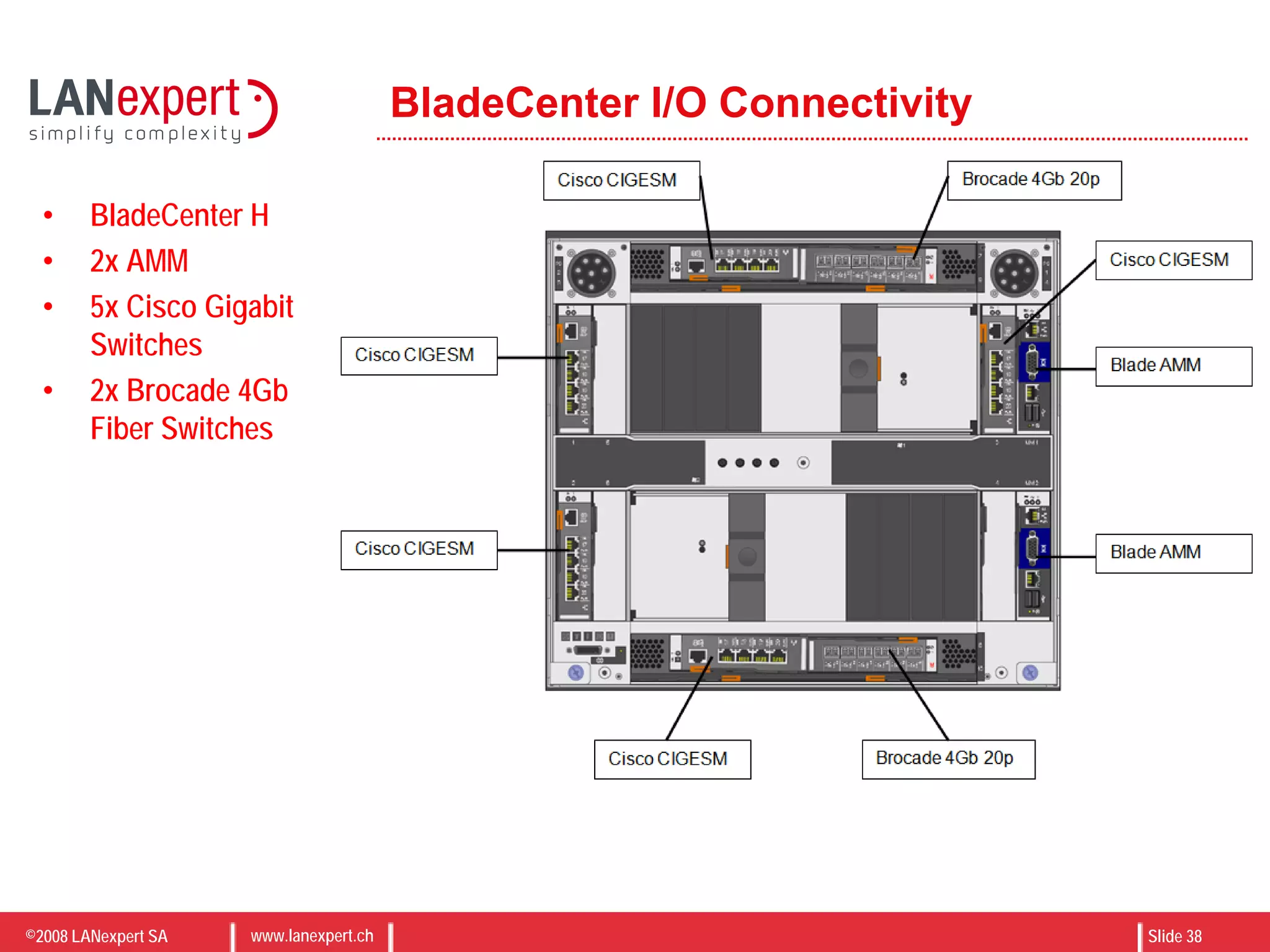
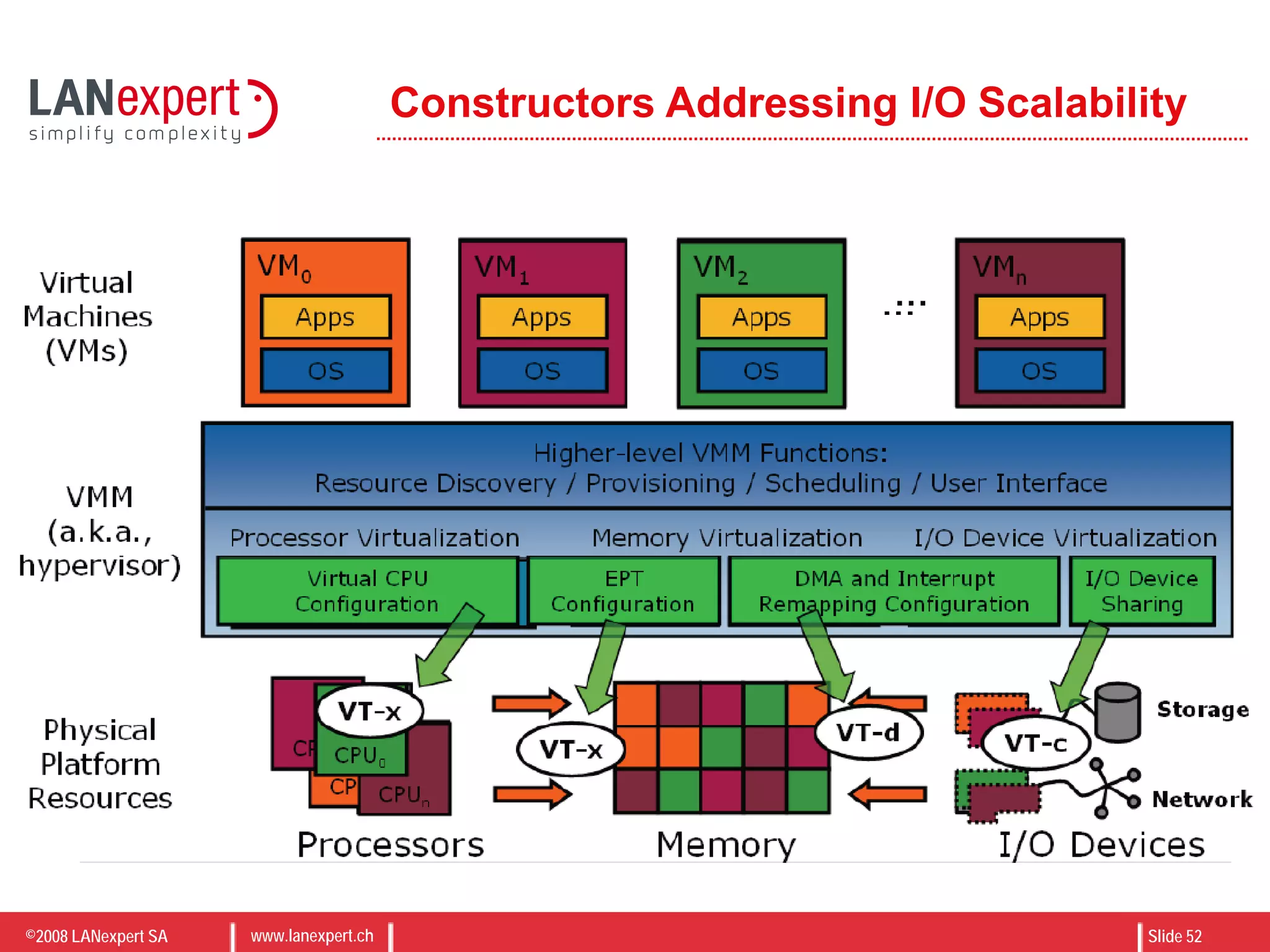
The document discusses virtualization on IBM BladeCenter, outlining the differences between consolidation and virtualization, as well as the evolution of CPU technology for virtualization management. It emphasizes the benefits of using IBM BladeCenter for server consolidation, including cost reduction and increased efficiency, and explores various virtualization technologies and their applications. Key components include VMware vSphere features, high availability, and disaster recovery management strategies.


![©2008 LANexpert SA www.lanexpert.ch Slide 3
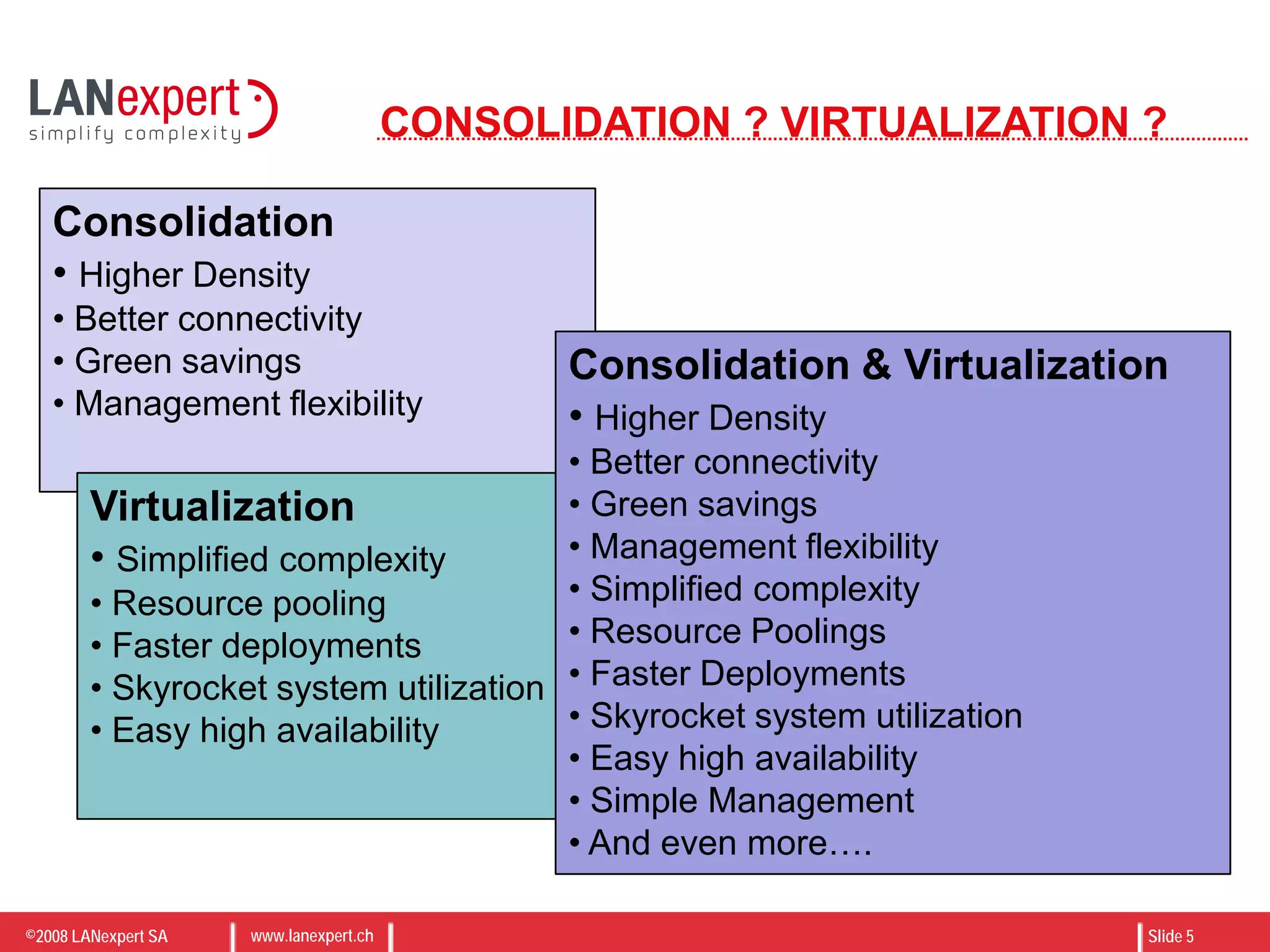
WHAT IS CONSOLIDATION ?
“[Consolidation is] an approach to the
efficient usage of server resources in
order to reduce the total number of
servers, increase datacenter density,
optimize connectivity, reduce energy and
TCO”
IBM BladeCenters are the most efficient
way to server consolidation
Higher density and server count per U
Integrated network backplane
Green technology at best TCO
Reduce Server Count
Increase Datacenter
density
Optimize connectivity
Reduce TCO
Green savings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virtualizationonibmbladecenter-1225792256455769-8/75/Virtualization-on-IBM-Blade-Center-3-2048.jpg)
![©2008 LANexpert SA www.lanexpert.ch Slide 4
WHAT IS VIRTUALIZATION ?
“[Virtualization is] a technique for hiding
the physical characteristics of computing
resources from the way in which other
systems, applications, or end users
interact with those resources”
In other words: Simplify Complexity
For computing, virtualization can be grouped in
two types:
• Resource virtualization (Storage, Network, etc.)
• Platform virtualization (Hypervisor)
Virtualization started
in 1960s by IBM…
Virtual Memory
VLAN, trunk, VPN
RAID, volume
manager
Storage virtualization
Emulation
Native virtualization
Paravirtualization
Application
virtualization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virtualizationonibmbladecenter-1225792256455769-8/75/Virtualization-on-IBM-Blade-Center-4-2048.jpg)