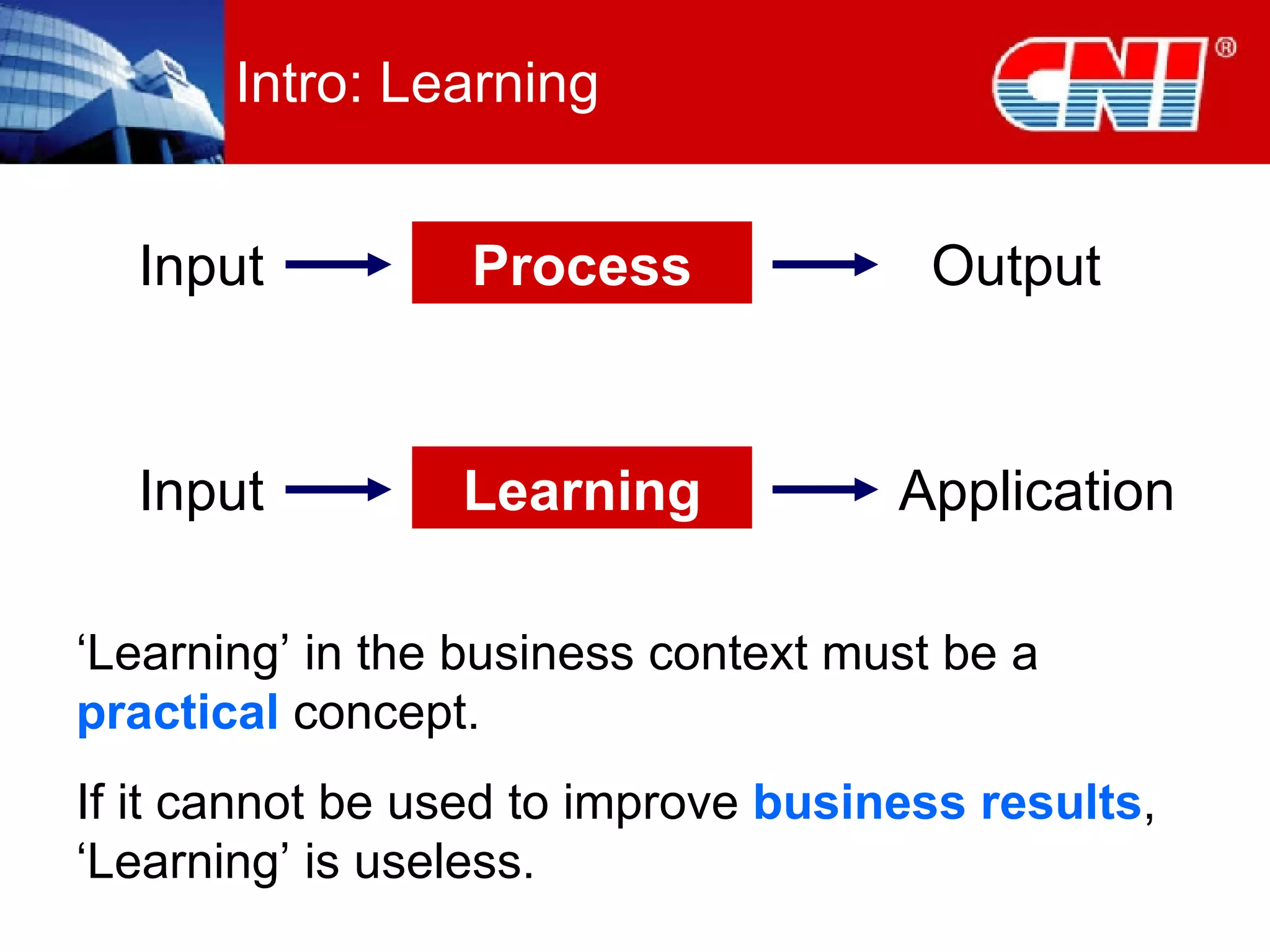
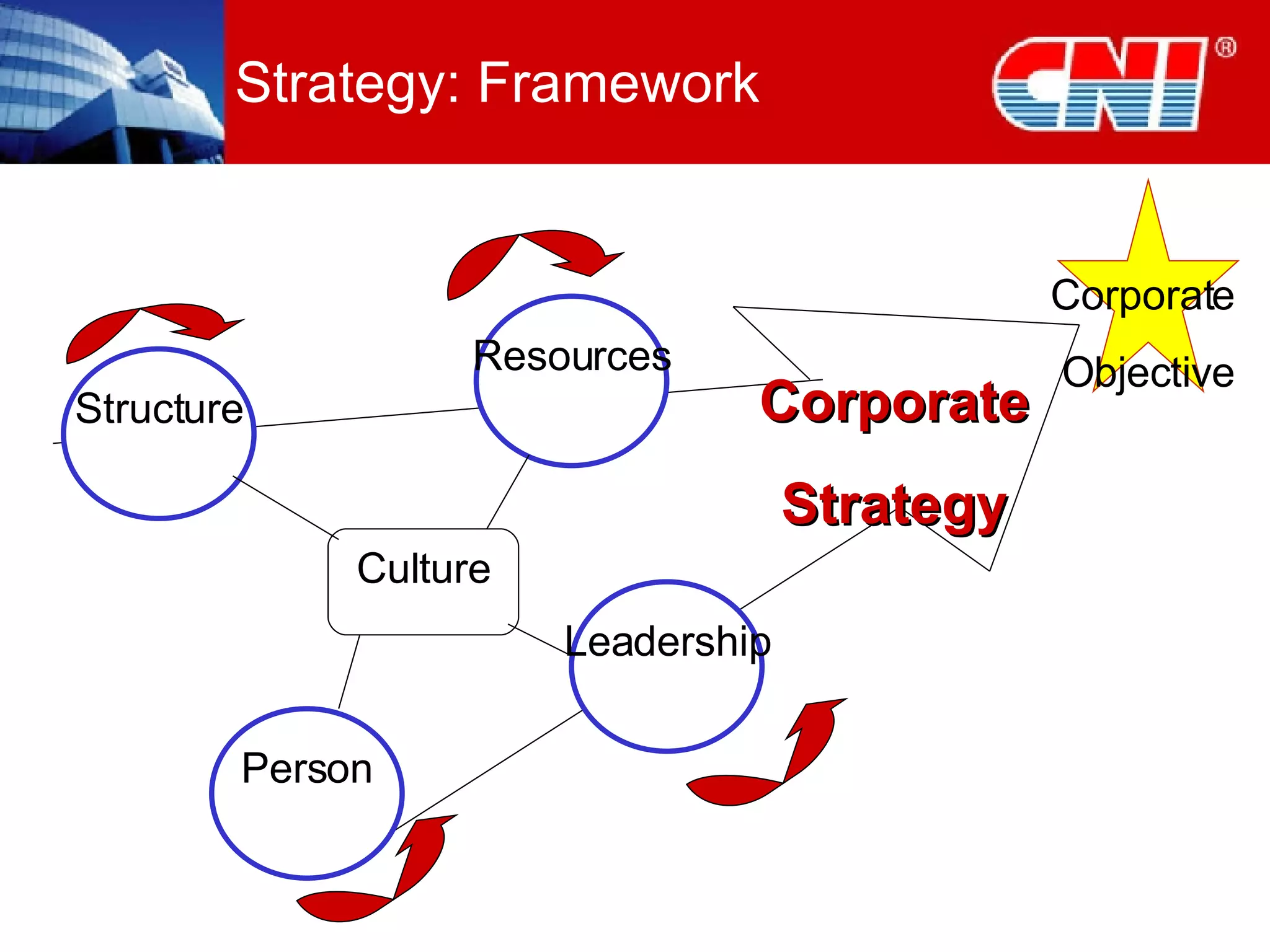
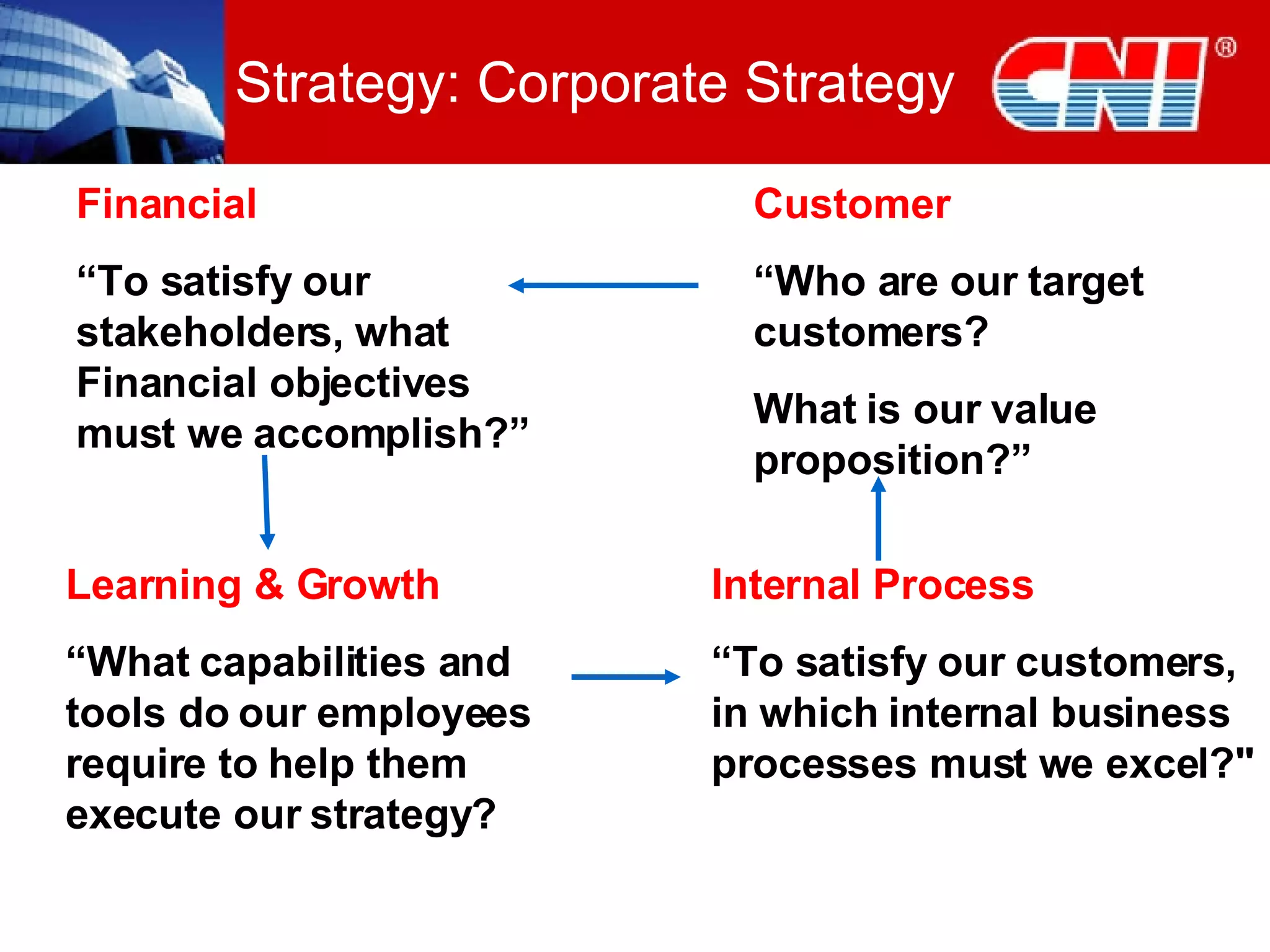
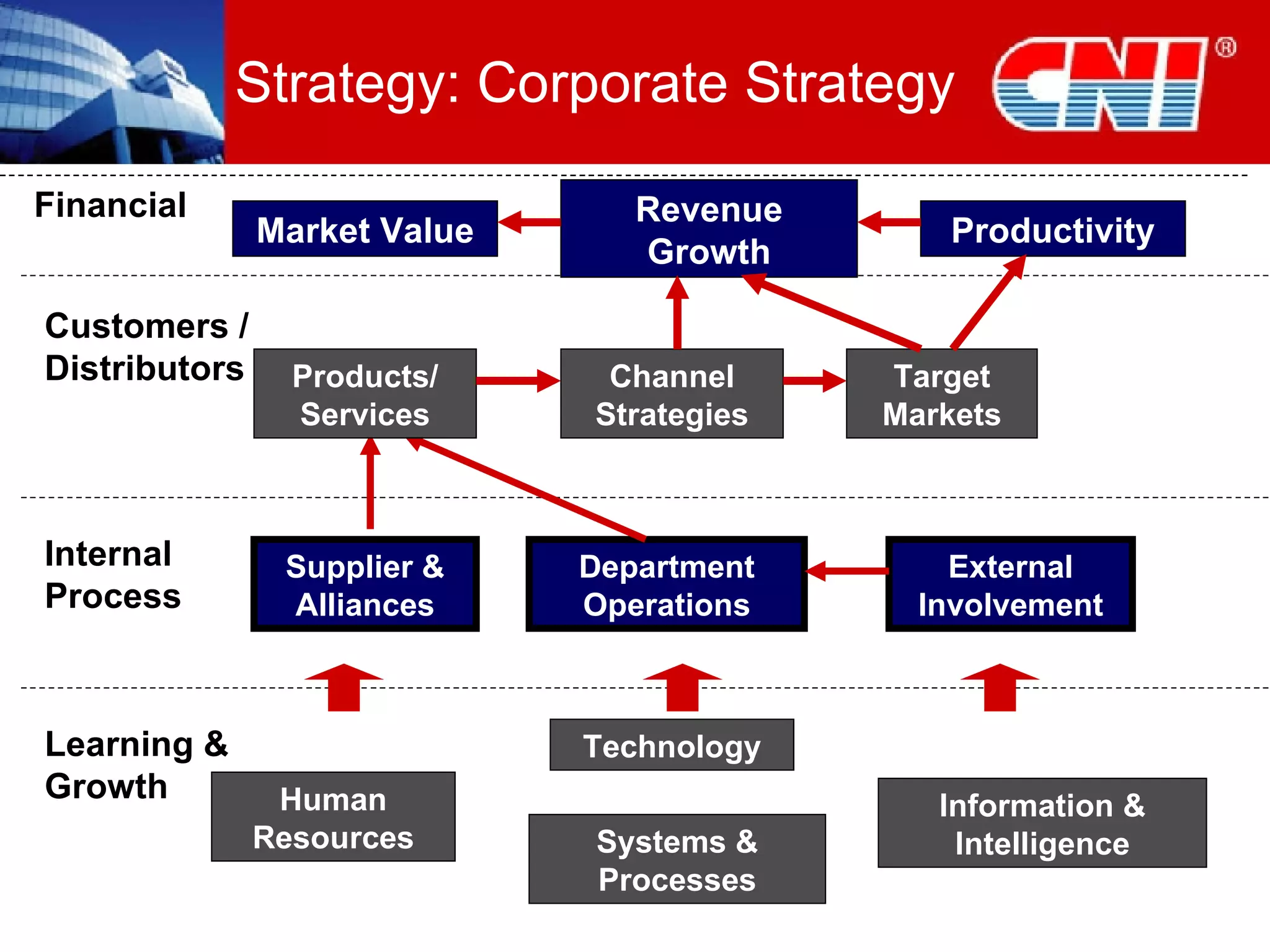
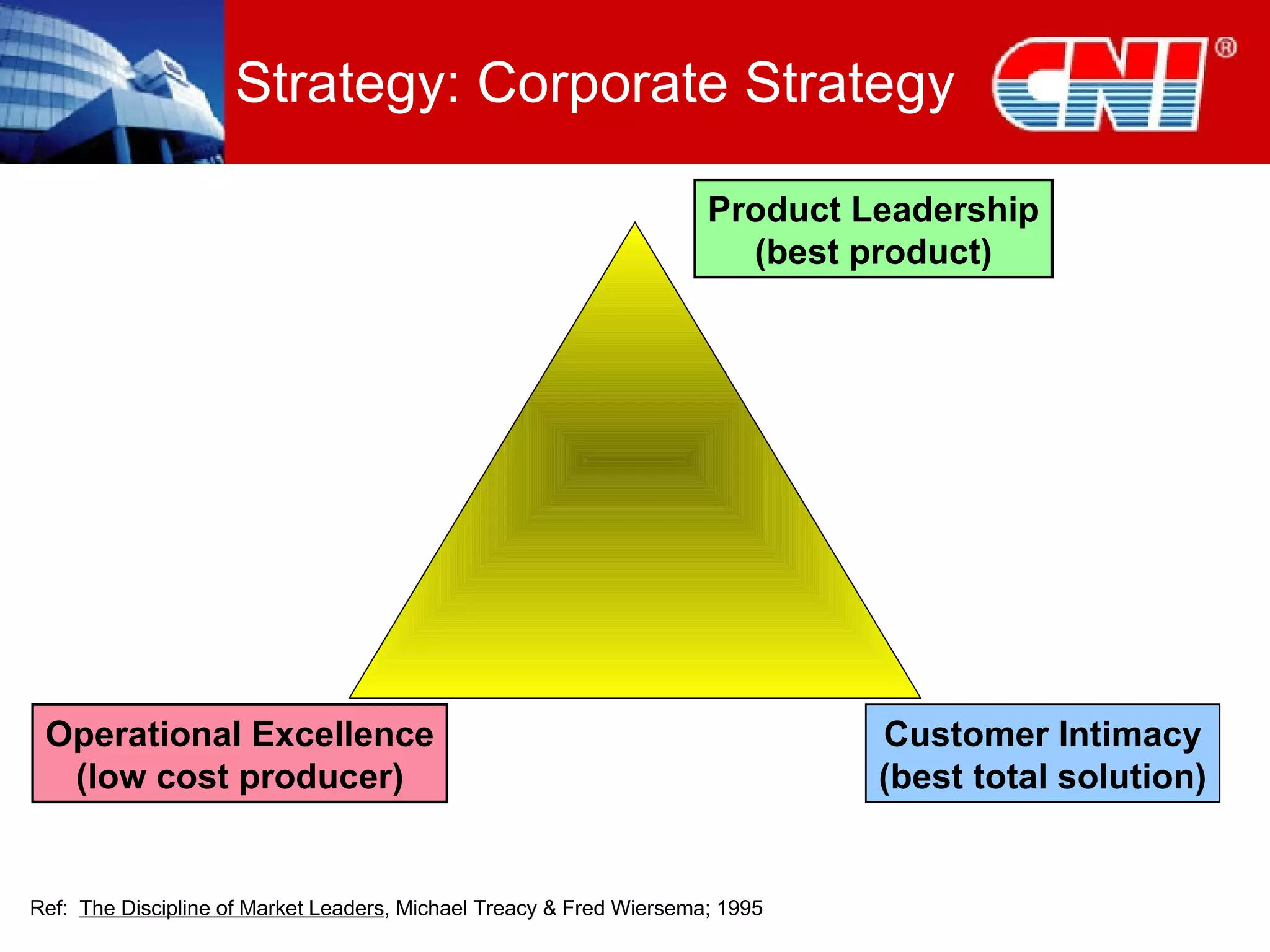
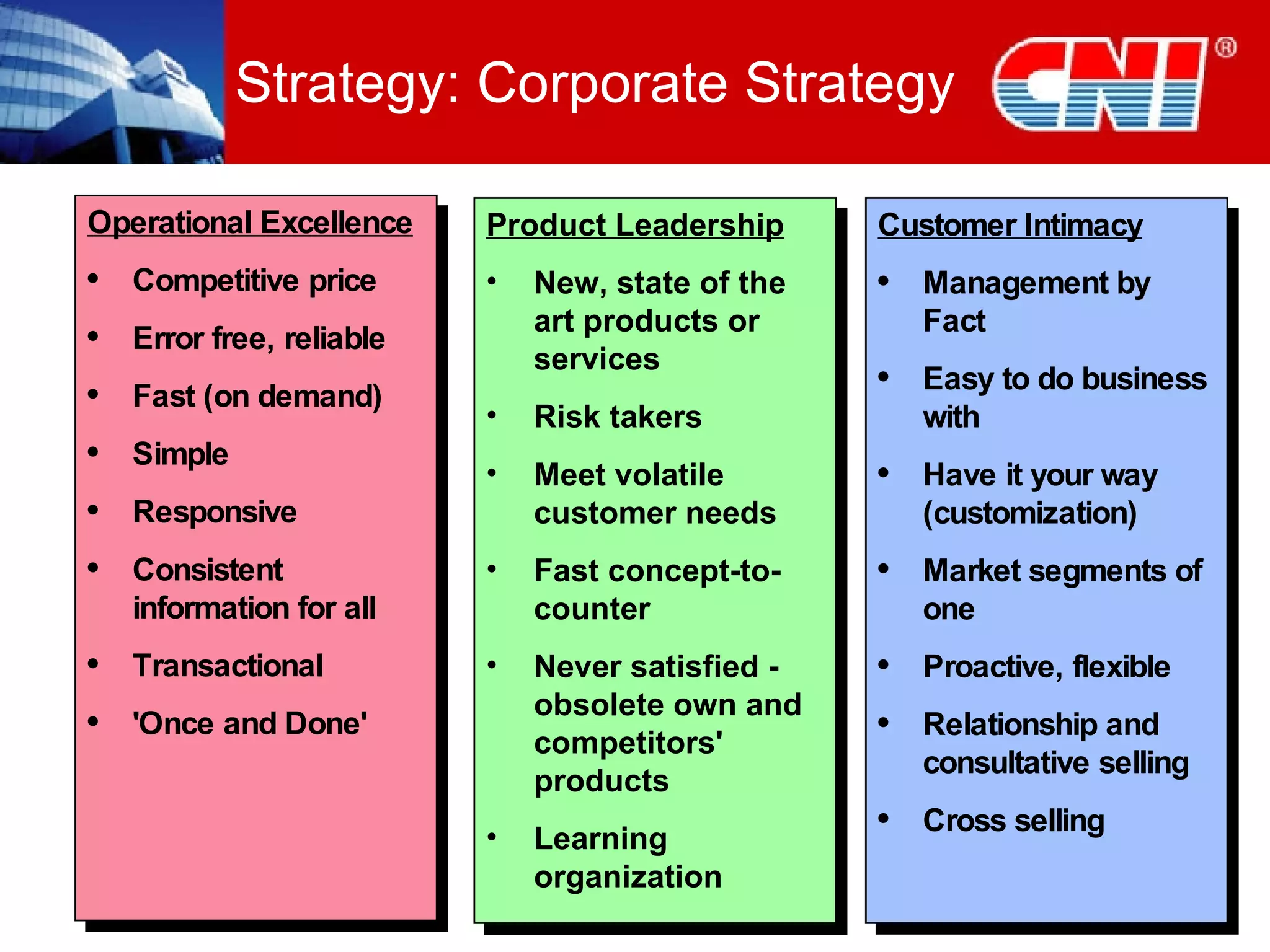
1. The document discusses CNI Holdings Berhad's framework for developing a continuous learning culture in the workplace. It focuses on establishing learning as a habit through organizational culture and strategies.
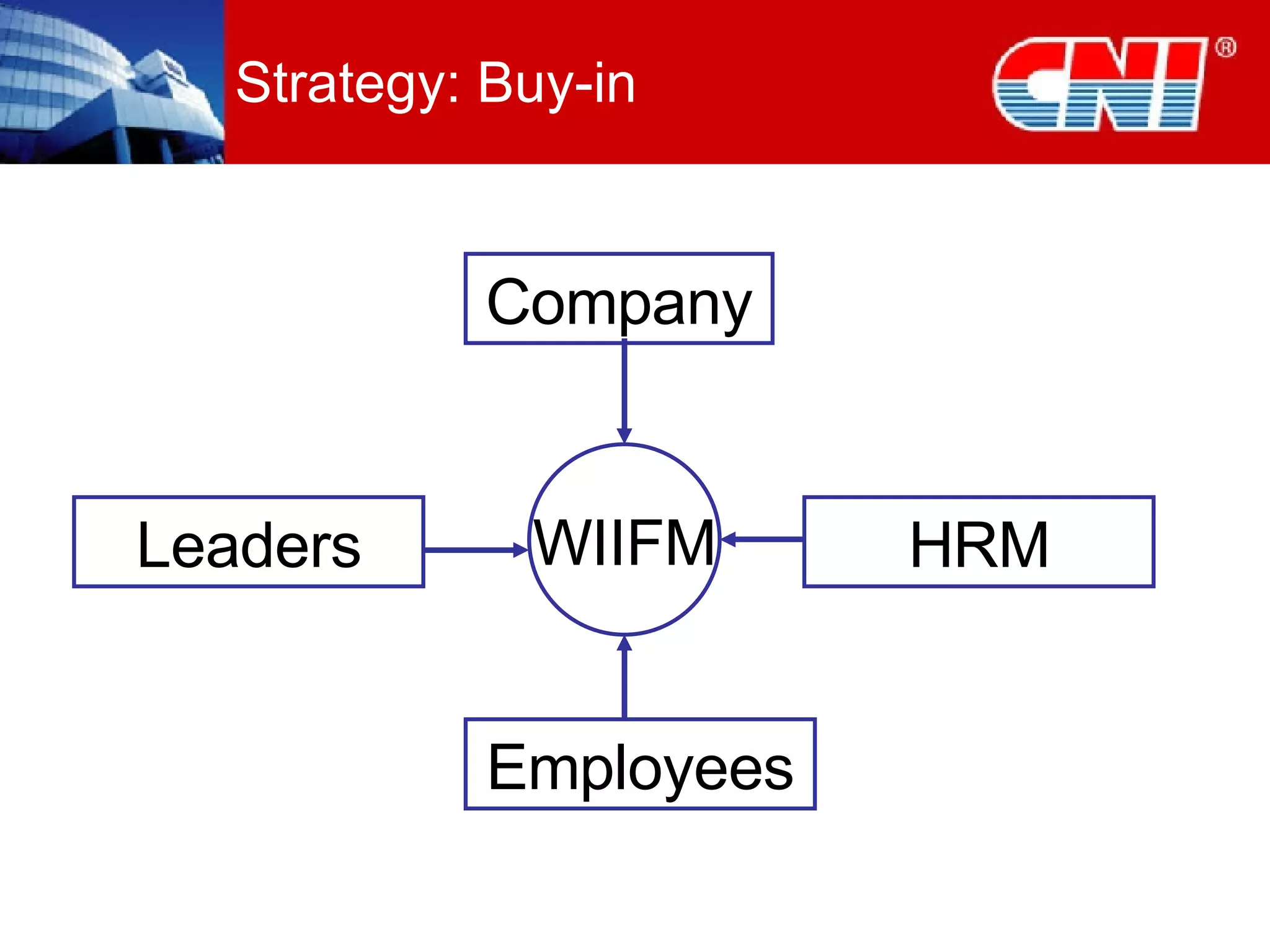
2. The framework addresses problems like short-term thinking and resistance to change. It promotes learning through modern approaches, job design, resources, leadership, and developing learning at the personal level.
3. Practical startup steps include linking training to strategy, addressing culture, focusing on outcomes over training, and demanding changes from training suppliers. The goal is to make learning an inherent part of jobs and independent through self-sustaining systems.



































![Thank You. soft copy of slides: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/continuous-learning-a-framework-for-developing-a-workplace-essential-habit-atcen-conference-1200534880209516-4/75/Continuous-Learning-A-framework-for-Developing-a-Workplace-Essential-Habit-Atcen-Conference-46-2048.jpg)