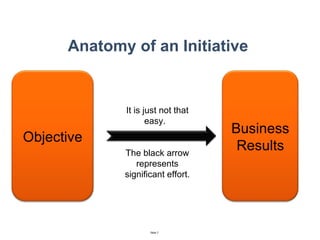
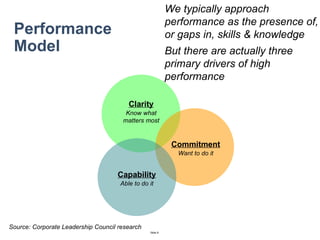
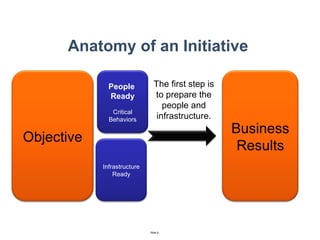
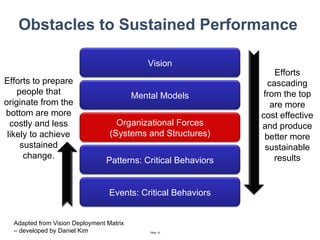
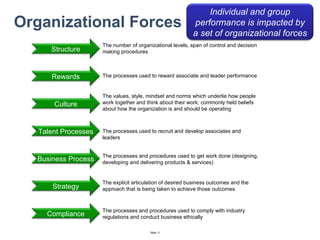
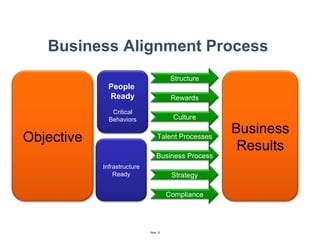
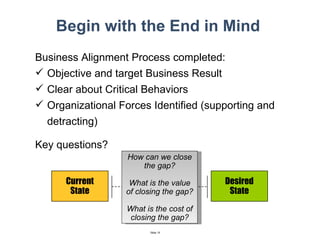
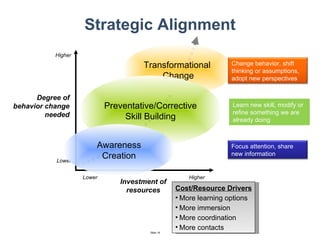
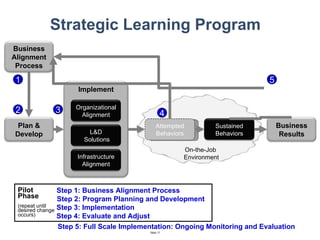
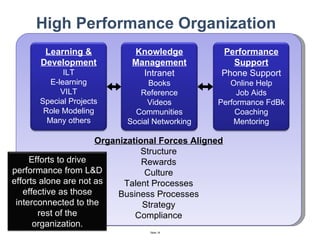
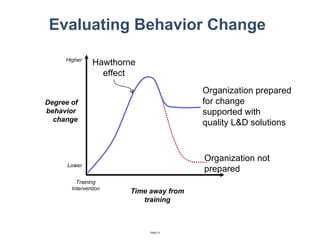
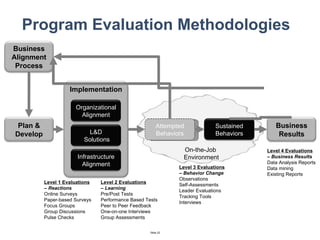
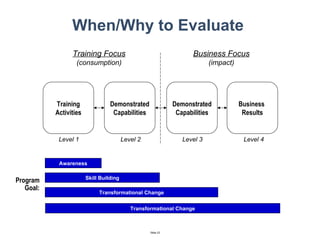
The document discusses a strategic business learning approach to overcome the challenges of workplace learning and development by aligning learning initiatives with business objectives. It emphasizes the importance of organizational alignment, critical behaviors, and the use of effective measurement strategies to ensure sustained behavioral change and maximize the ROI of learning programs. Key processes include preparing infrastructure, engaging in program planning, and evaluating progress to achieve transformational change in performance outcomes.