Embed presentation
Download to read offline


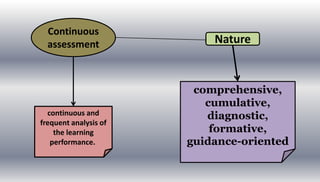

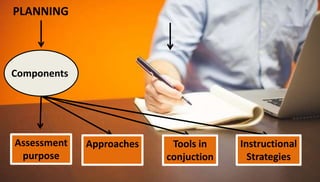

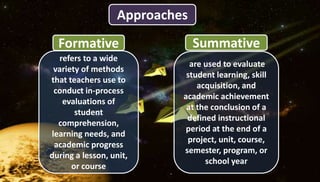
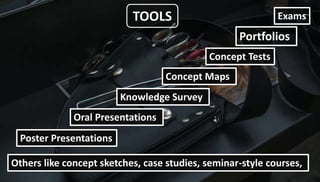





This document discusses planning for continuous assessment in classroom learning. It defines continuous assessment as the frequent and ongoing analysis of student learning performance. Some key features of continuous assessment mentioned are that it should be regular, frequent, use various forms, provide regular feedback, and help develop student competency. When planning continuous assessment, teachers should determine what to assess, why to assess, how to assess, and who to assess. They should also consider using formative approaches, which evaluate student learning as part of the lesson, and summative approaches, which evaluate learning at the end of an instructional period. The document lists various tools that can be used for continuous assessment, including exams, concept maps, observations, interviews and rubrics.











