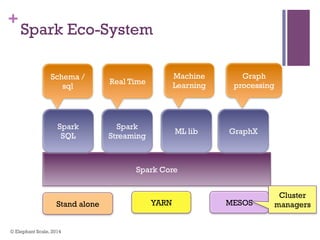
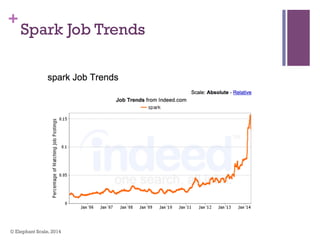
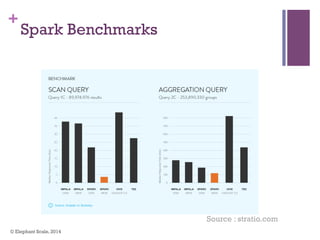
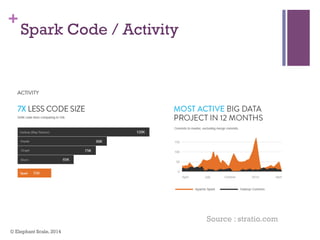
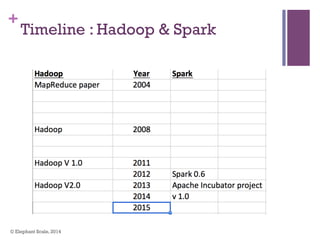
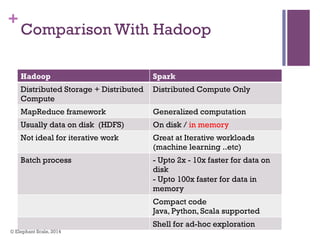
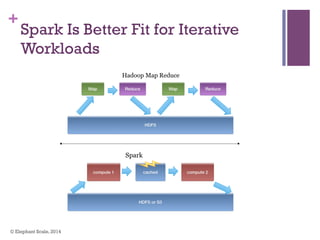
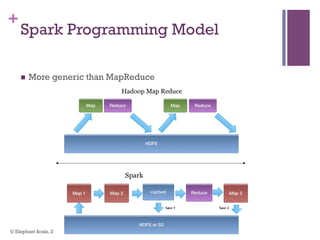
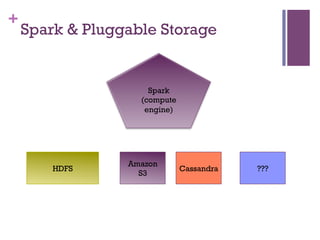
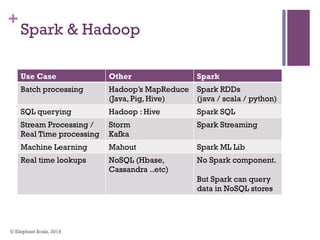
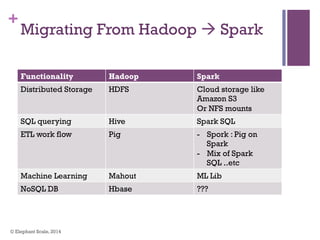
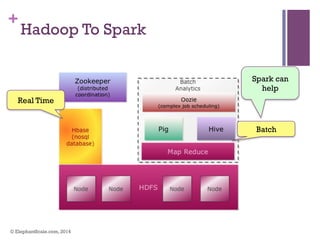
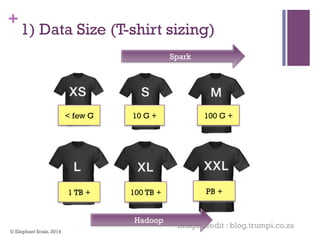
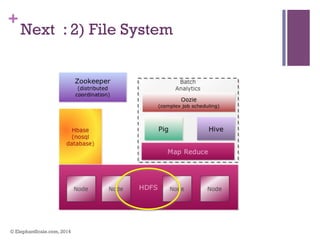
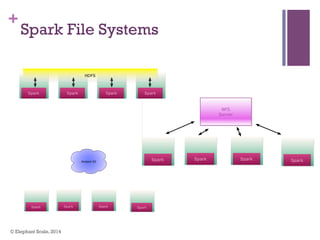
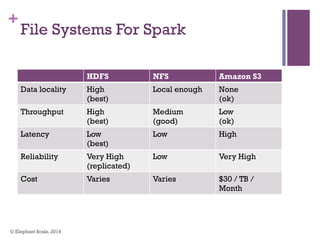
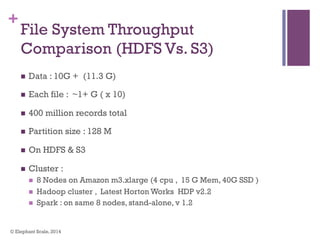
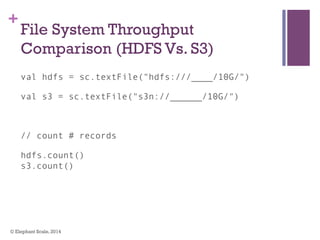
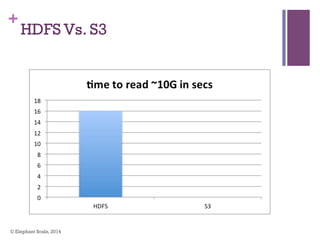
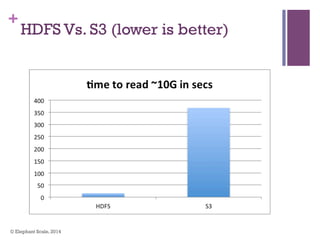
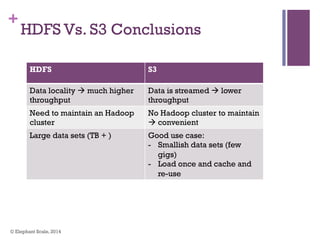
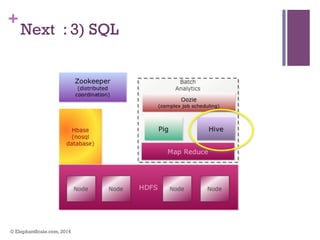
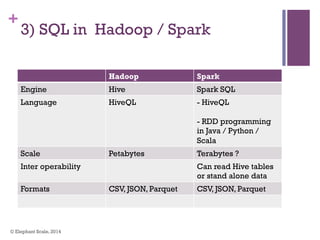
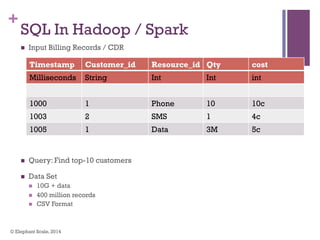
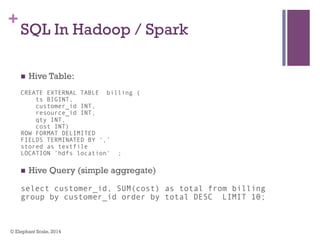
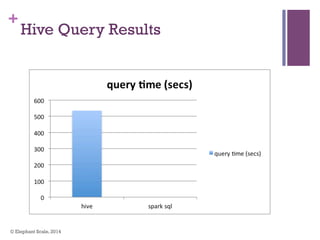
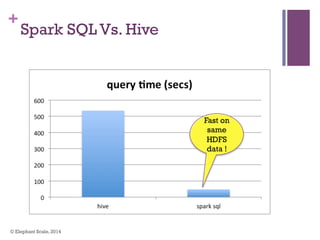
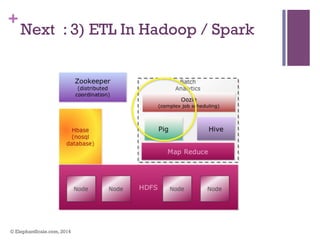
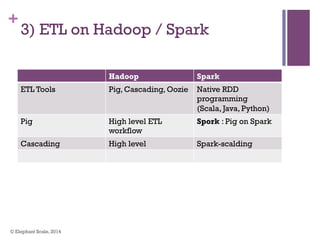
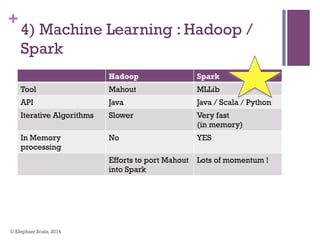
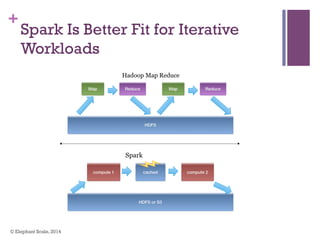
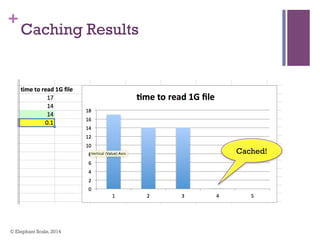
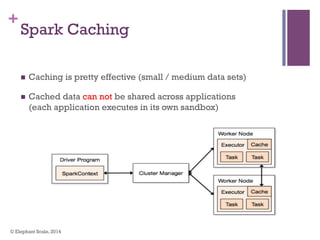
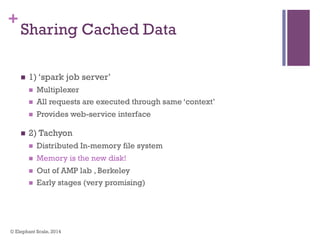
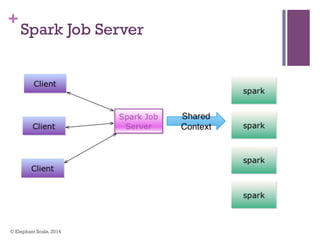
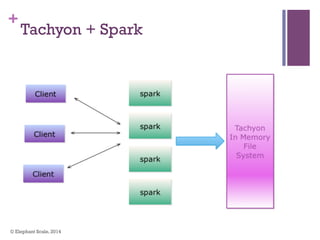
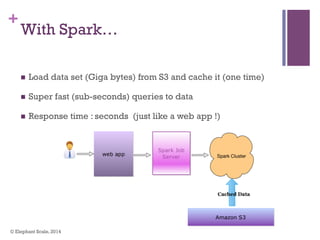
The document discusses the transition from Hadoop to Spark, highlighting Spark's advantages in speed, flexibility, and suitability for iterative workloads and data science applications. It compares the two technologies in terms of architecture, performance, and ease of use, particularly for smaller to medium-sized datasets and real-time processing. The author encourages users to consider using Spark in conjunction with Hadoop and presents various use cases and functionalities of Spark within the big data ecosystem.