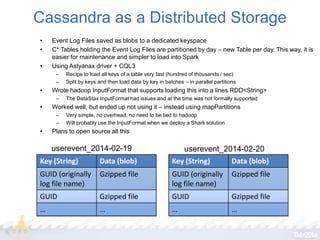
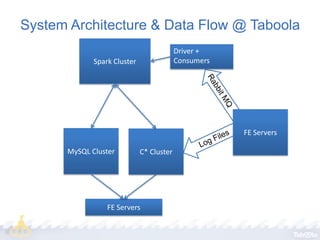
Taboola utilizes Apache Spark to process terabytes of data daily for real-time content recommendations and analytics, handling over 3 billion daily recommendations. The company benefits from Spark's in-memory computing capabilities, facilitating faster data processing compared to traditional Hadoop methods. Key technologies employed include Mesos for resource management, Cassandra for data storage, and various monitoring tools to optimize Spark's performance.






![Example: Log Mining
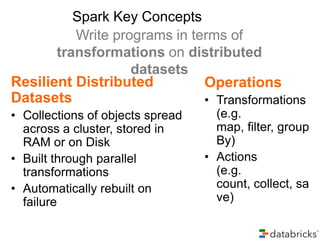
Transformed RDD
Load error messages from a log into
memory, then interactively search for various
patterns
Cache 1
Base RDD
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://...”)
results
Worker
errors = lines.filter(lambda s: s.startswith(“ERROR”))
tasks
messages = errors.map(lambda s: s.split(“t”)[2])
messages.cache()
messages.filter(lambda s: “mysql” in s).count()
Driver
Action
Block 1
Cache 2
Worker
messages.filter(lambda s: “php” in s).count()
Cache 3
. . .
Full-text search of Wikipedia
• 60GB on 20 EC2 machine
• 0.5 sec vs. 20s for on-disk
Worker
Block 3
Block 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reversim2014-140225063511-phpapp01/85/Taboola-s-experience-with-Apache-Spark-presentation-Reversim-2014-12-320.jpg)
![Execution Graph @ Taboola
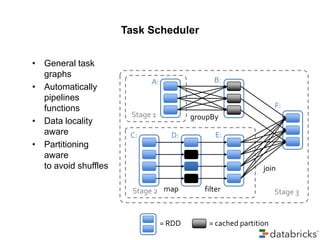
rdd1 = Context.parallize([data])
• Data start point (dates, etc)
rdd2 =
rdd1.mapPartitions(loadfunc())
• Loading data from external sources
(Cassandra, MySQL, etc)
rdd3 = rdd2.reduce(reduceFunc())
rdd4 =
rdd3.mapPartitions(saverfunc())
rdd4.count()
• Aggregating the data and storing
results
• Saving the results to a DB
• Executing the above graph by
forcing an output operation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reversim2014-140225063511-phpapp01/85/Taboola-s-experience-with-Apache-Spark-presentation-Reversim-2014-16-320.jpg)