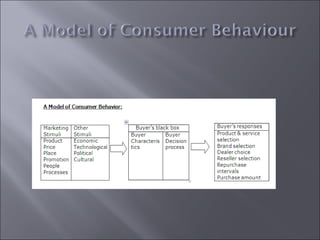
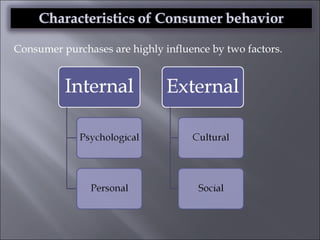
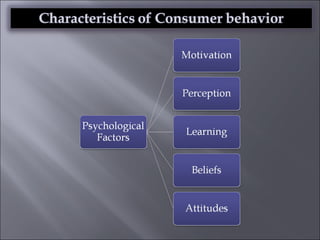
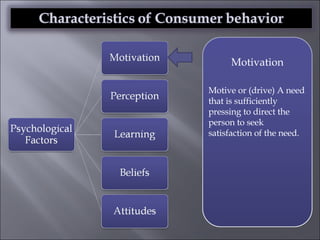
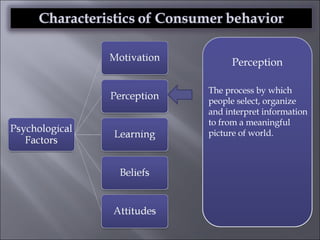
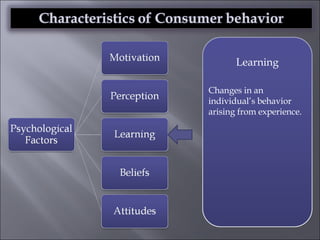
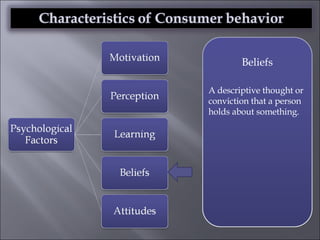
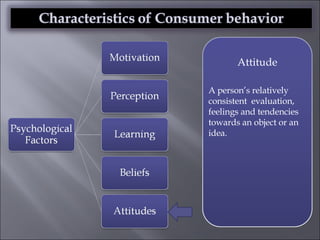
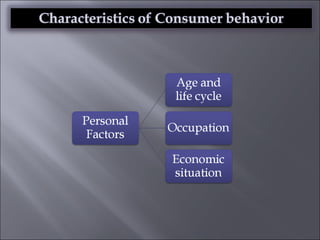
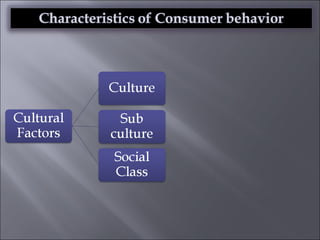
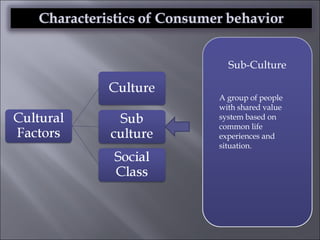
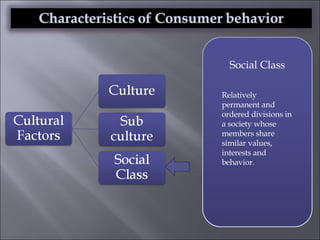
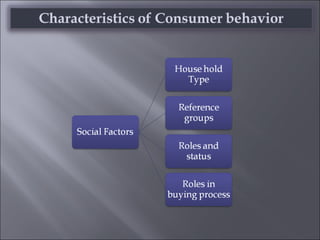
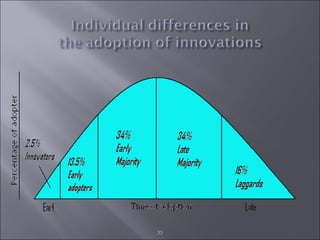
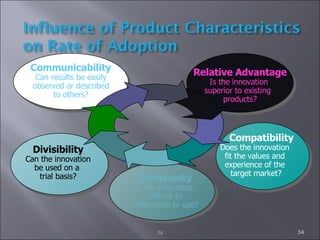
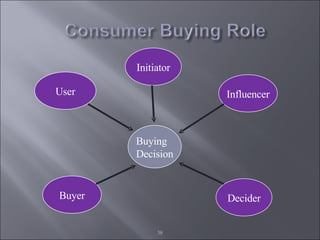
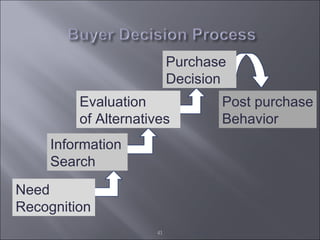
The document discusses various topics related to consumer behavior, including key concepts like motivation, perception, and the consumer decision-making process. It describes factors that influence consumer behavior such as culture, social class, and the stages of adopting new products. Various consumer behavior theories are also summarized, including those proposed by Freud, Maslow and others relating to psychological motivations and needs.