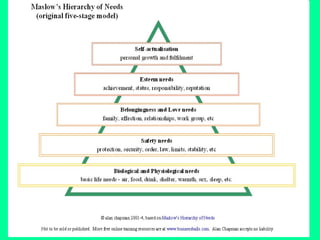
Motivation is driven by needs and desires that cause people to act. Maslow's hierarchy of needs proposes that more basic needs like physiological and safety must be met before higher-level needs can be a motivation. A 1992 Georgia tax amnesty campaign was successful because its ads appealed to tax offenders' basic needs for security, social values of citizenship, and goal of avoiding penalties by informing them they could pay overdue taxes without penalty during the amnesty period.