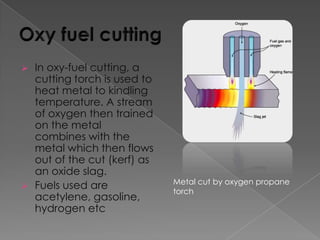
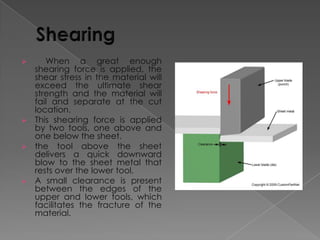
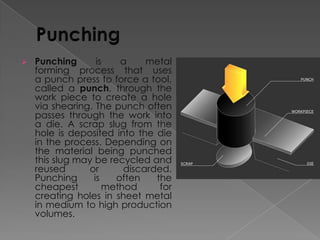
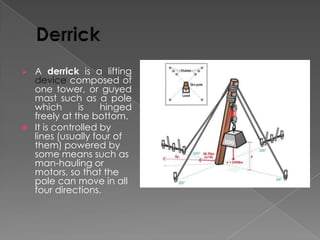
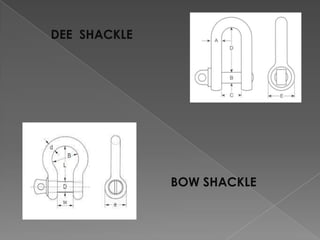
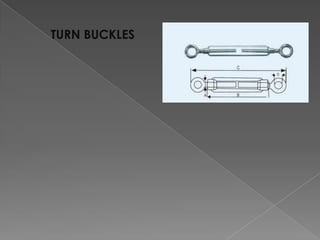
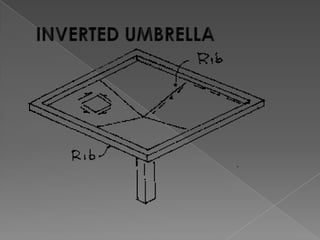
The document discusses various manufacturing processes used in metal fabrication including cutting, welding, assembling, finishing, bending, punching, drilling, painting and other processes. It provides details on specific cutting techniques like laser cutting, plasma cutting, oxy-fuel cutting and shearing. It also summarizes welding methods like laser, plasma and oxy-acetylene cutting. Other topics covered include surface preparation techniques for painting like wire brushing, pickling and sand blasting. Materials handling equipment is also listed including cranes, derricks, winches and other tools.