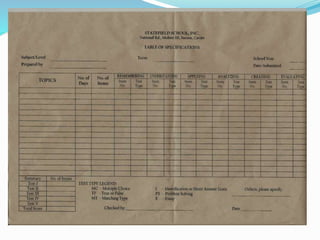
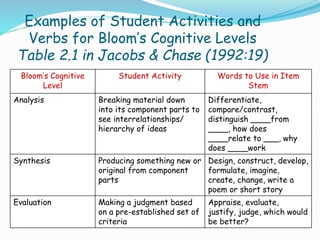
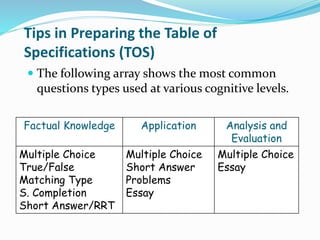
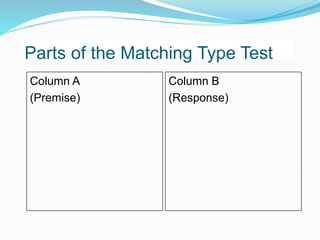
This document provides information and examples for constructing different types of tests, including structured response items, constructed response items, and examples at various cognitive levels. It discusses key characteristics of good tests such as validity, reliability, and usability. Examples of different question types are provided, such as true/false, multiple choice, matching, short answer, and essay. Guidelines are offered for writing effective item stems and response options to avoid issues like negative wording, ambiguity, and guessing. Bloom's taxonomy is referenced for aligning question types and verbs with different cognitive levels.