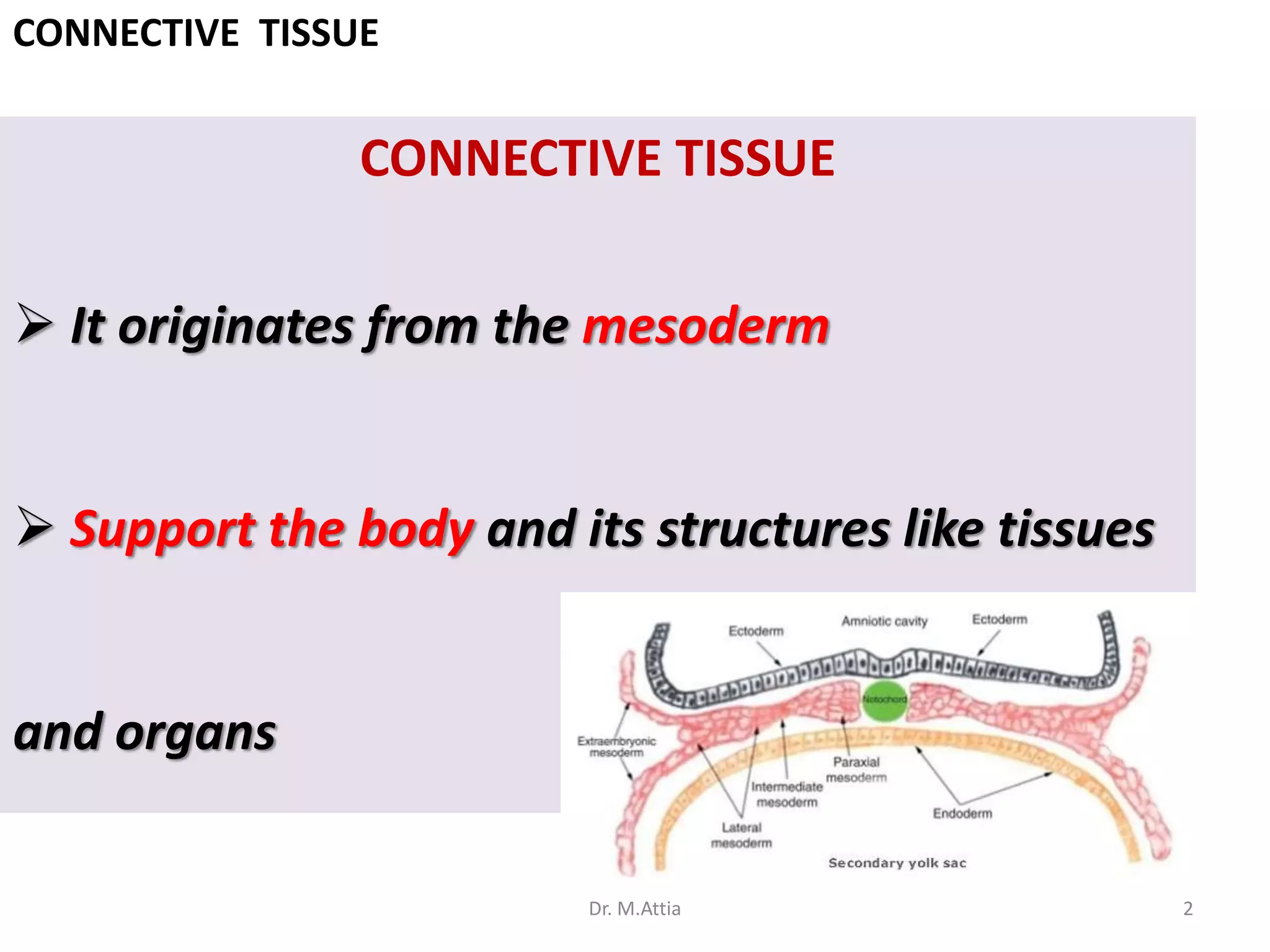
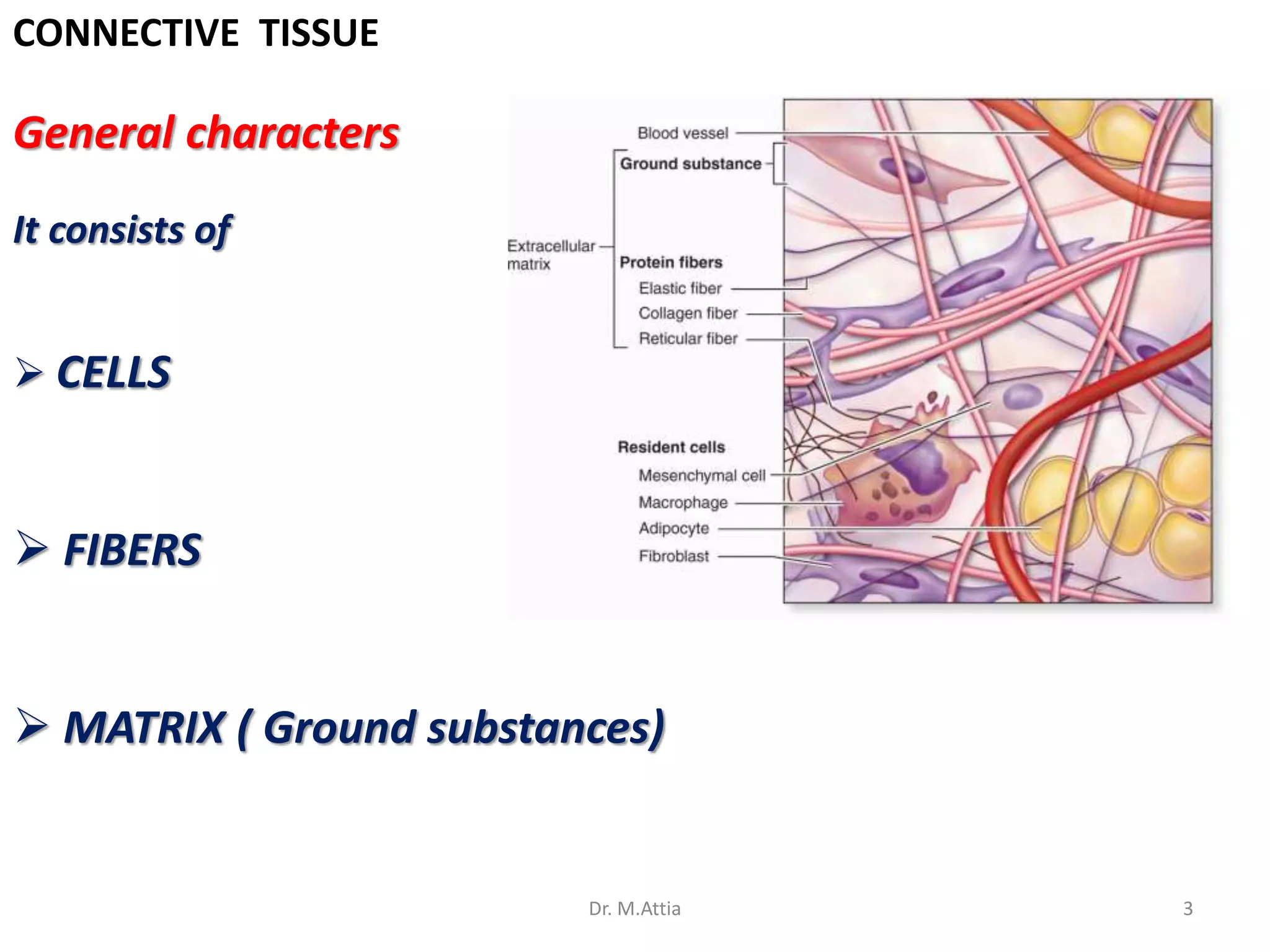
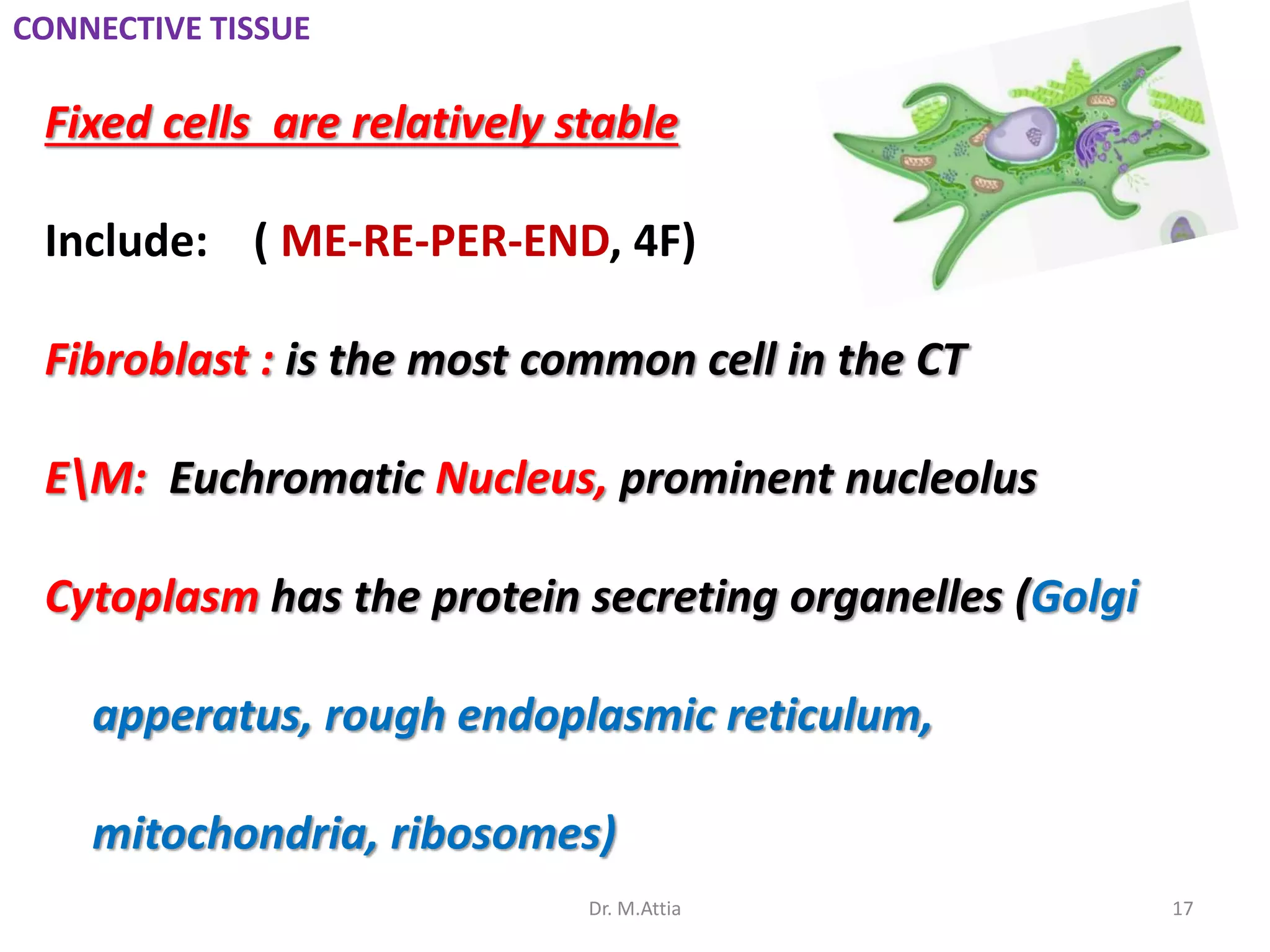
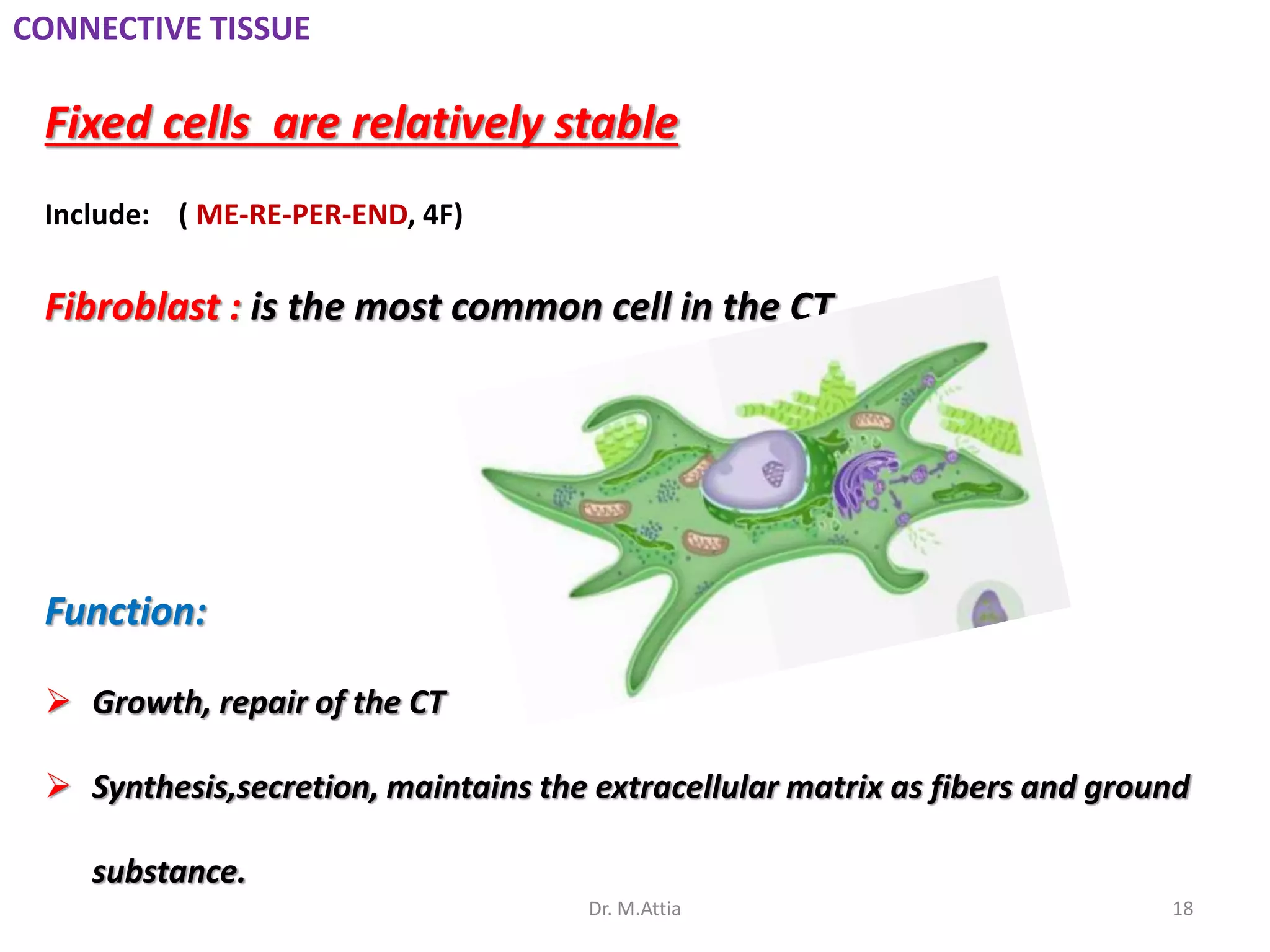
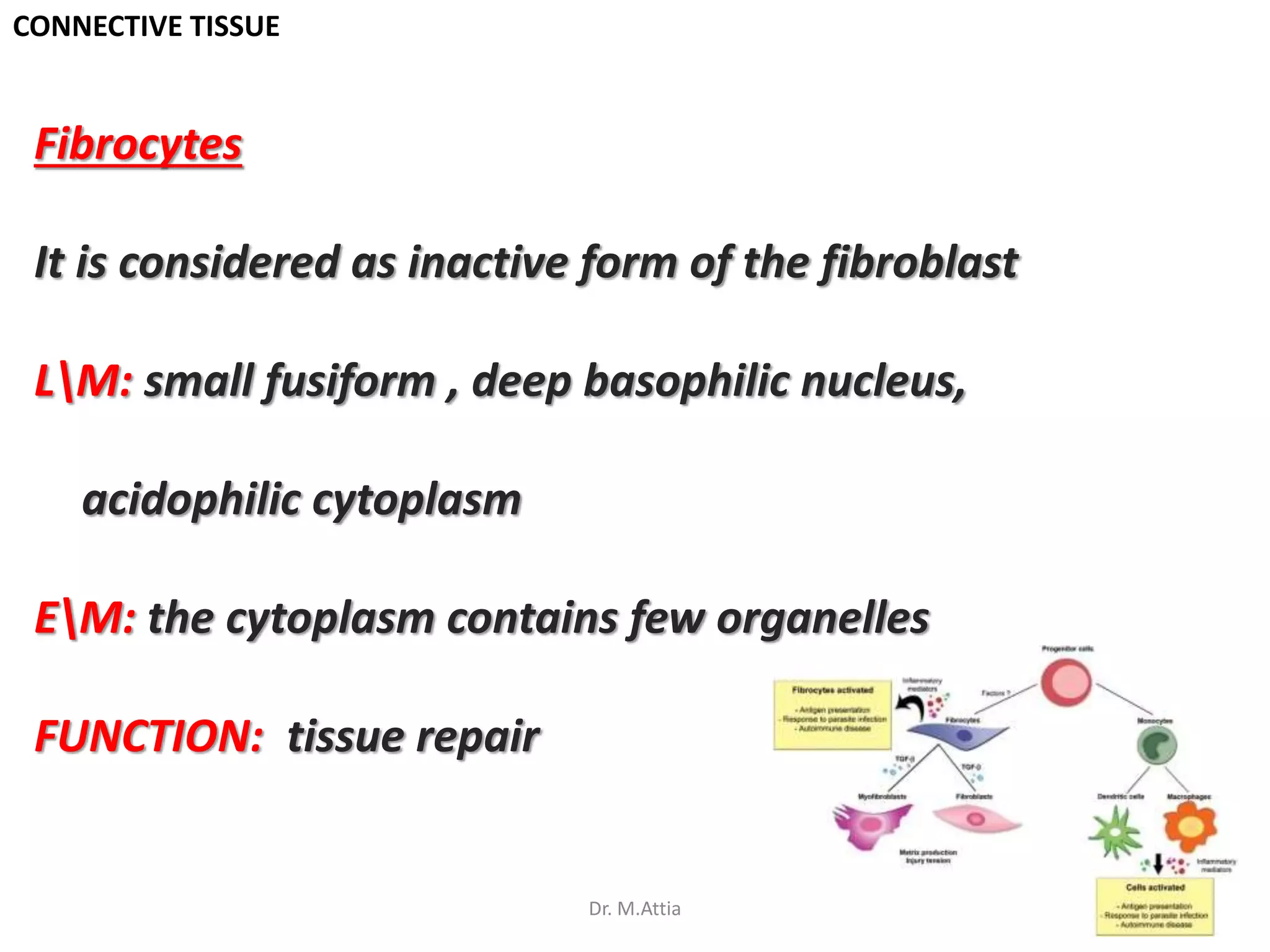
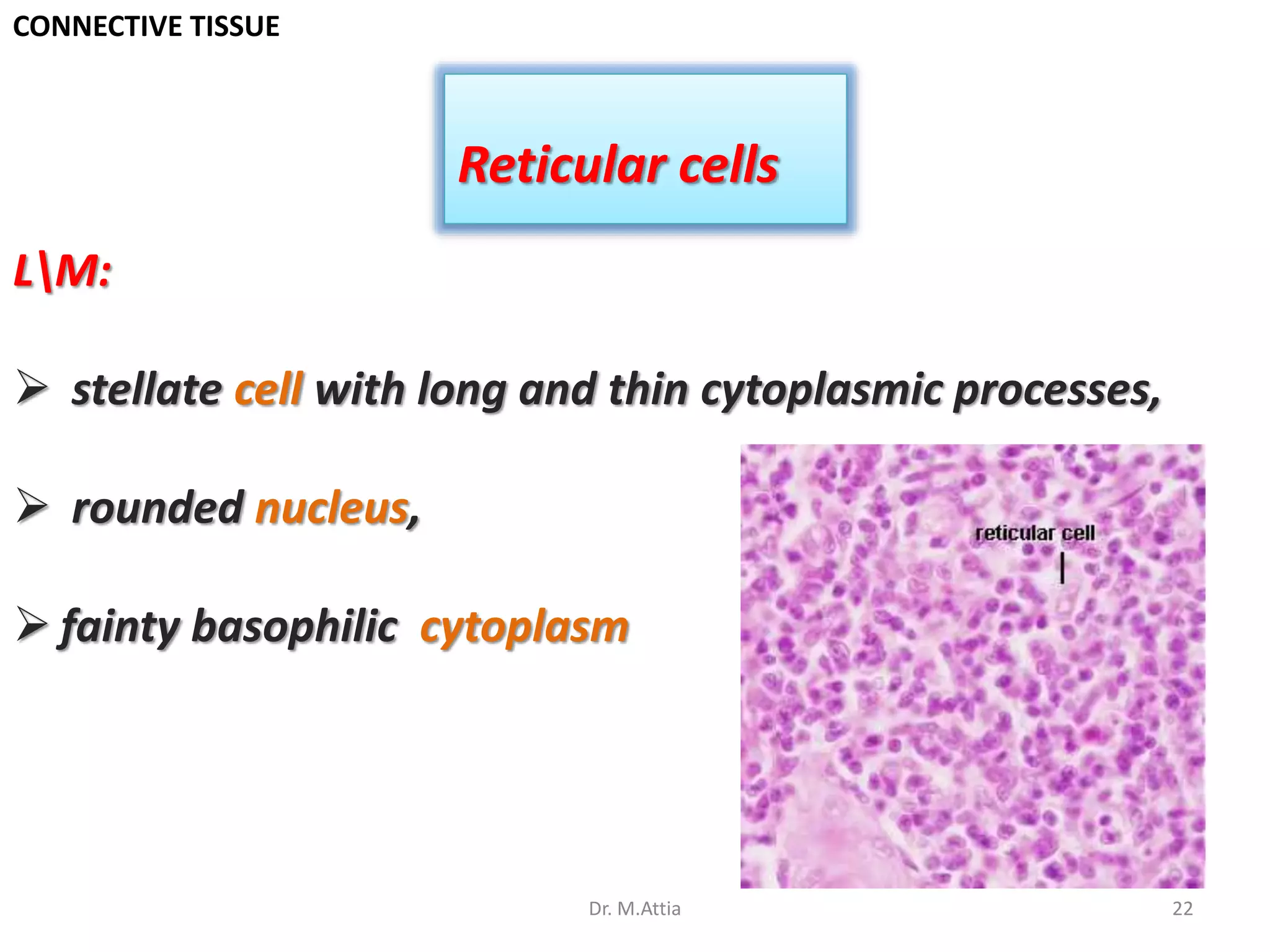
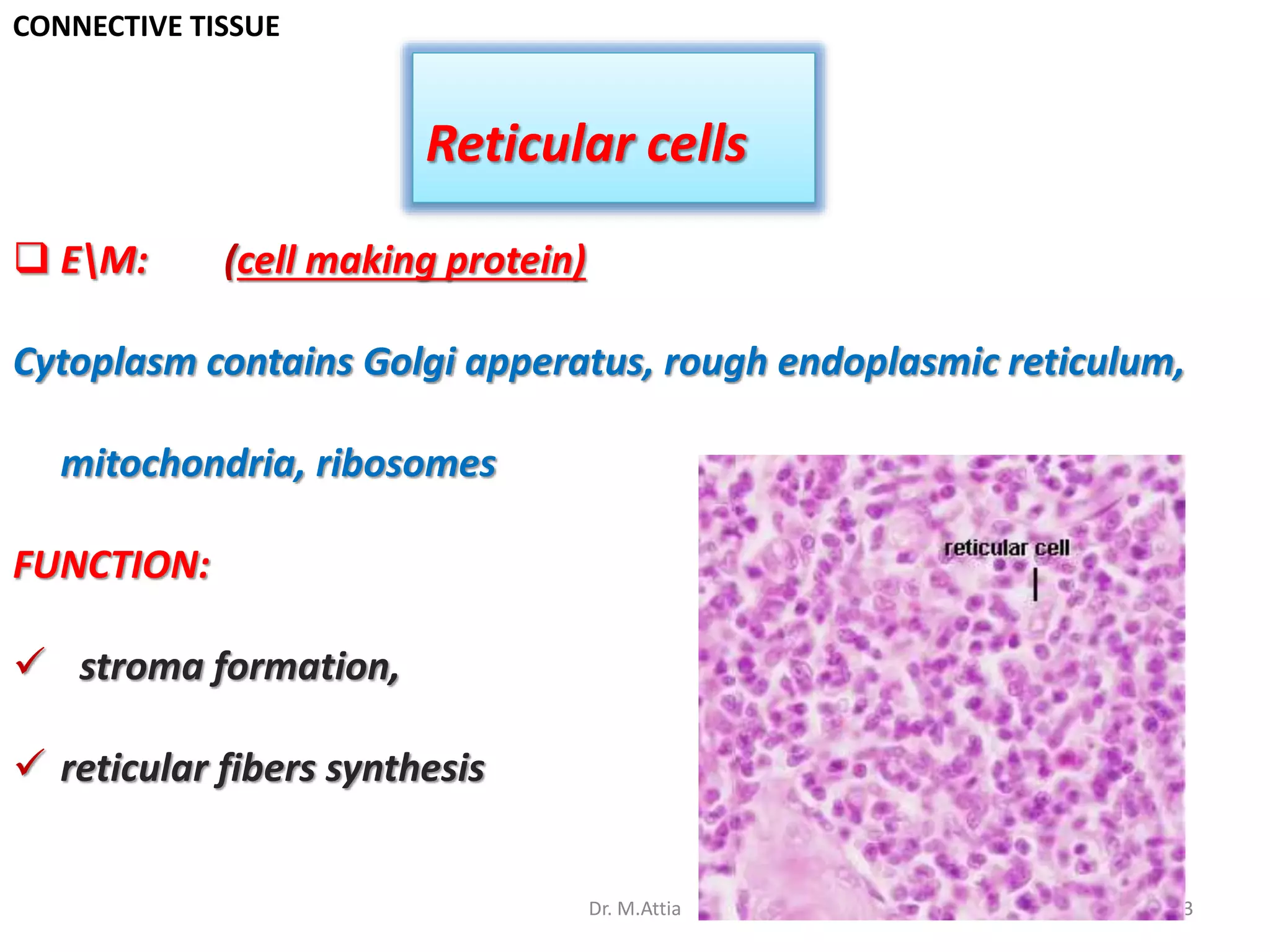
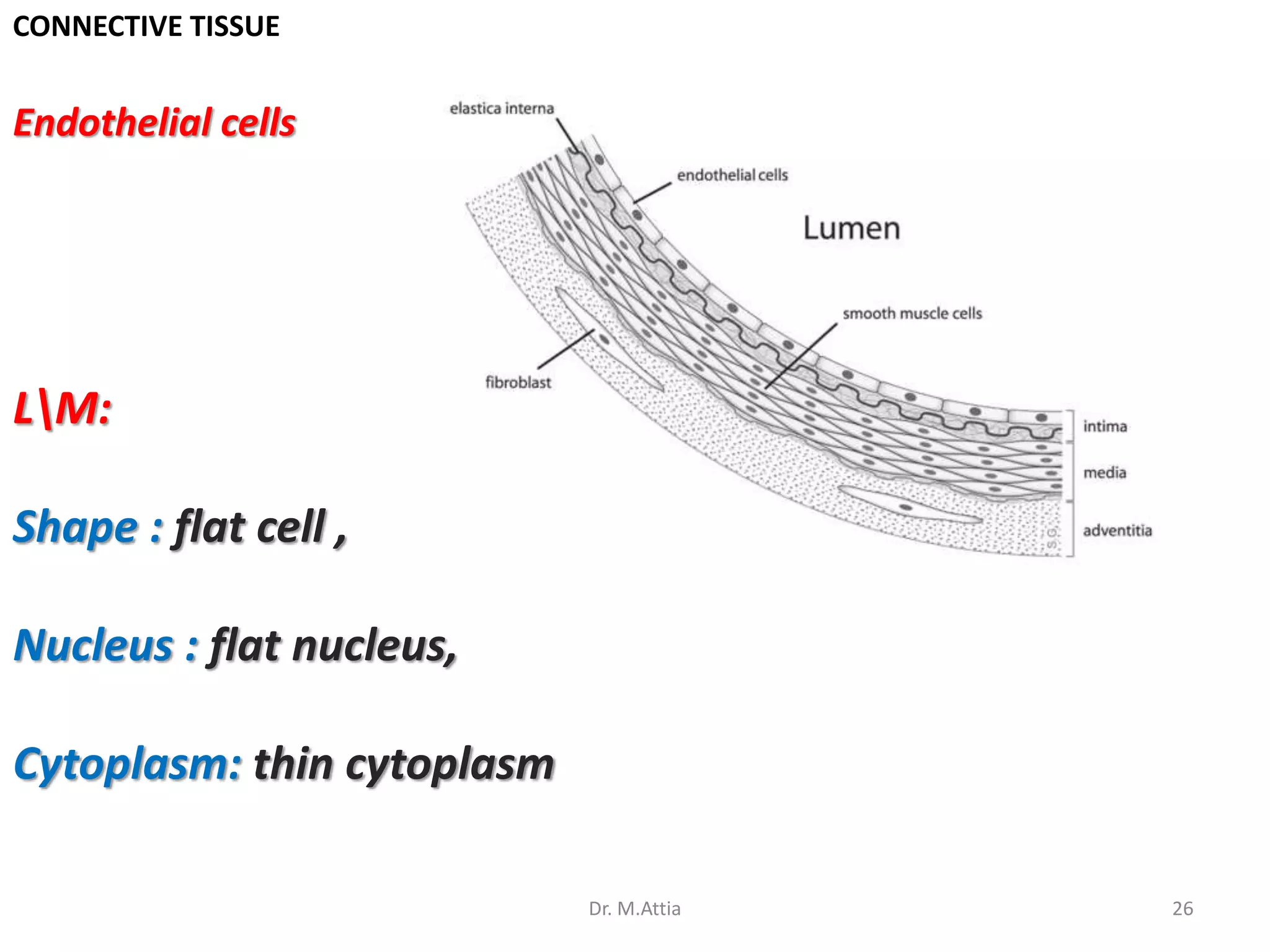
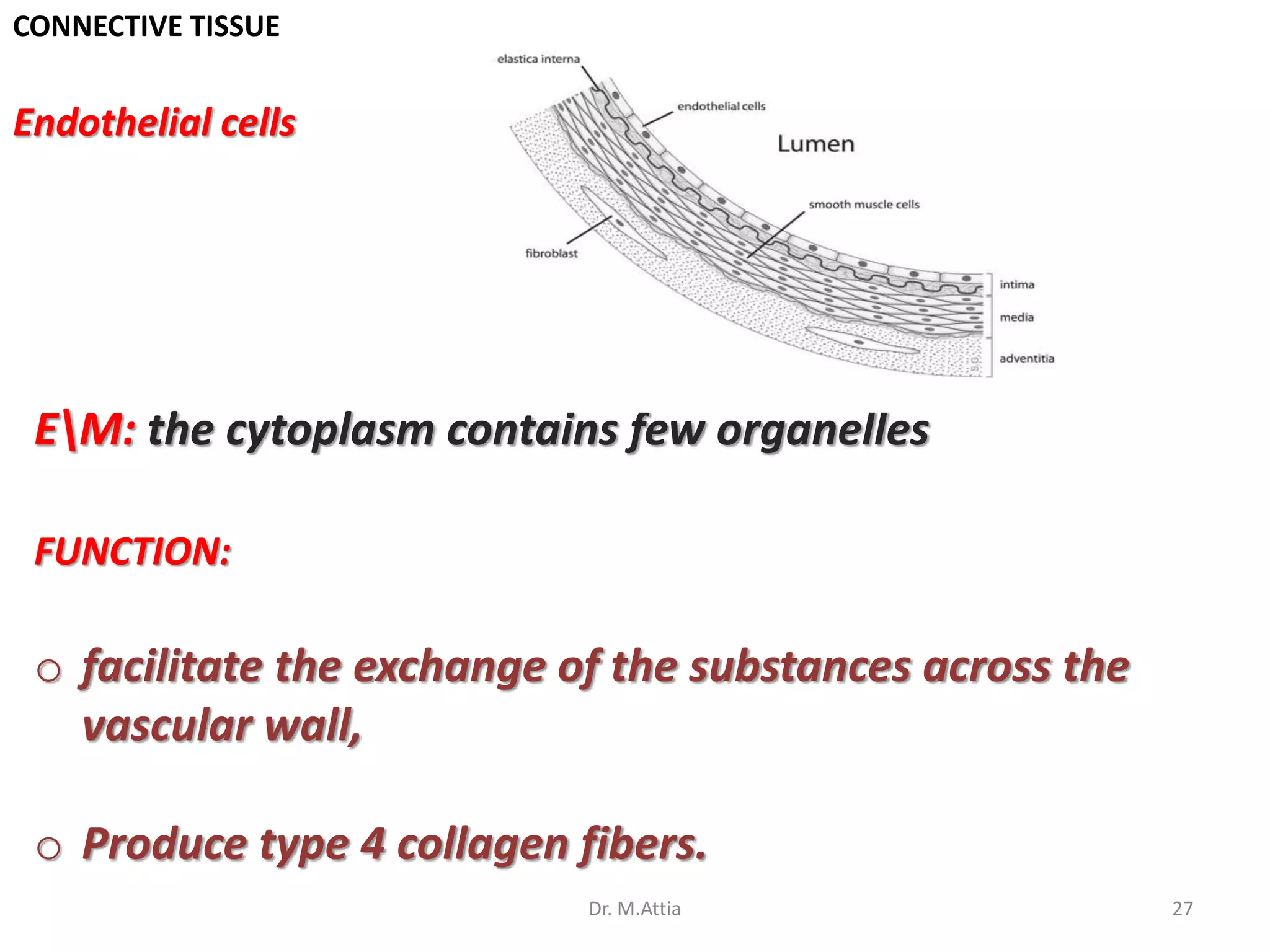
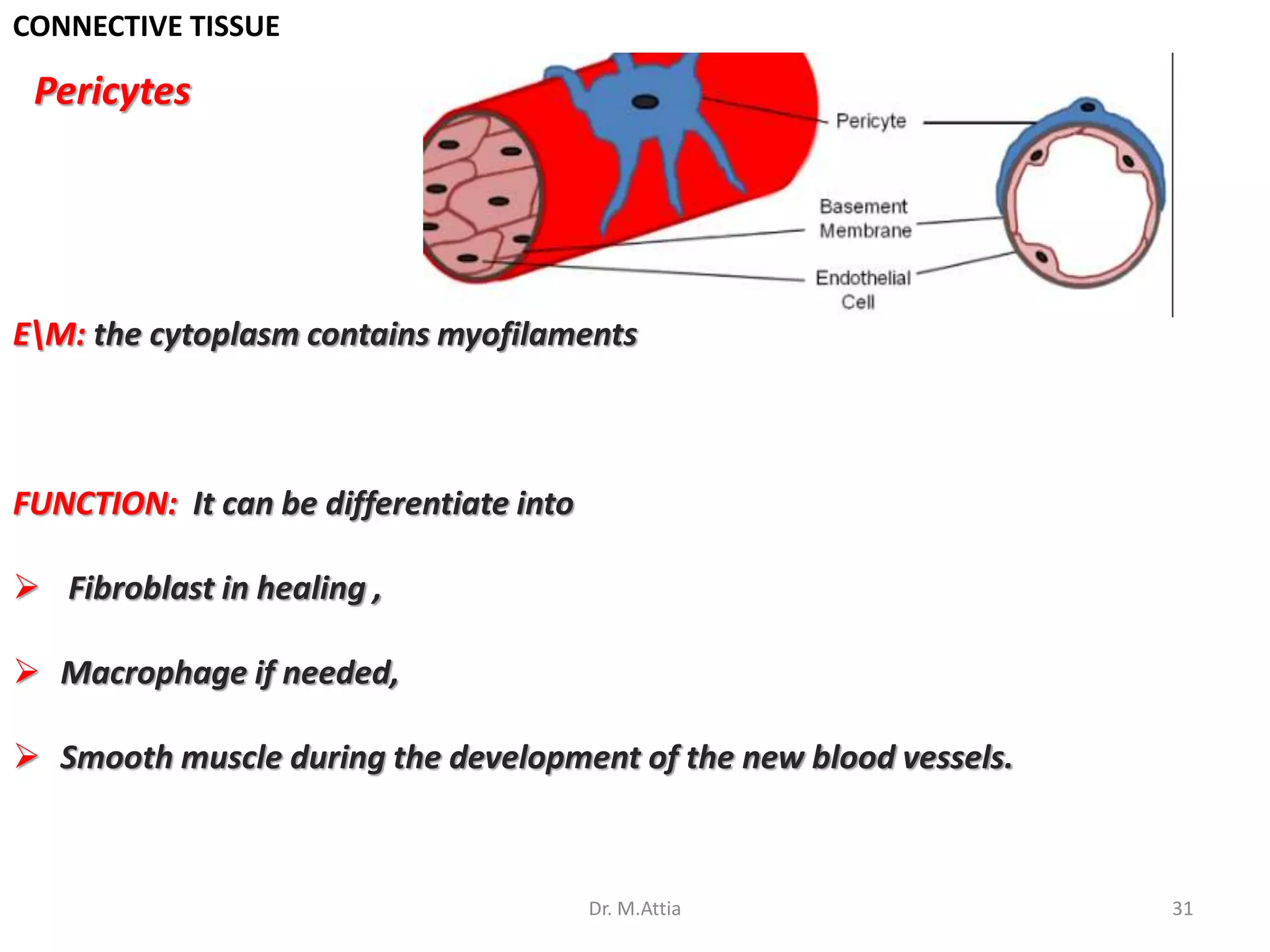
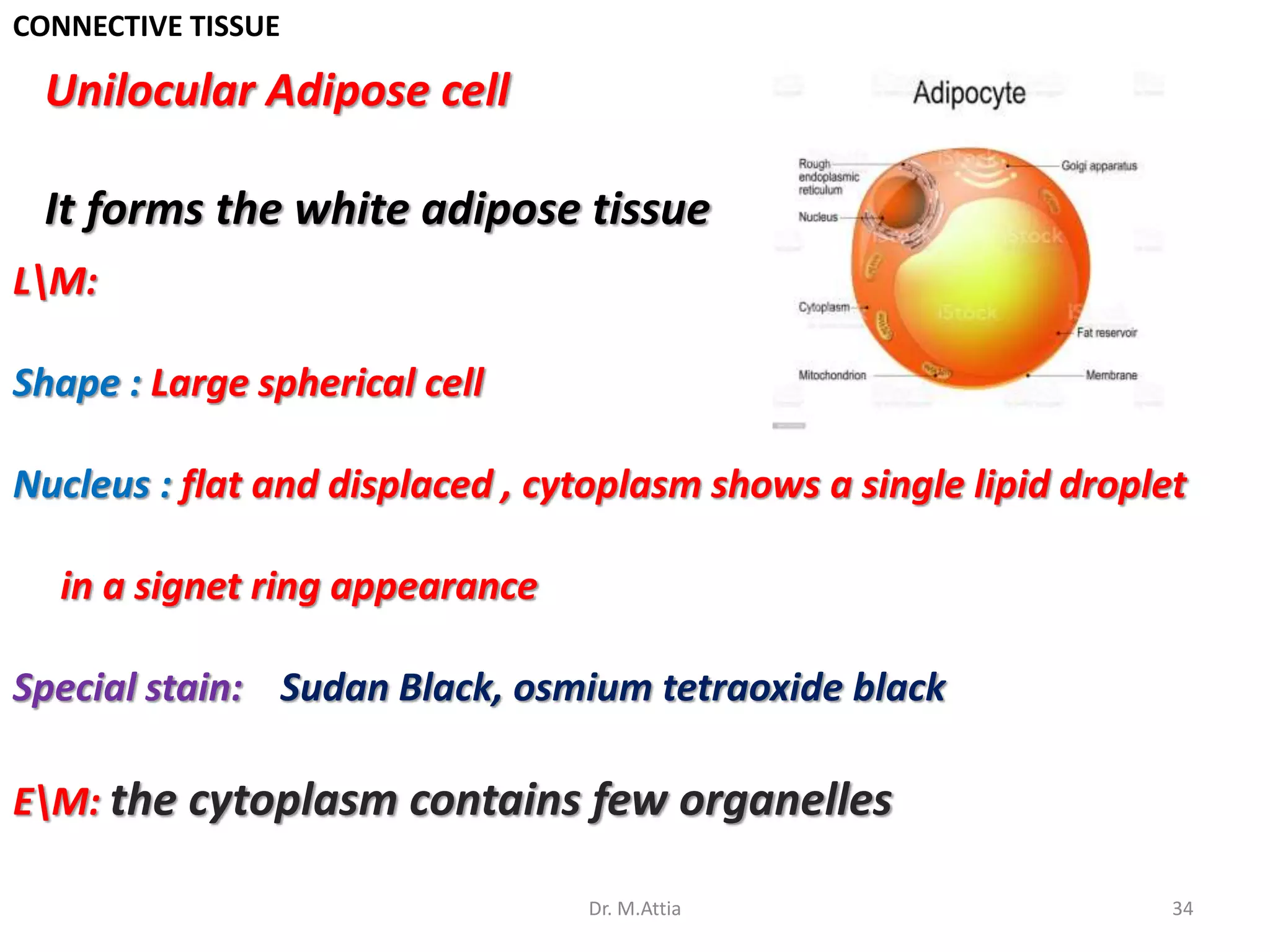
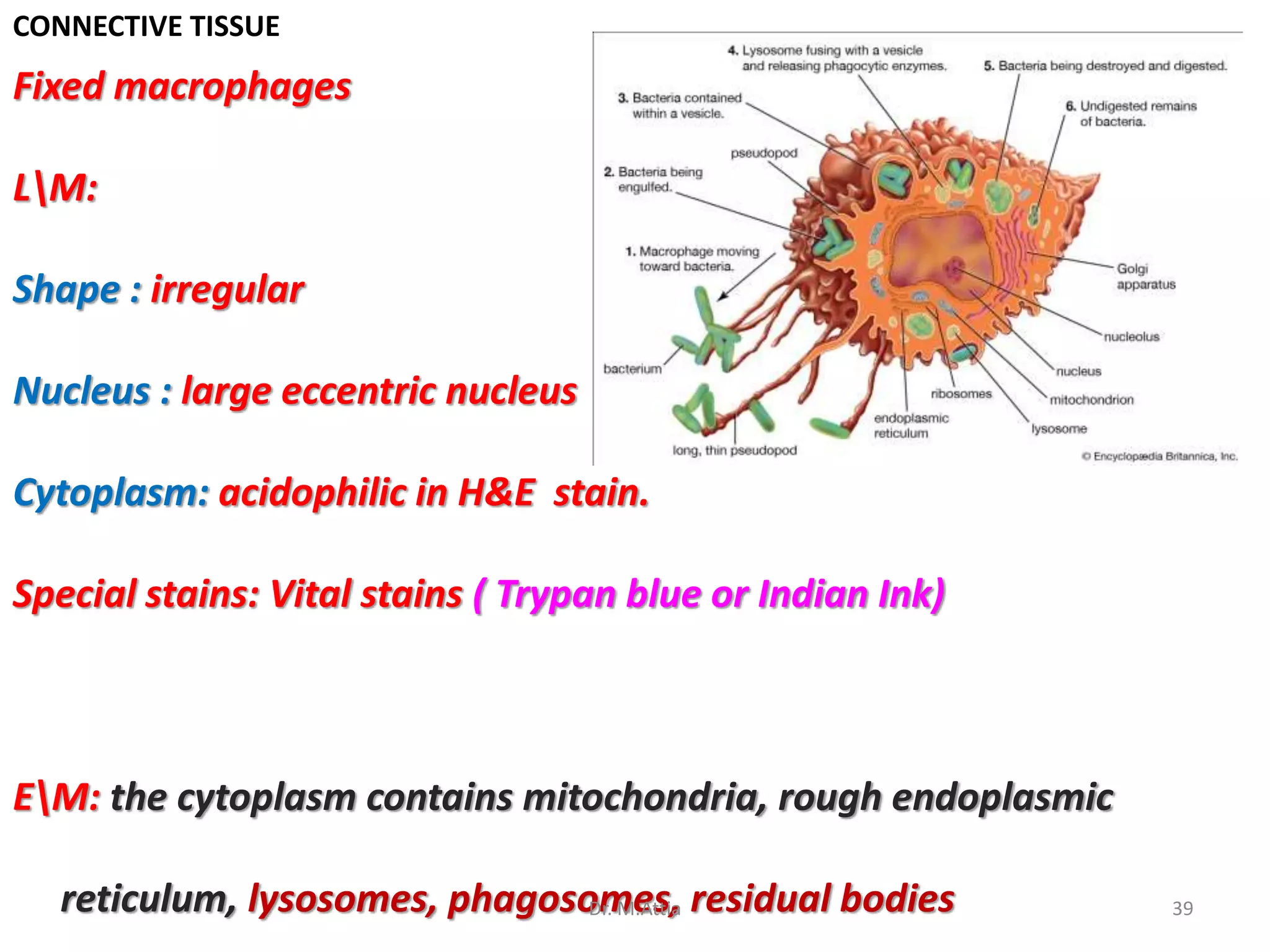
Connective tissue originates from mesoderm and supports the body's structures. It consists of cells, fibers, and a ground substance. There are several types of connective tissue cells including mesenchymal cells, fibroblasts, fibrocytes, reticular cells, endothelial cells, pericytes, fat cells, and fixed macrophages. Connective tissue performs important functions such as structural support, metabolism, defense, tissue repair, and energy storage.