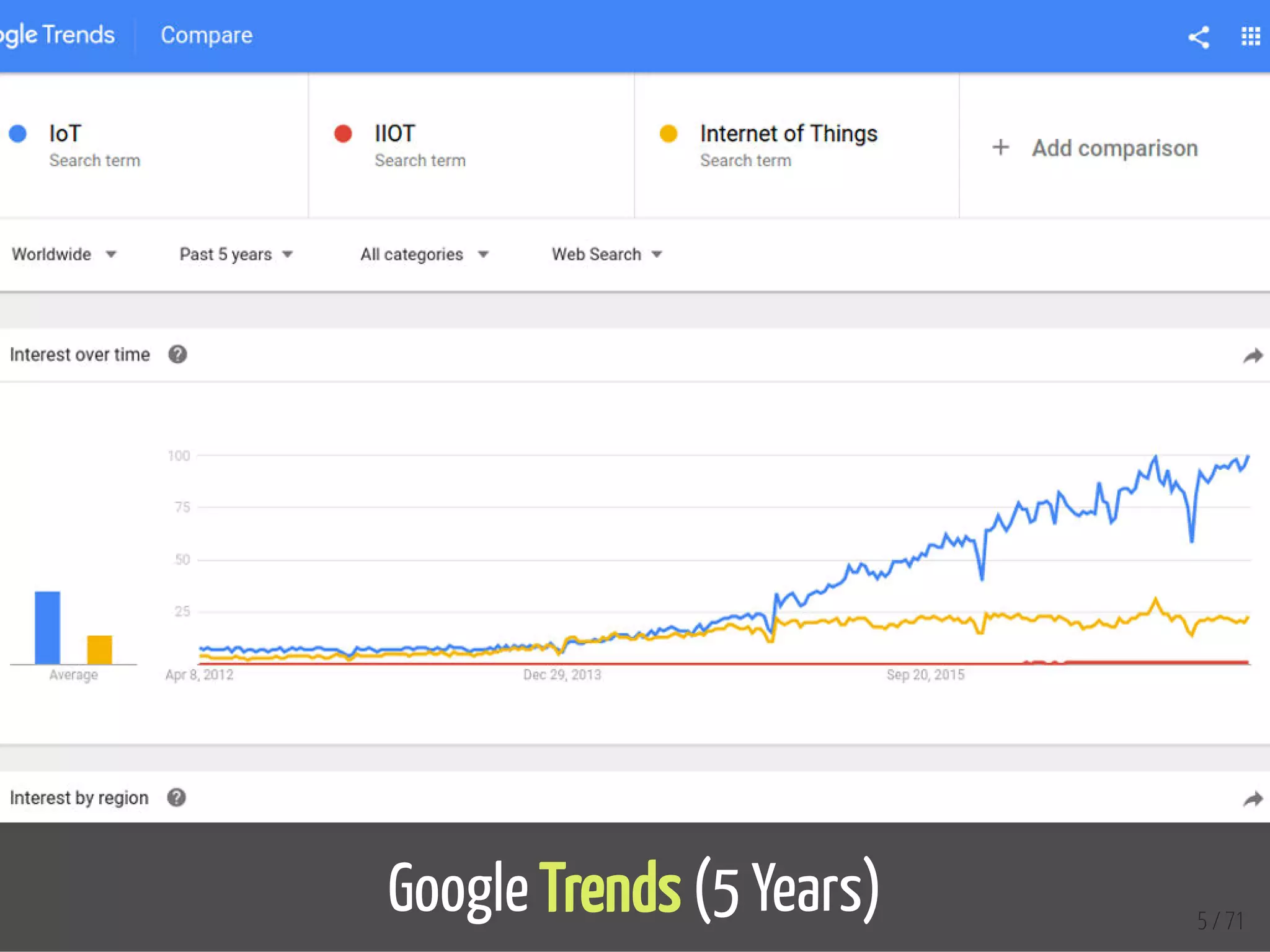
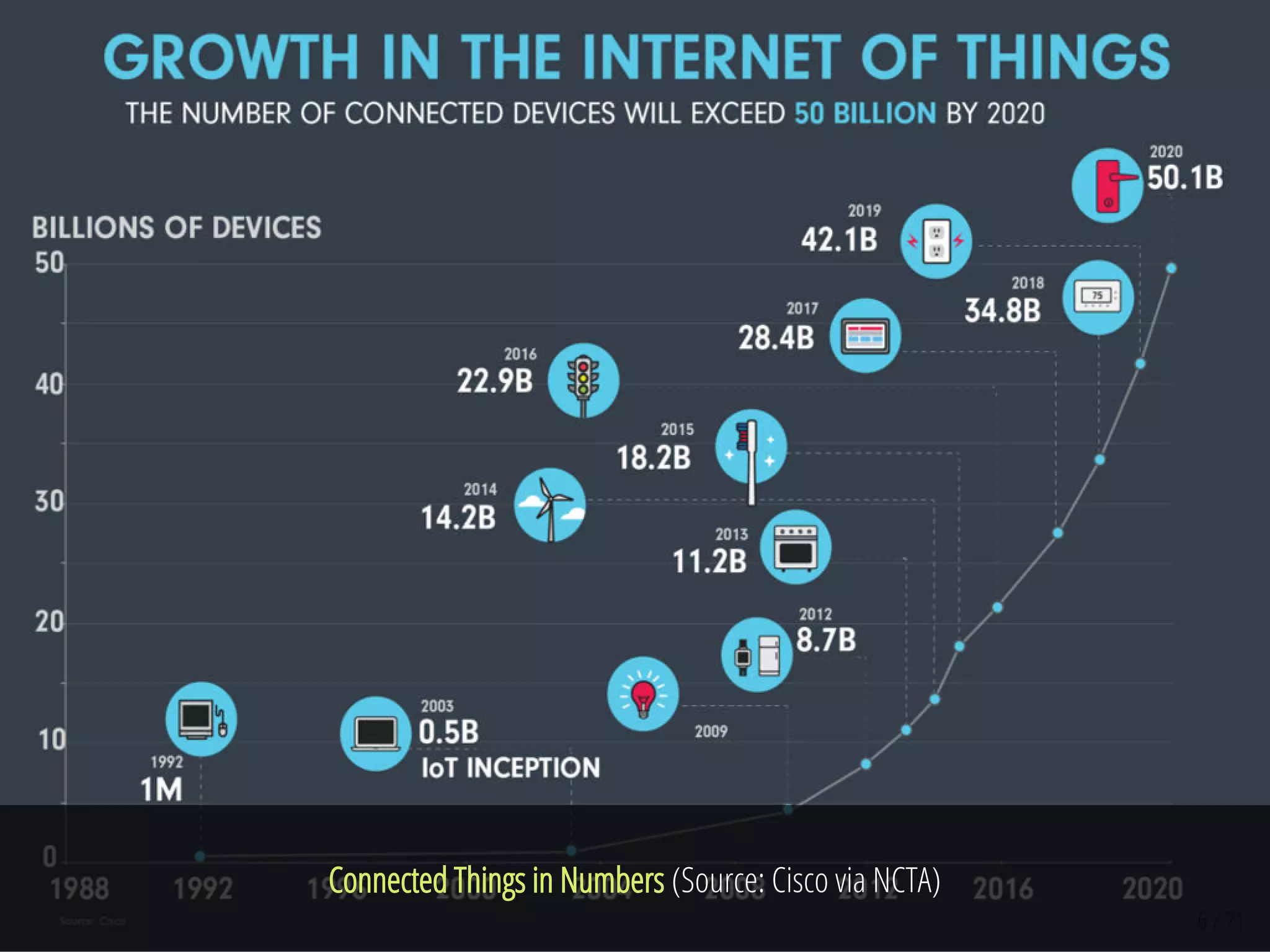
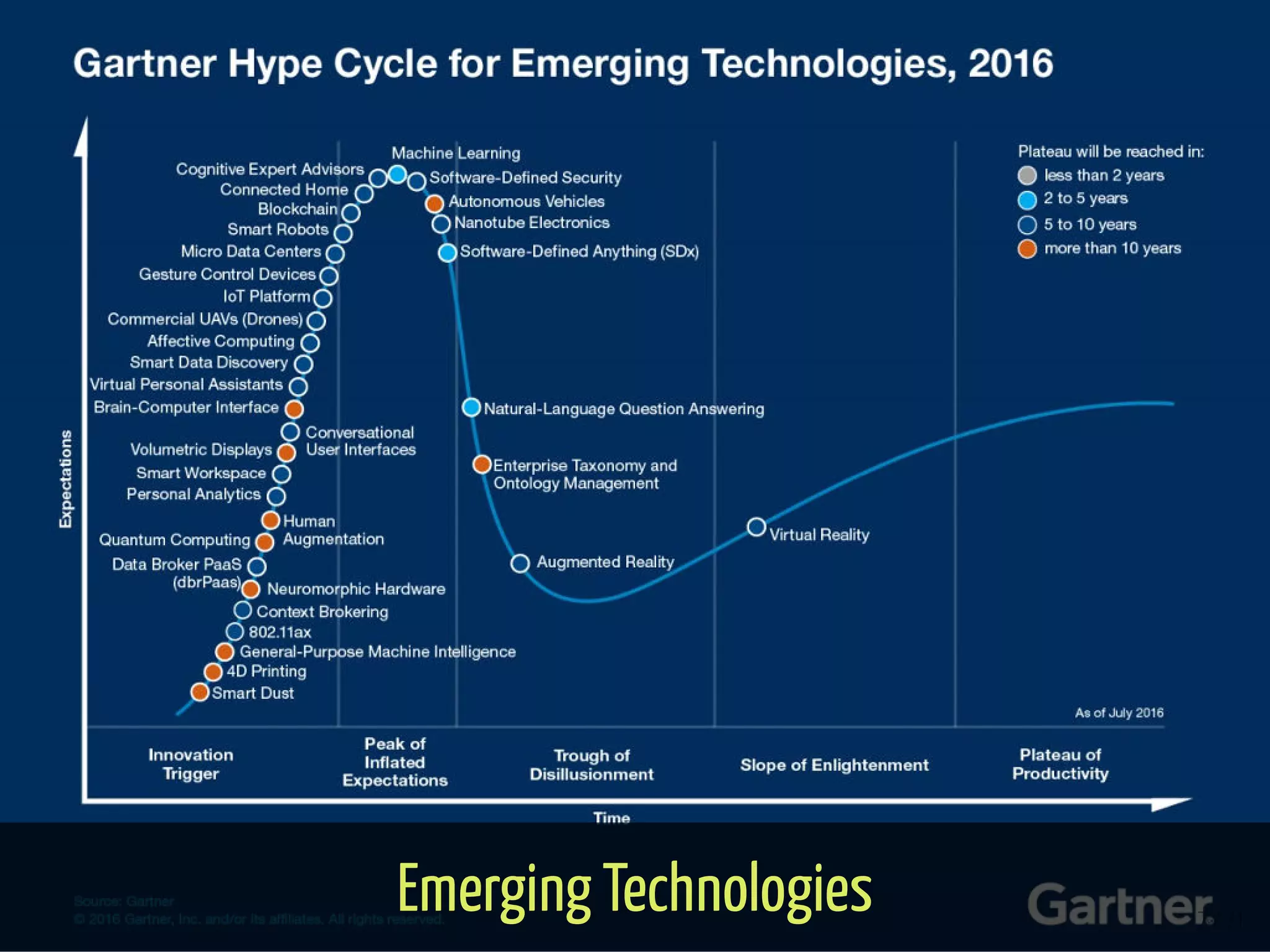
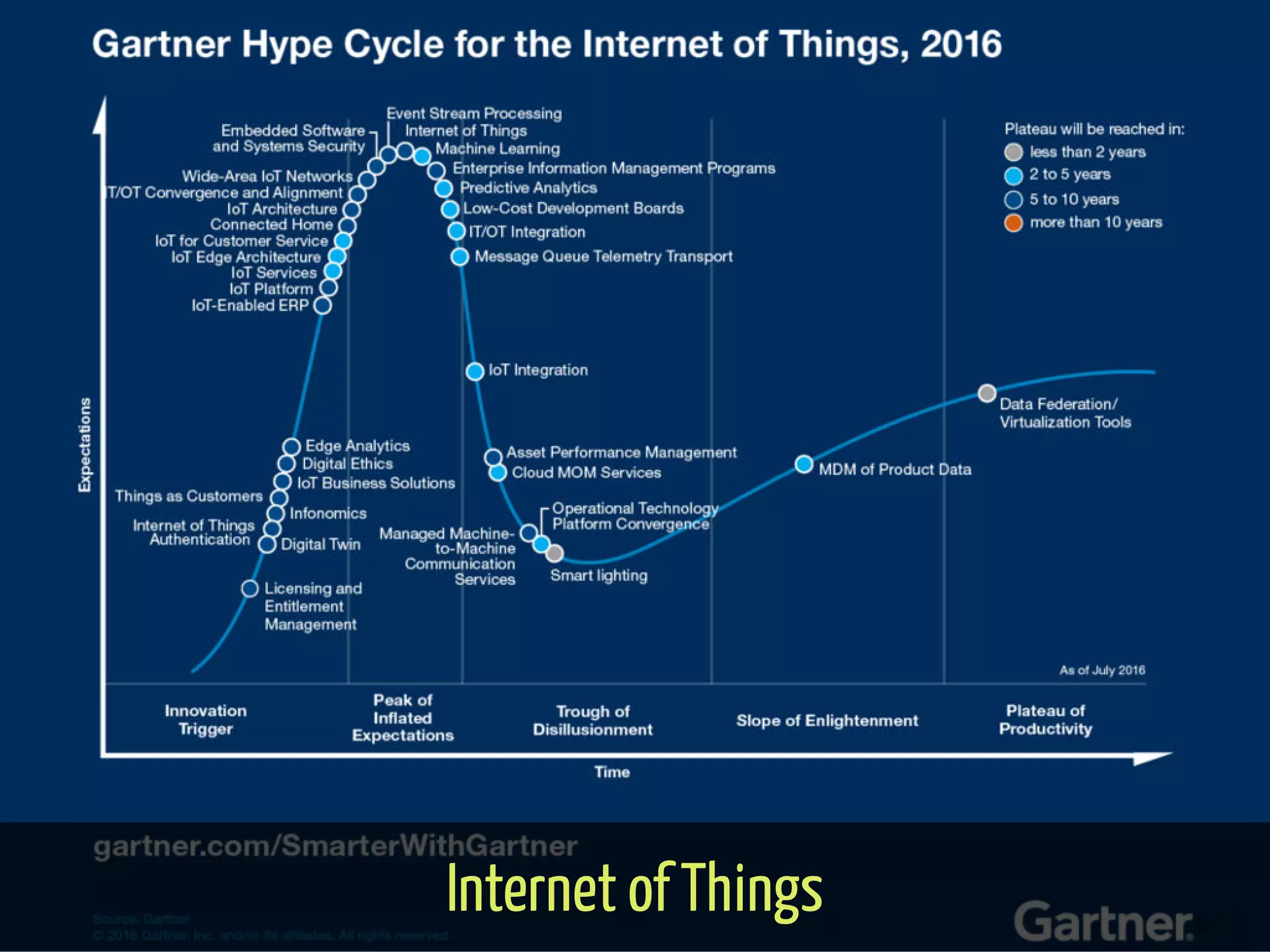
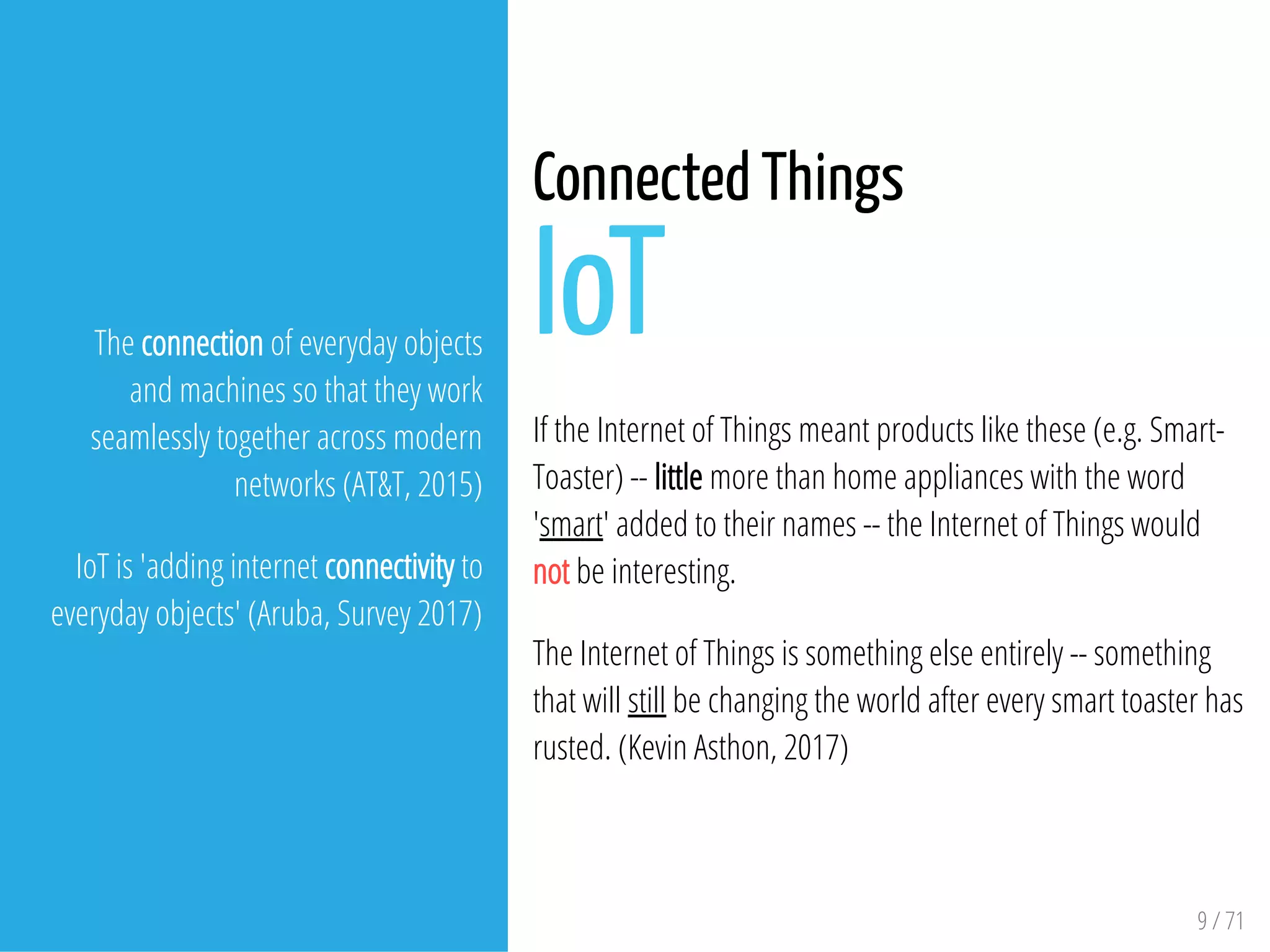
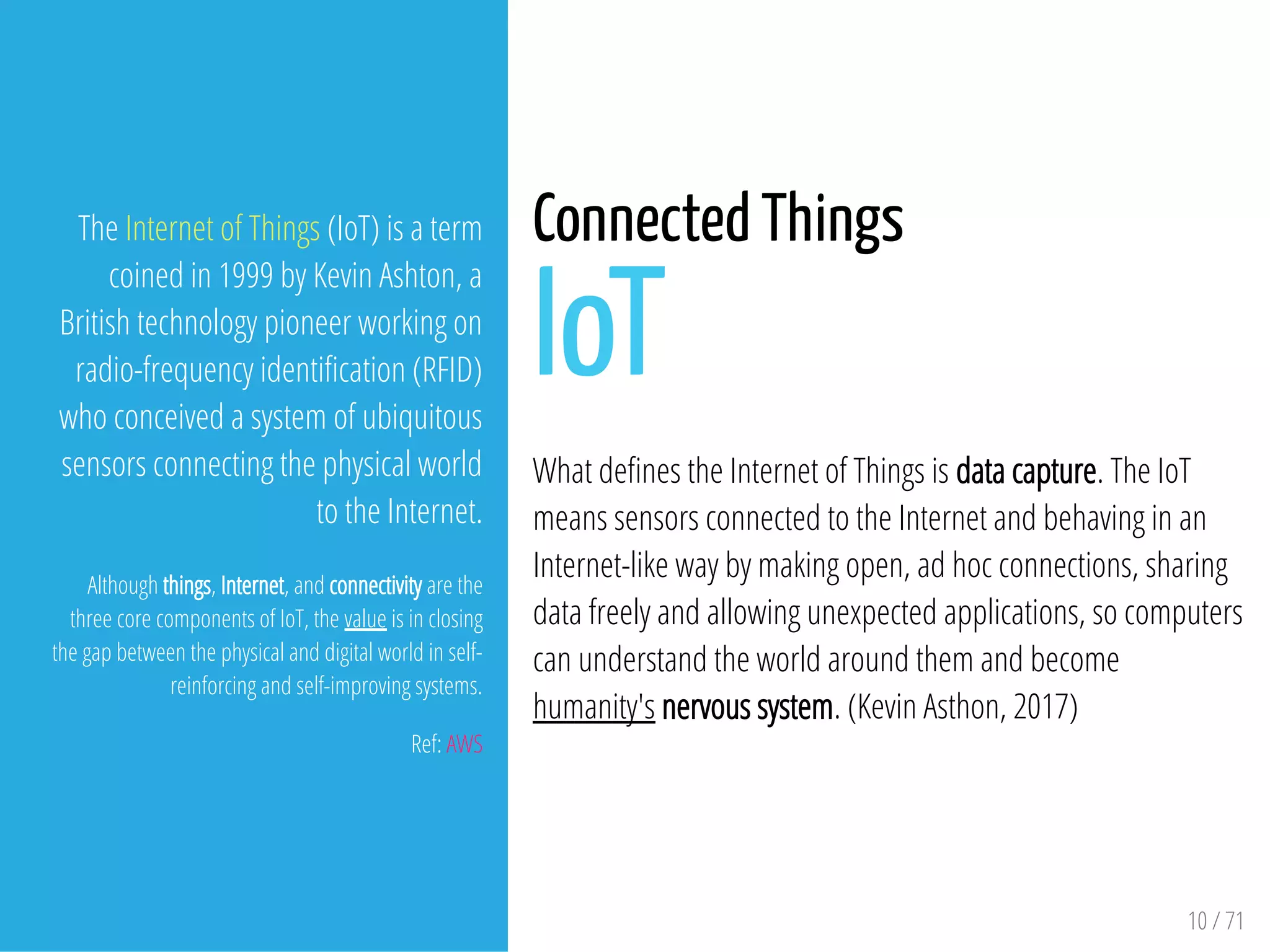
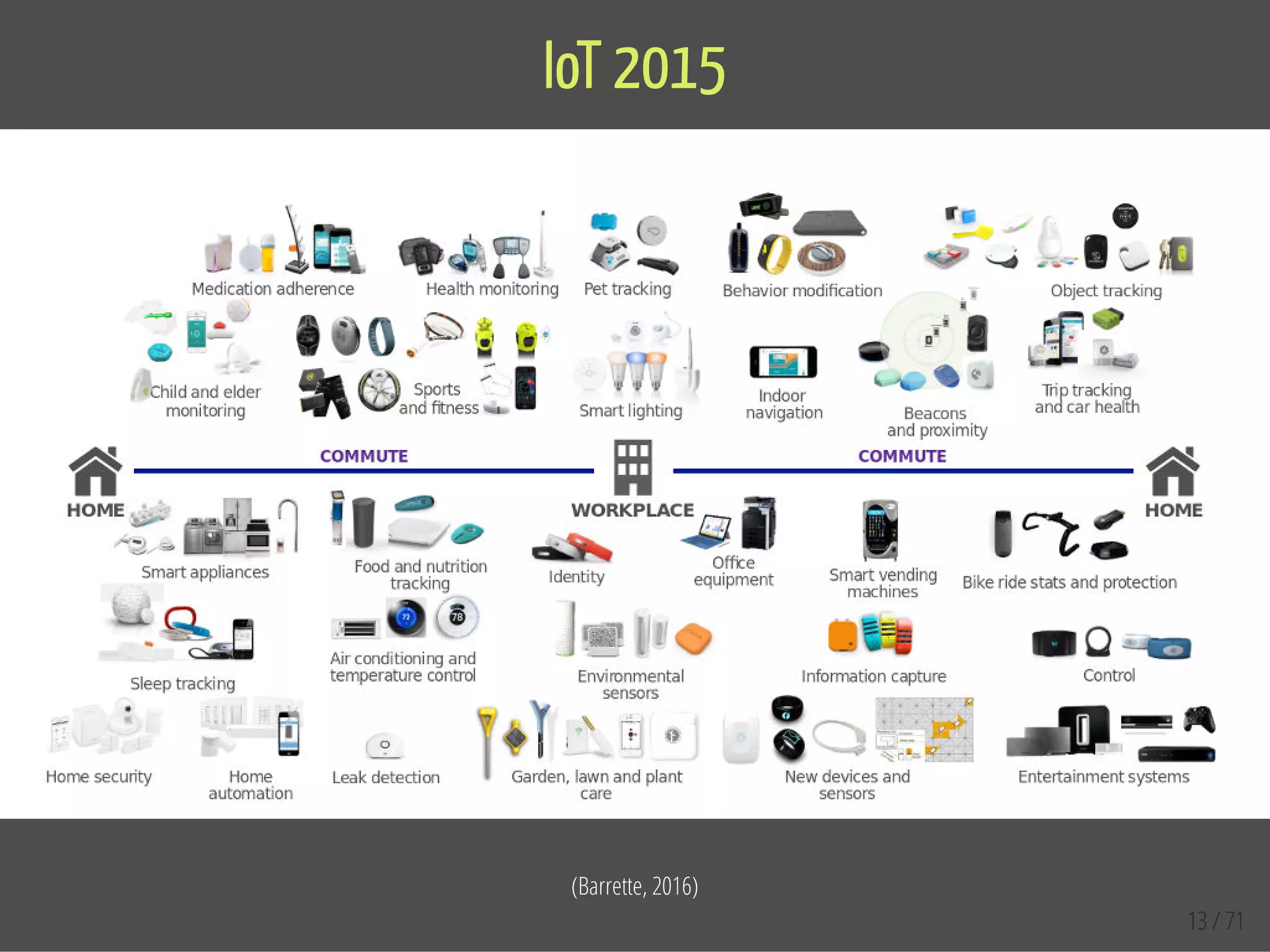
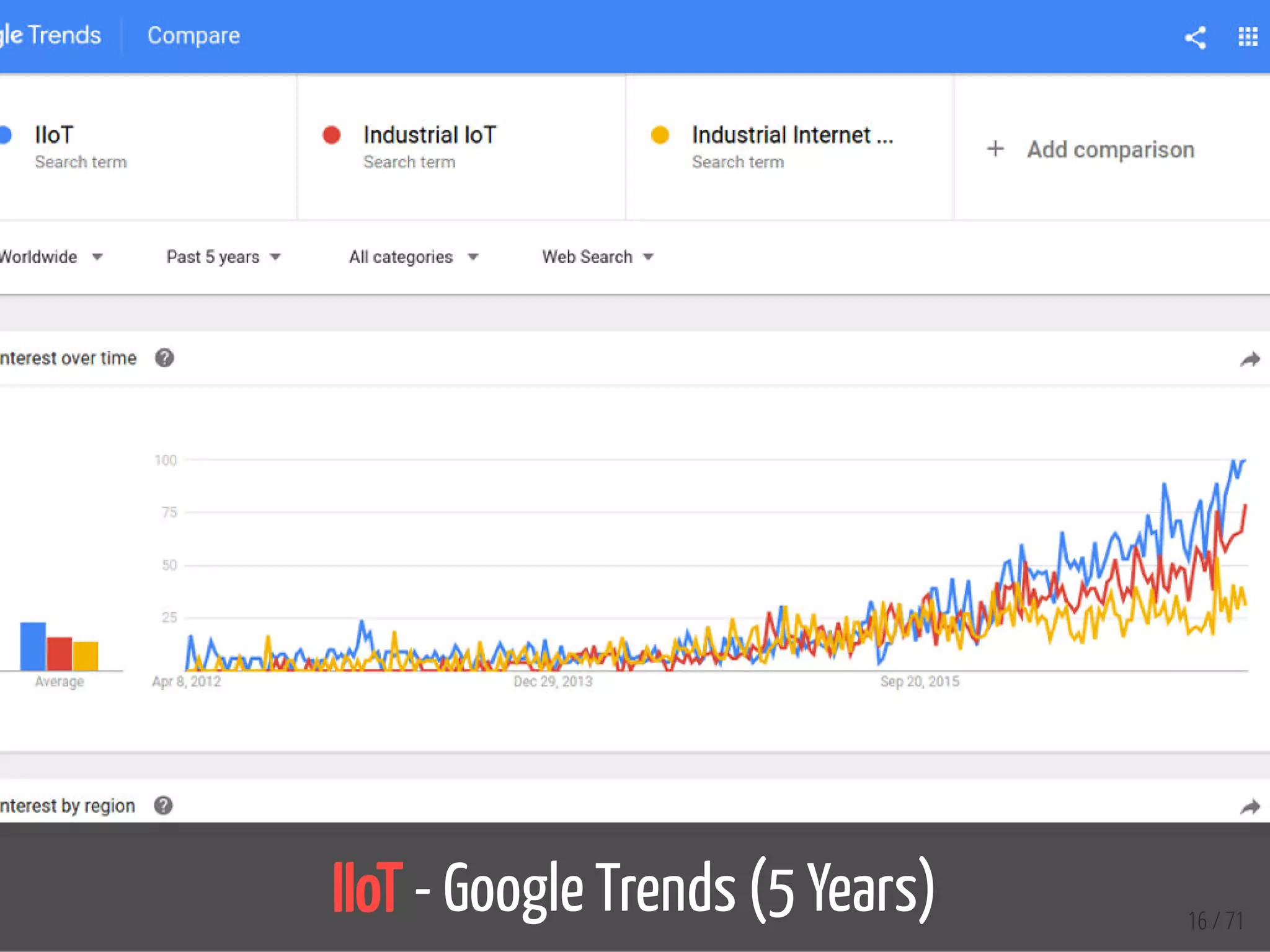
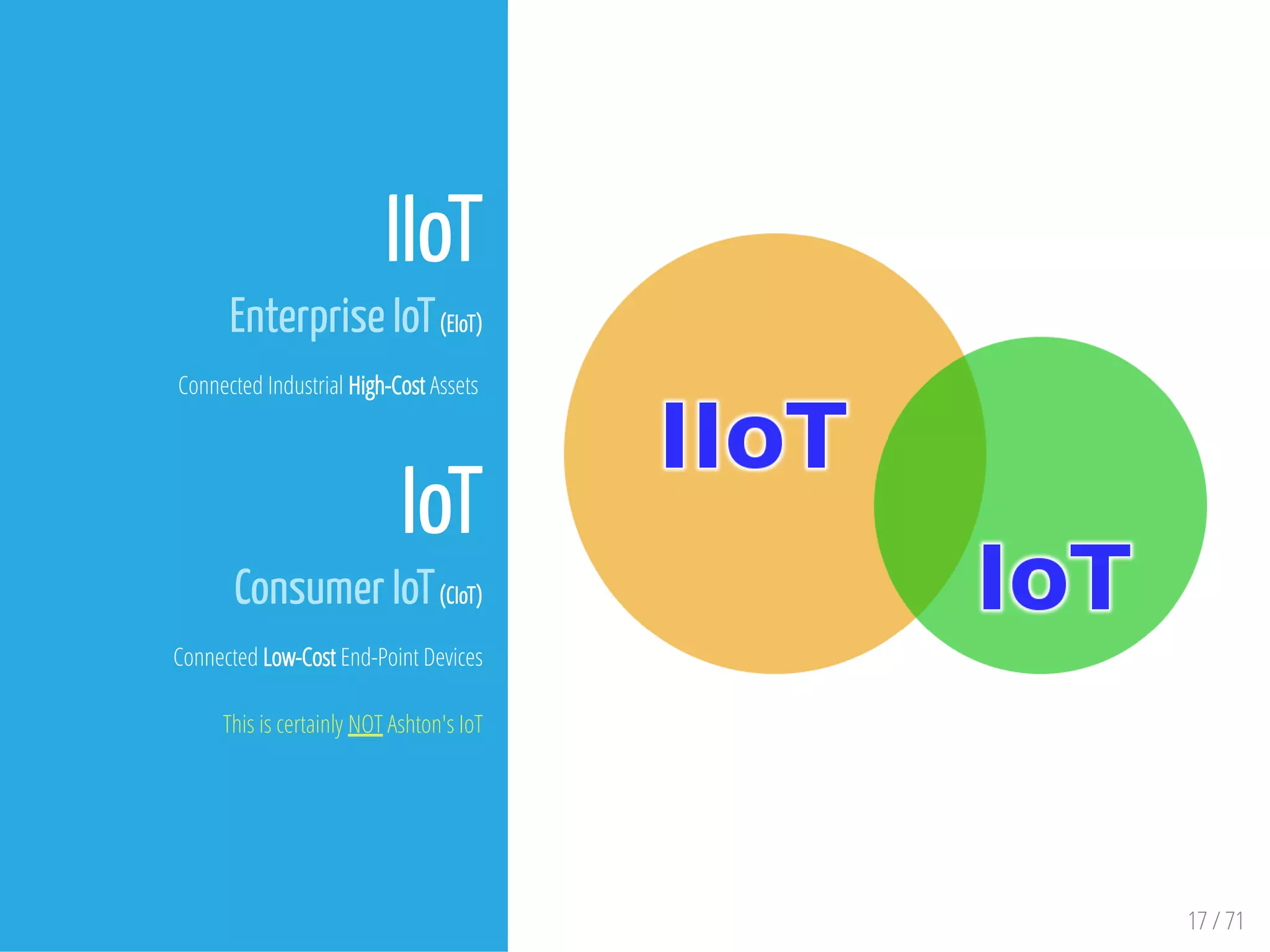
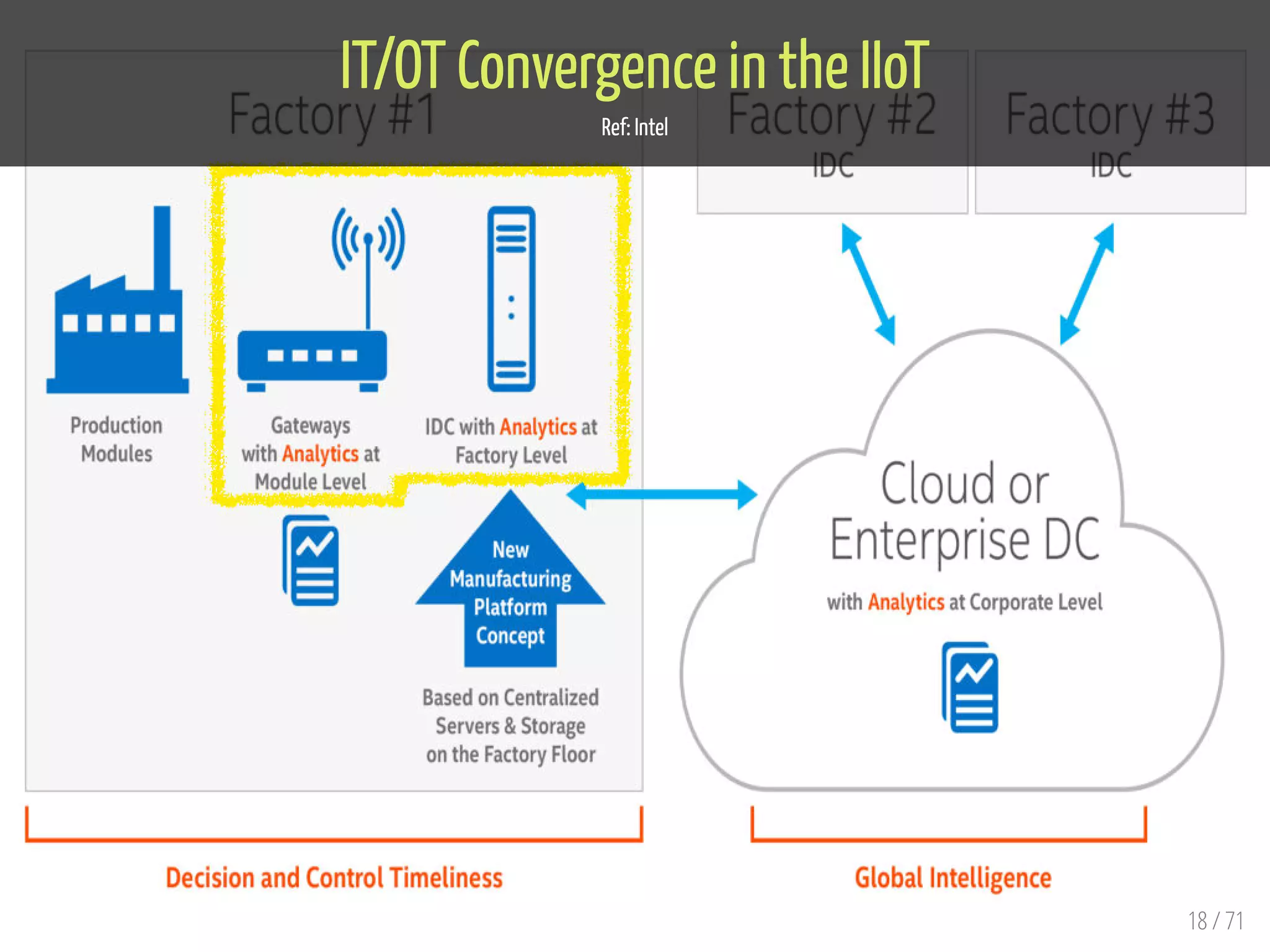
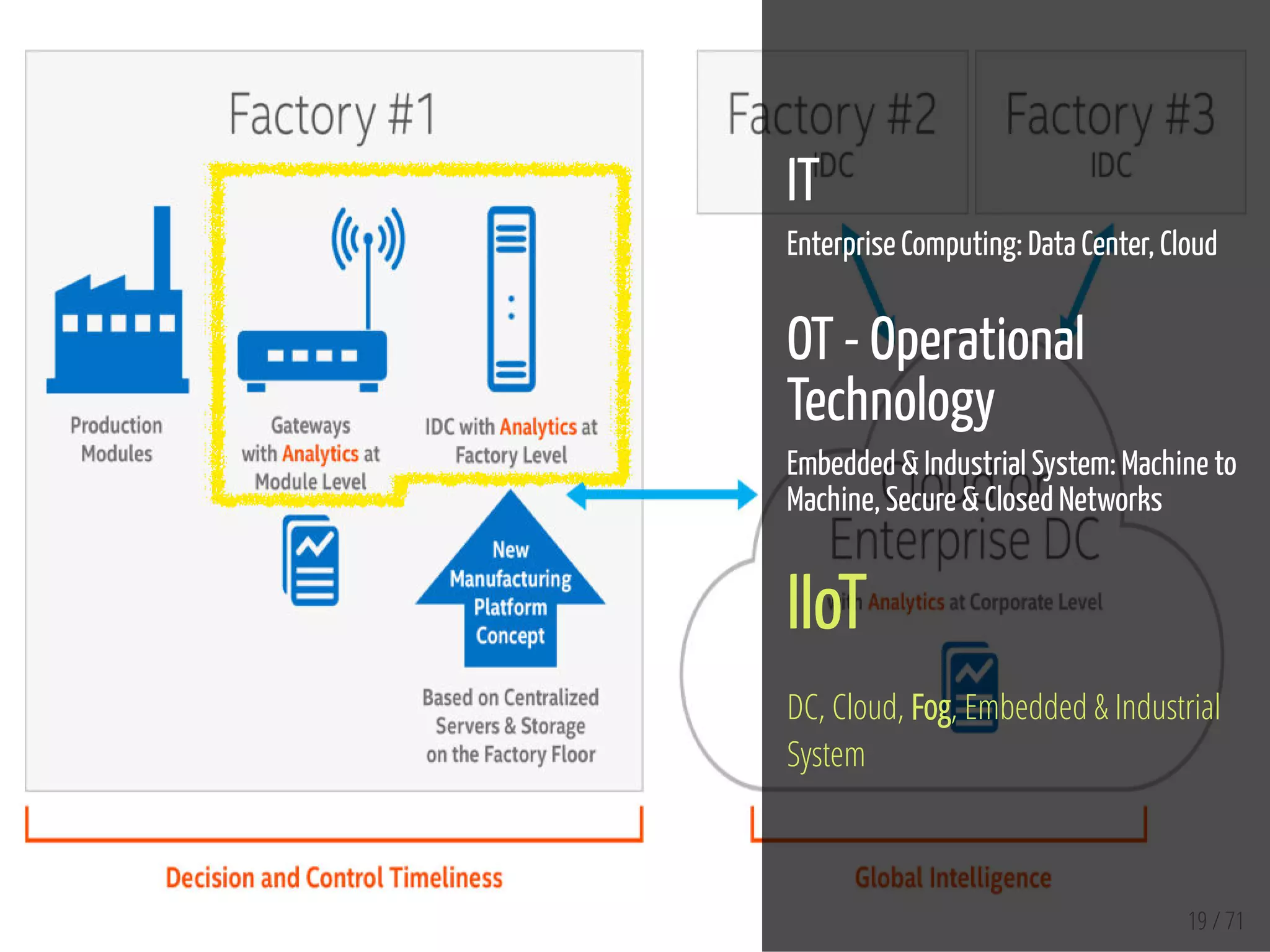
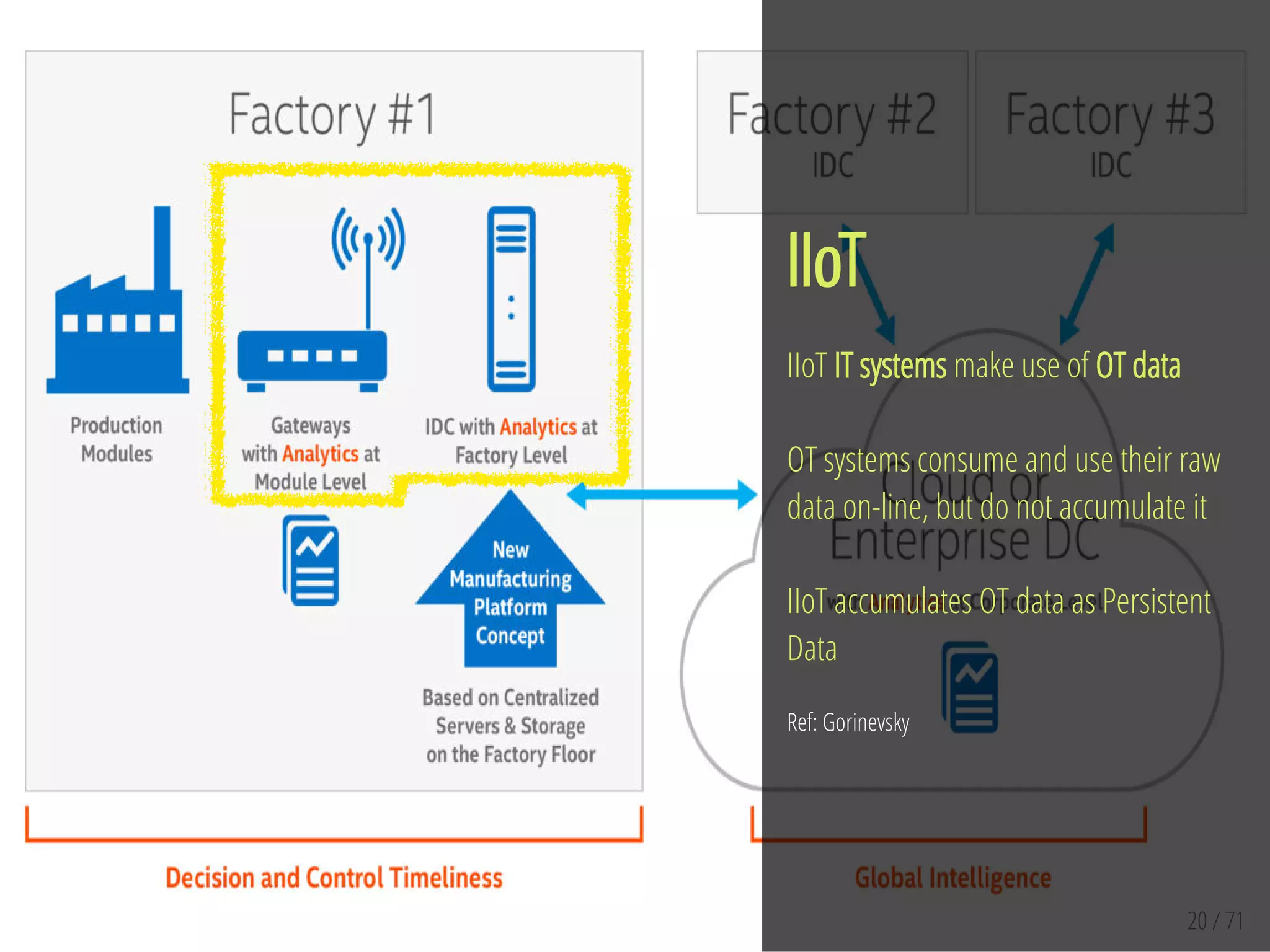
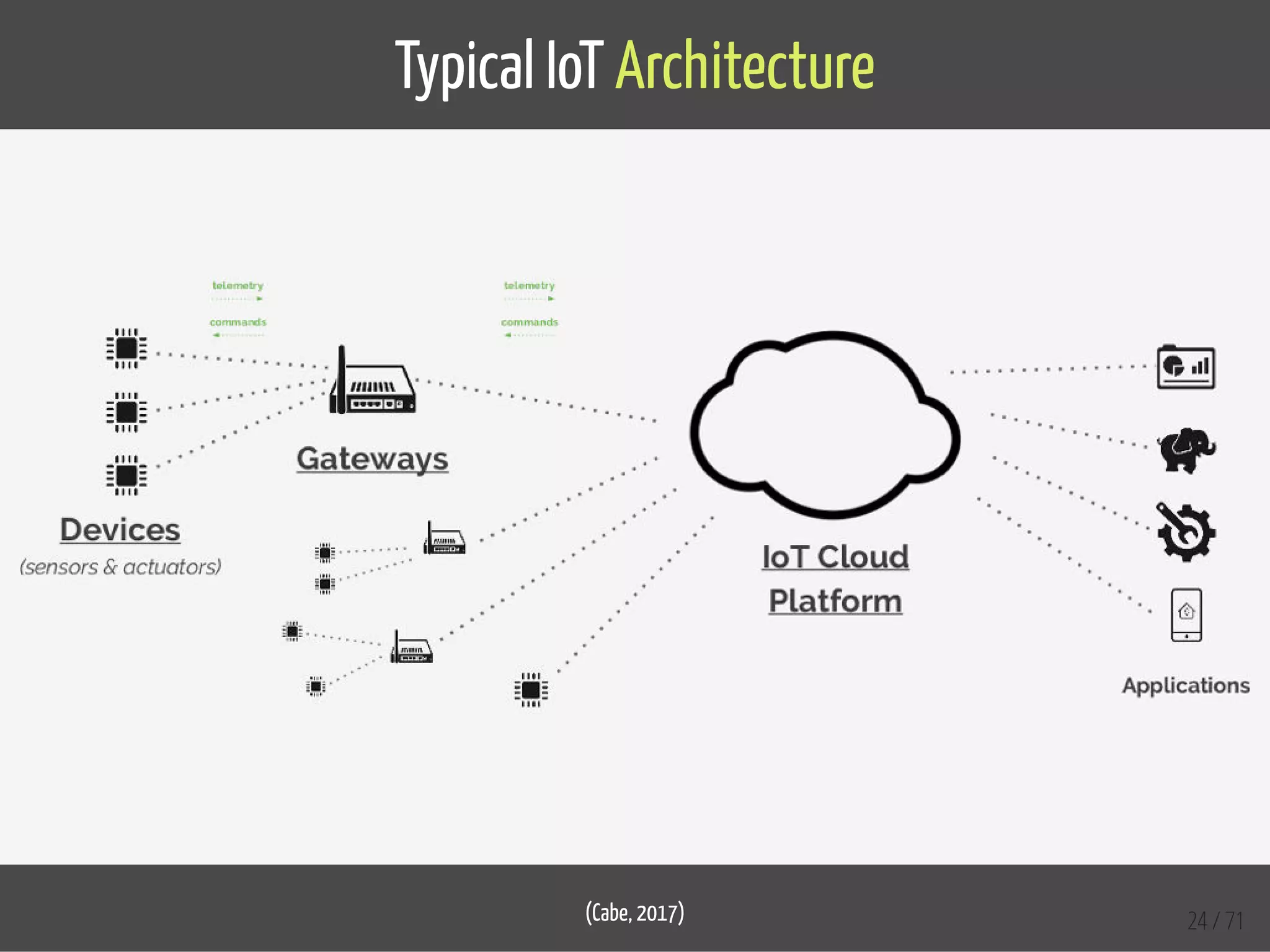
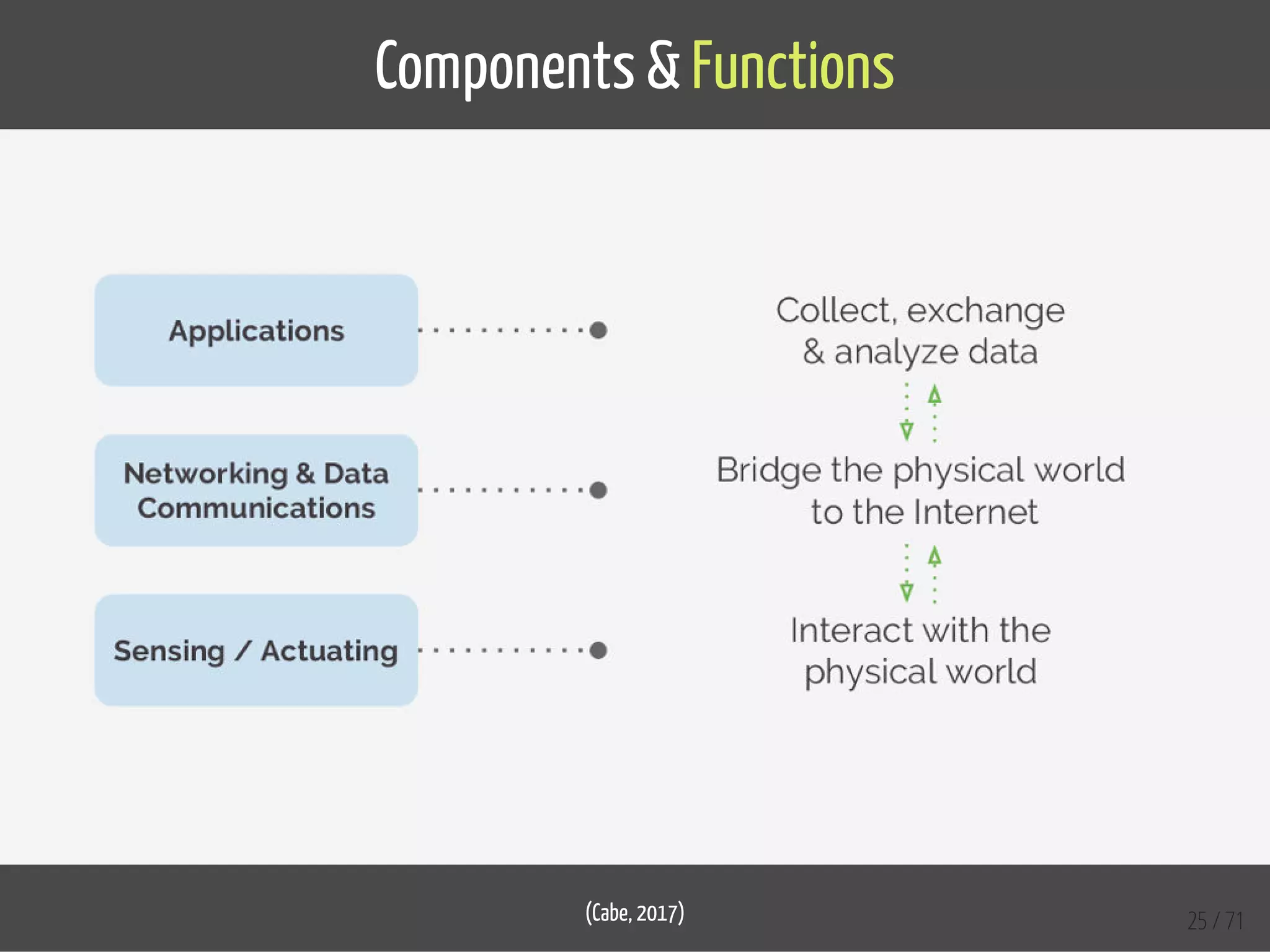
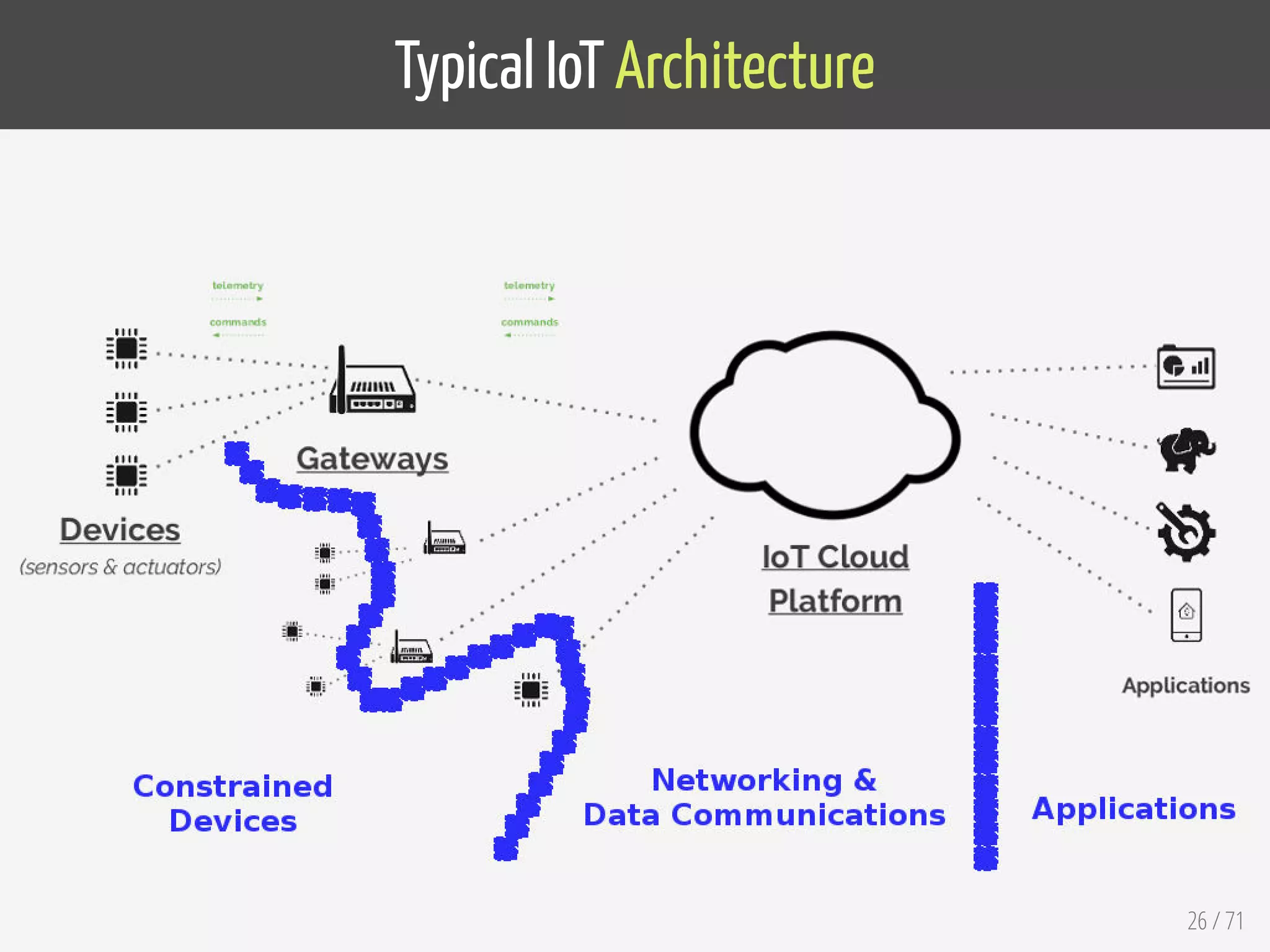
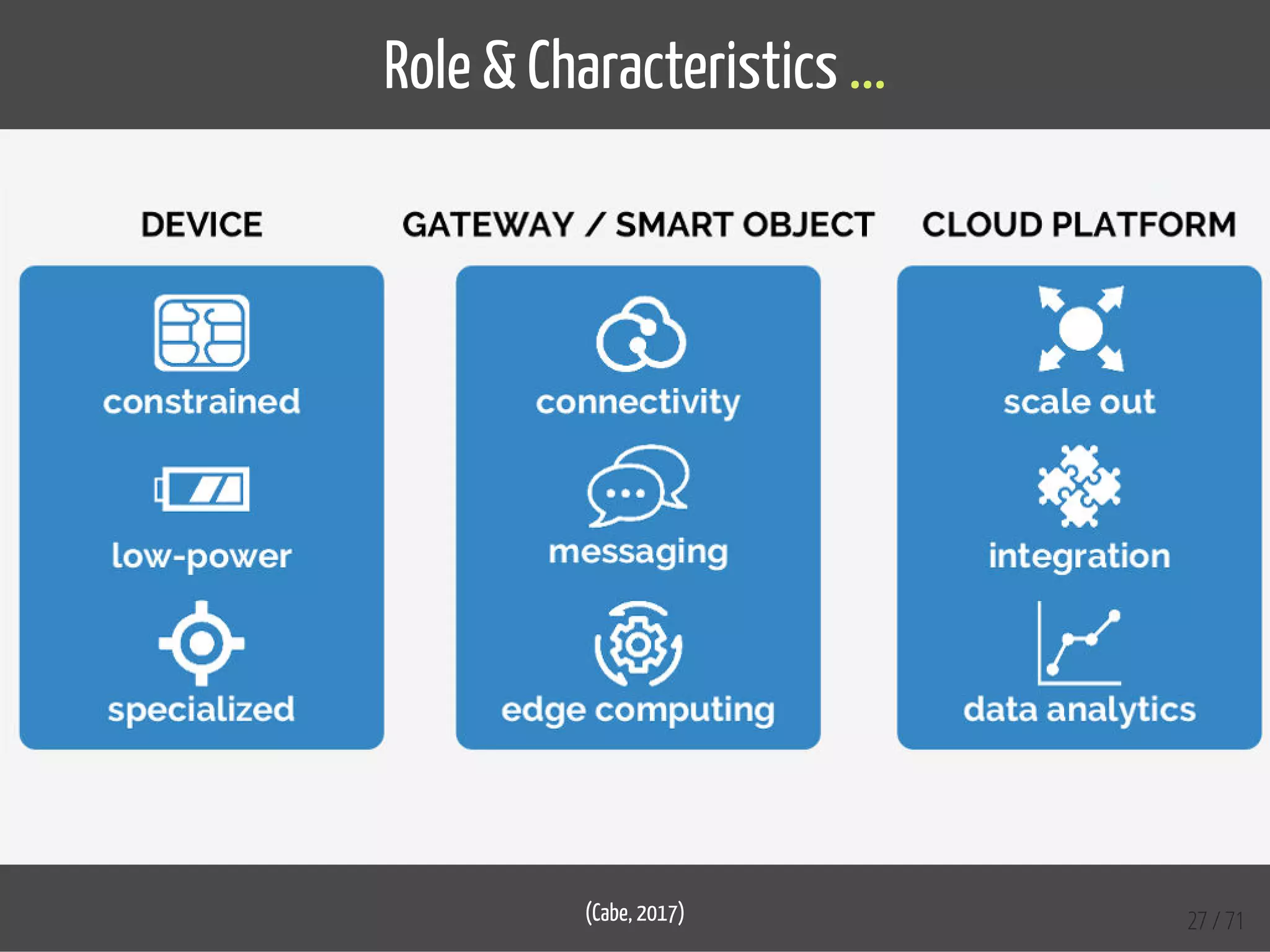
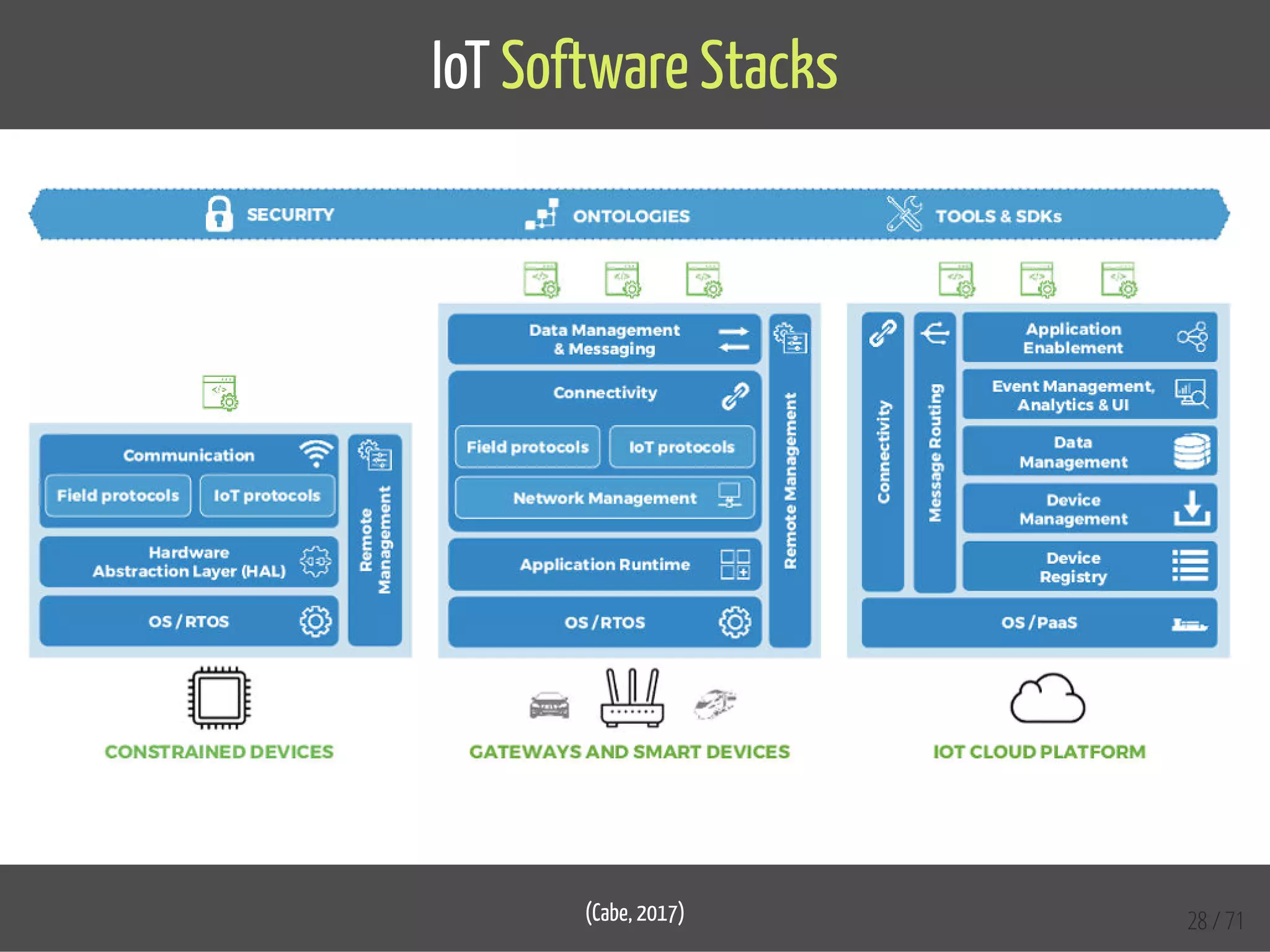
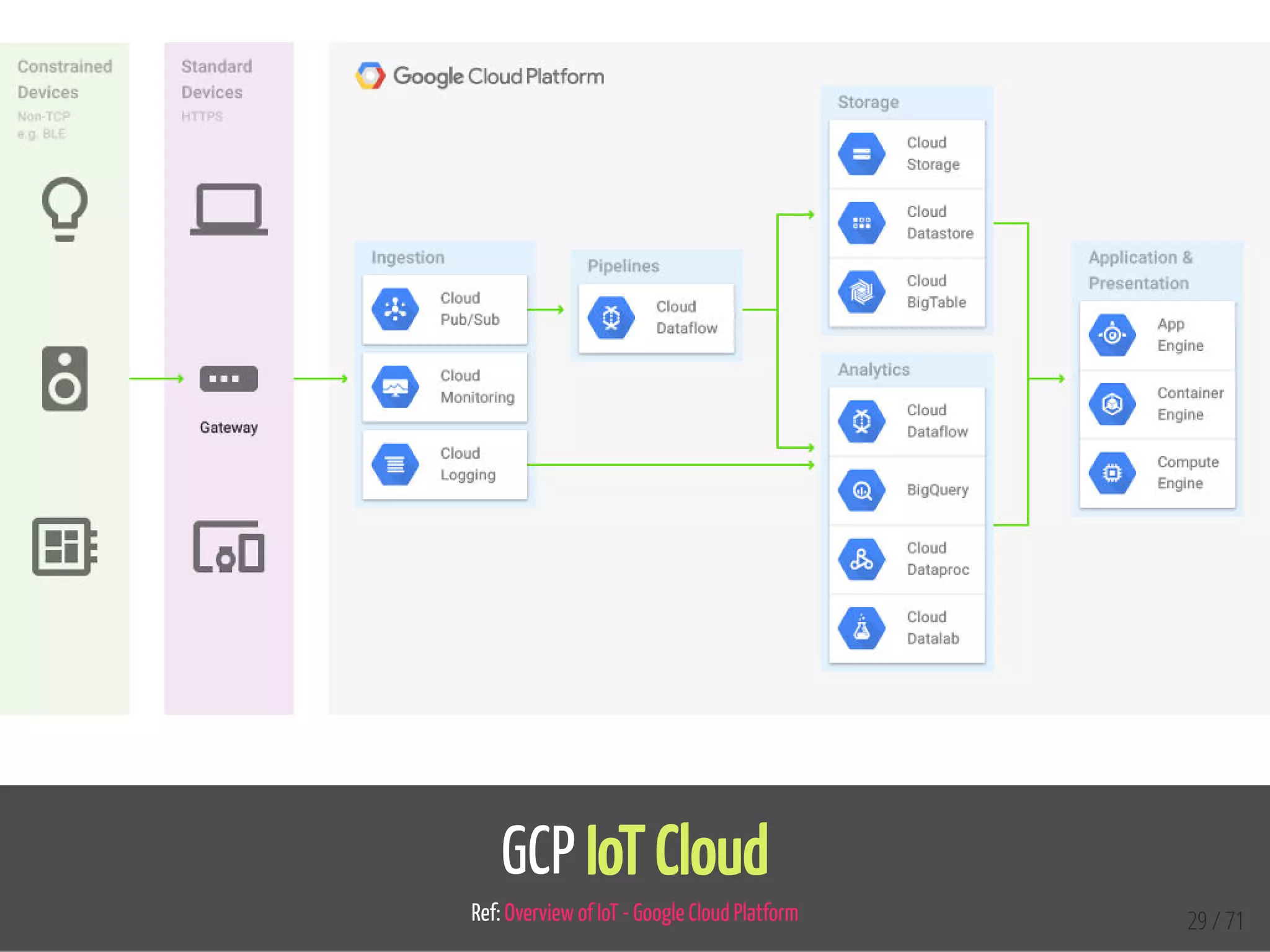
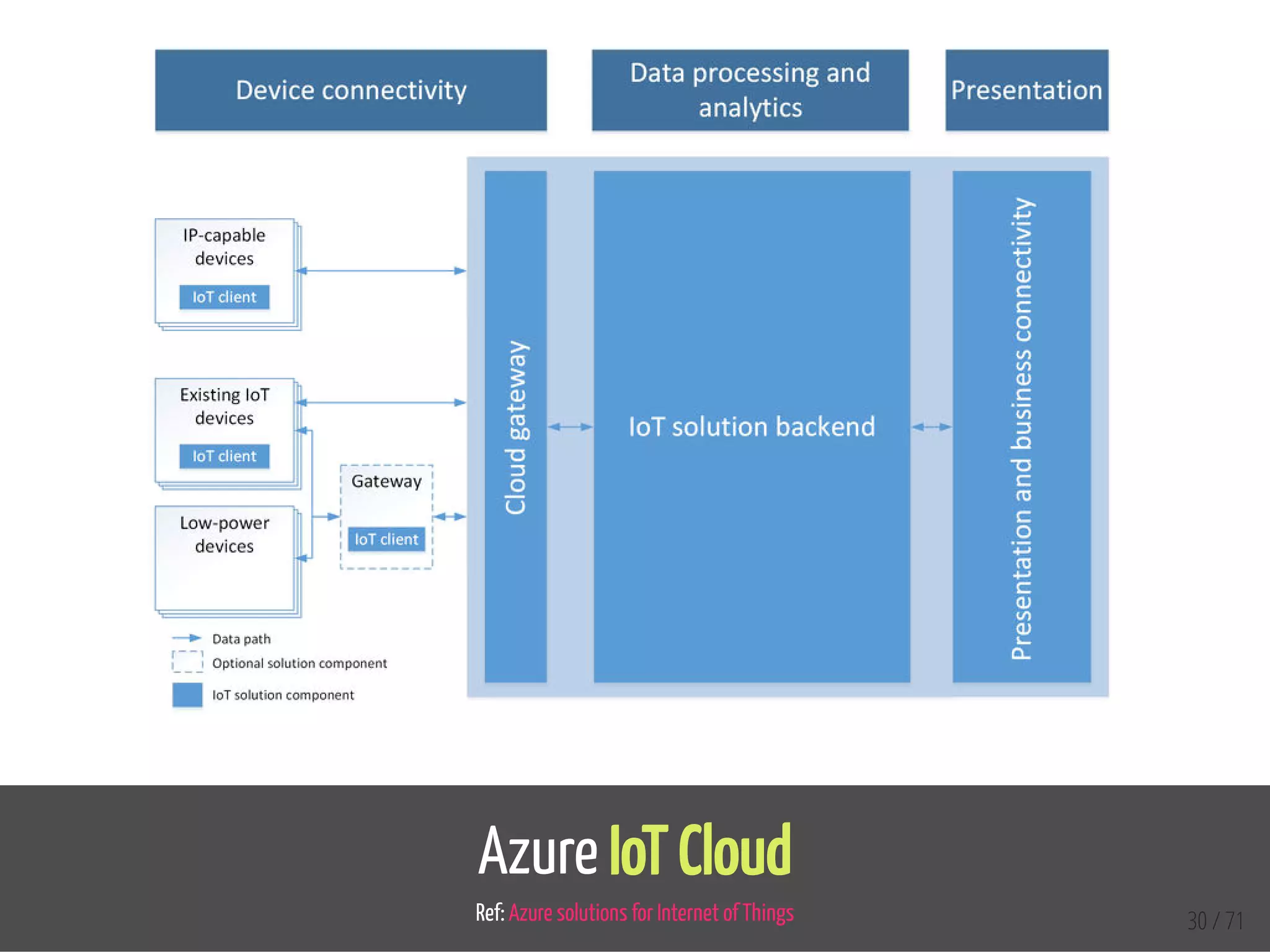
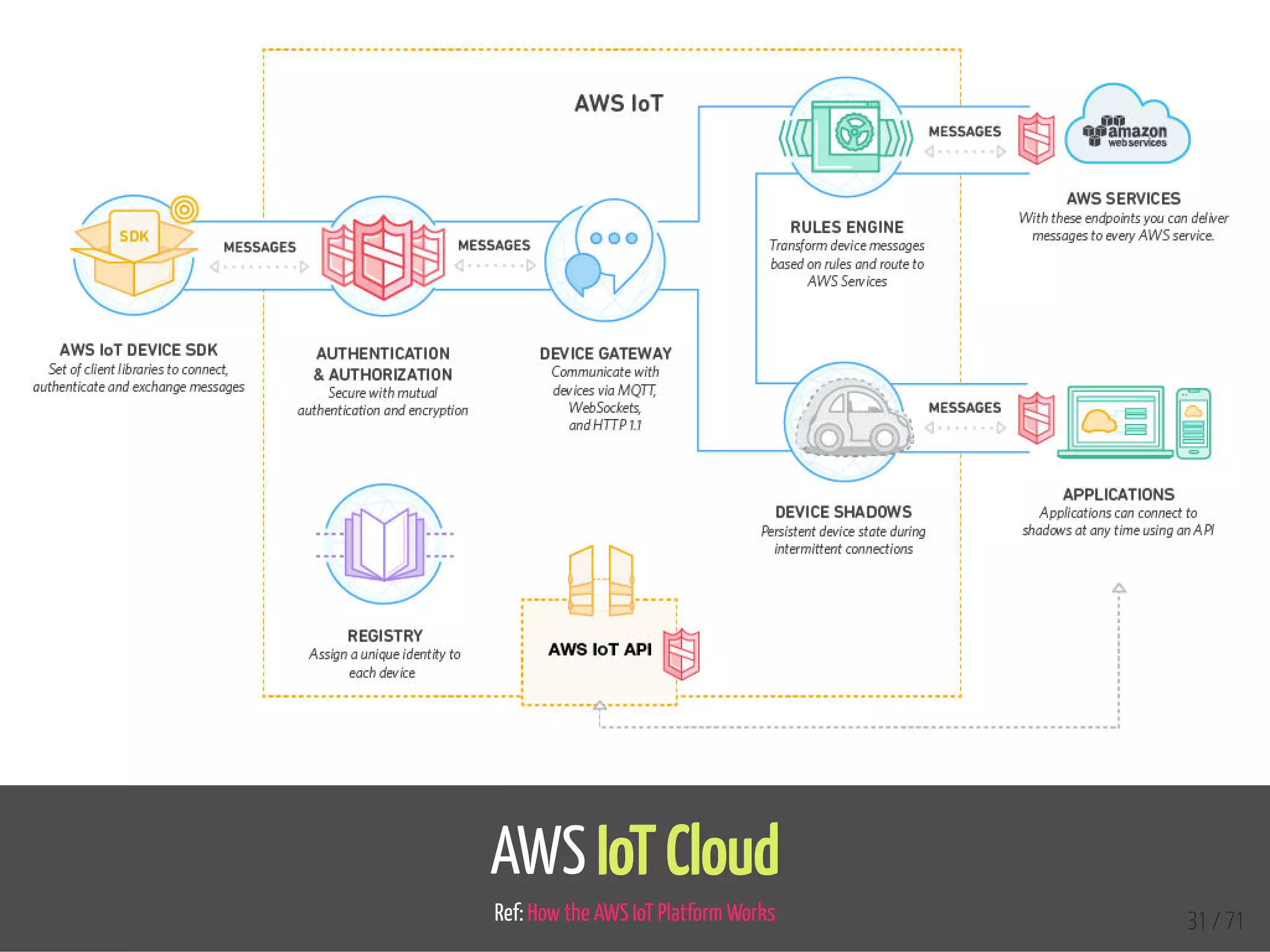
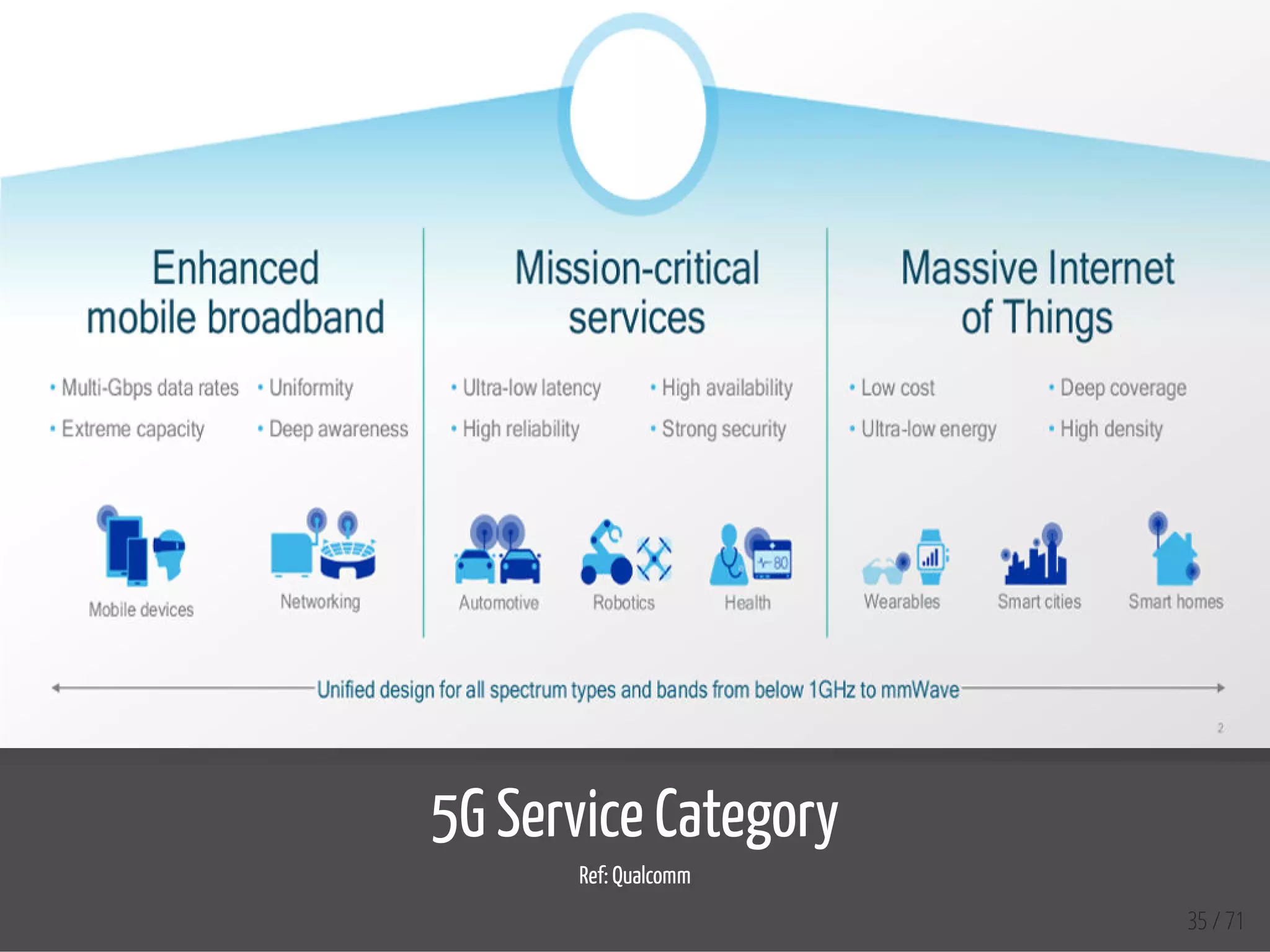
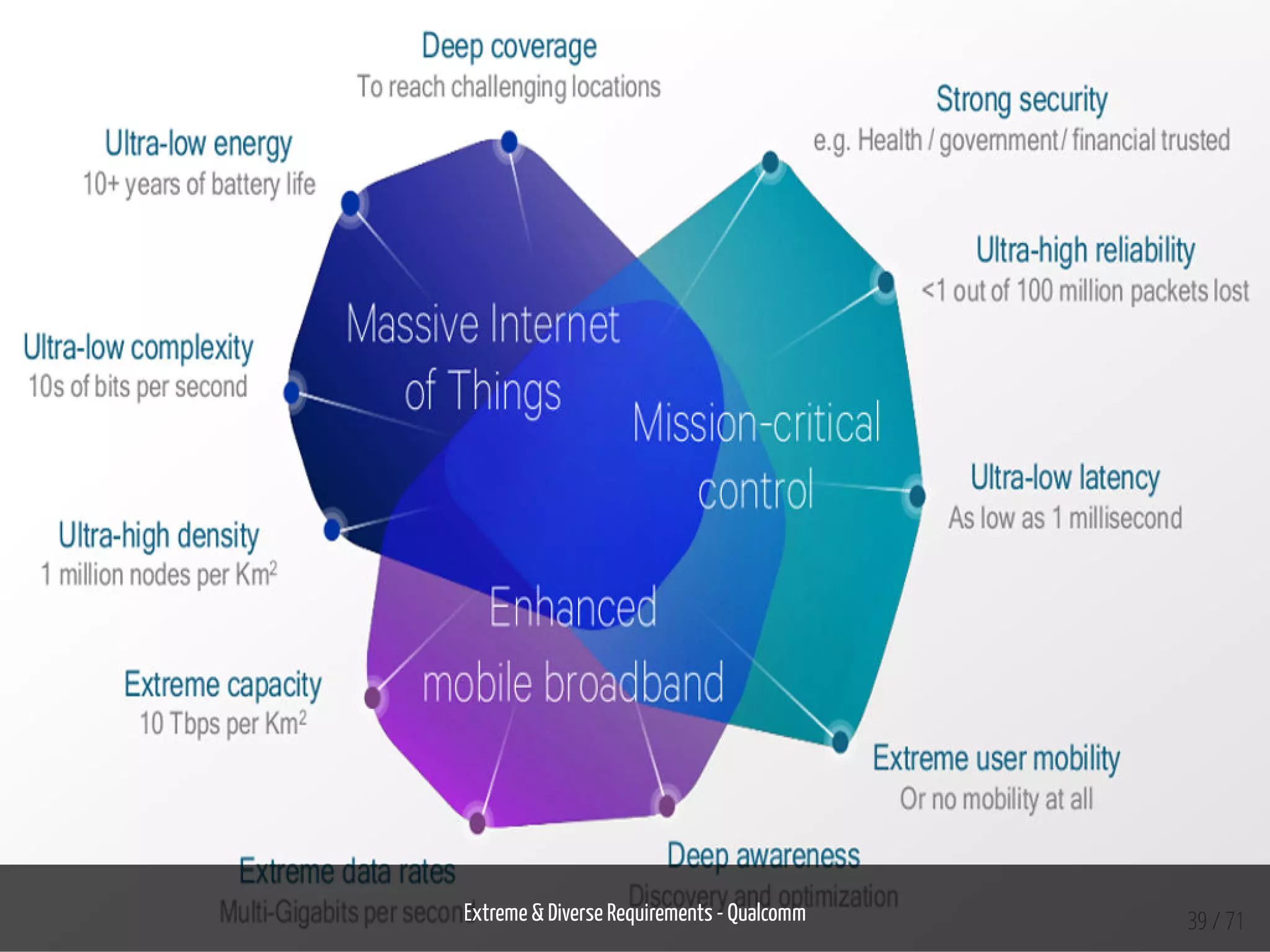
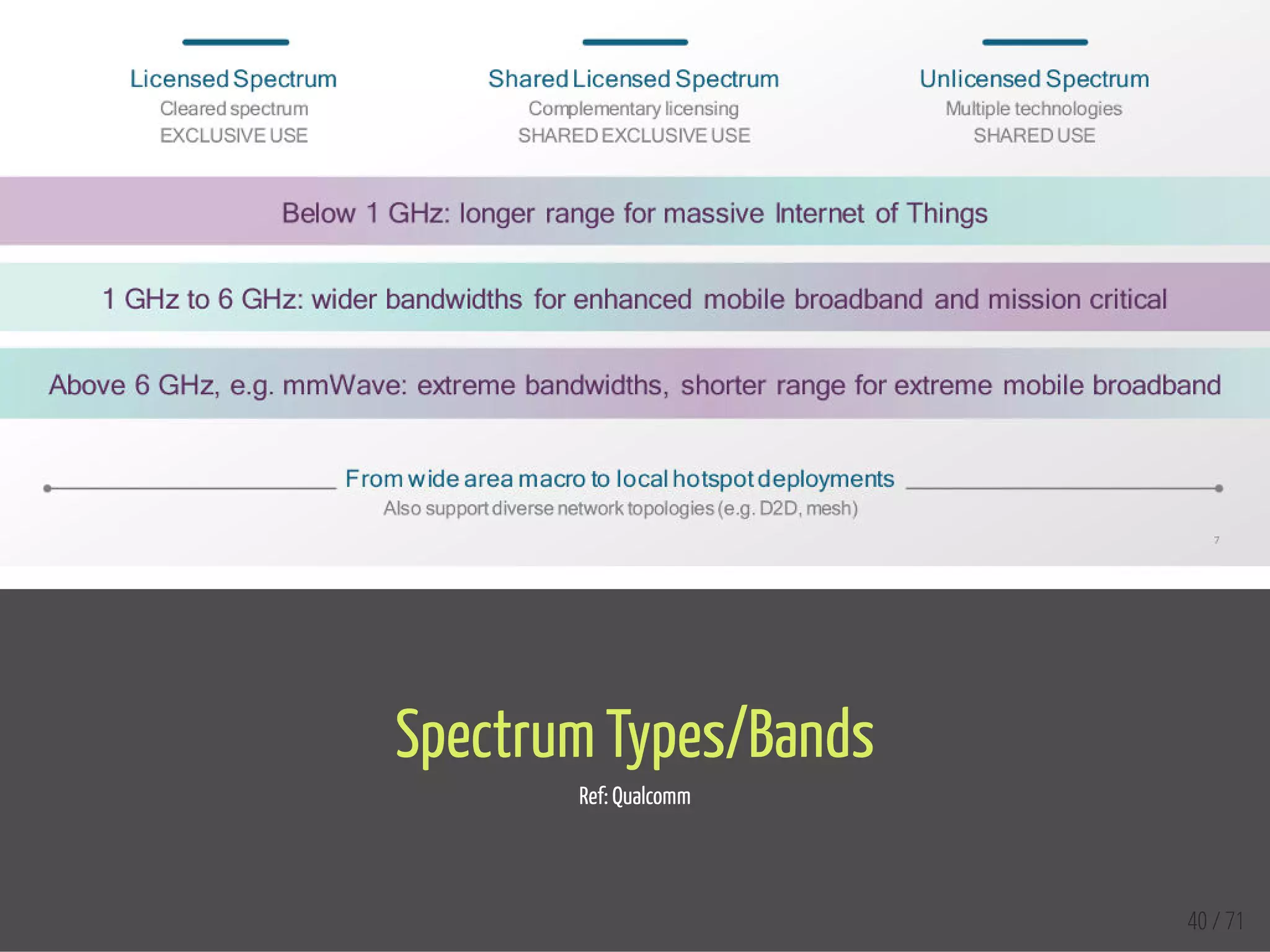
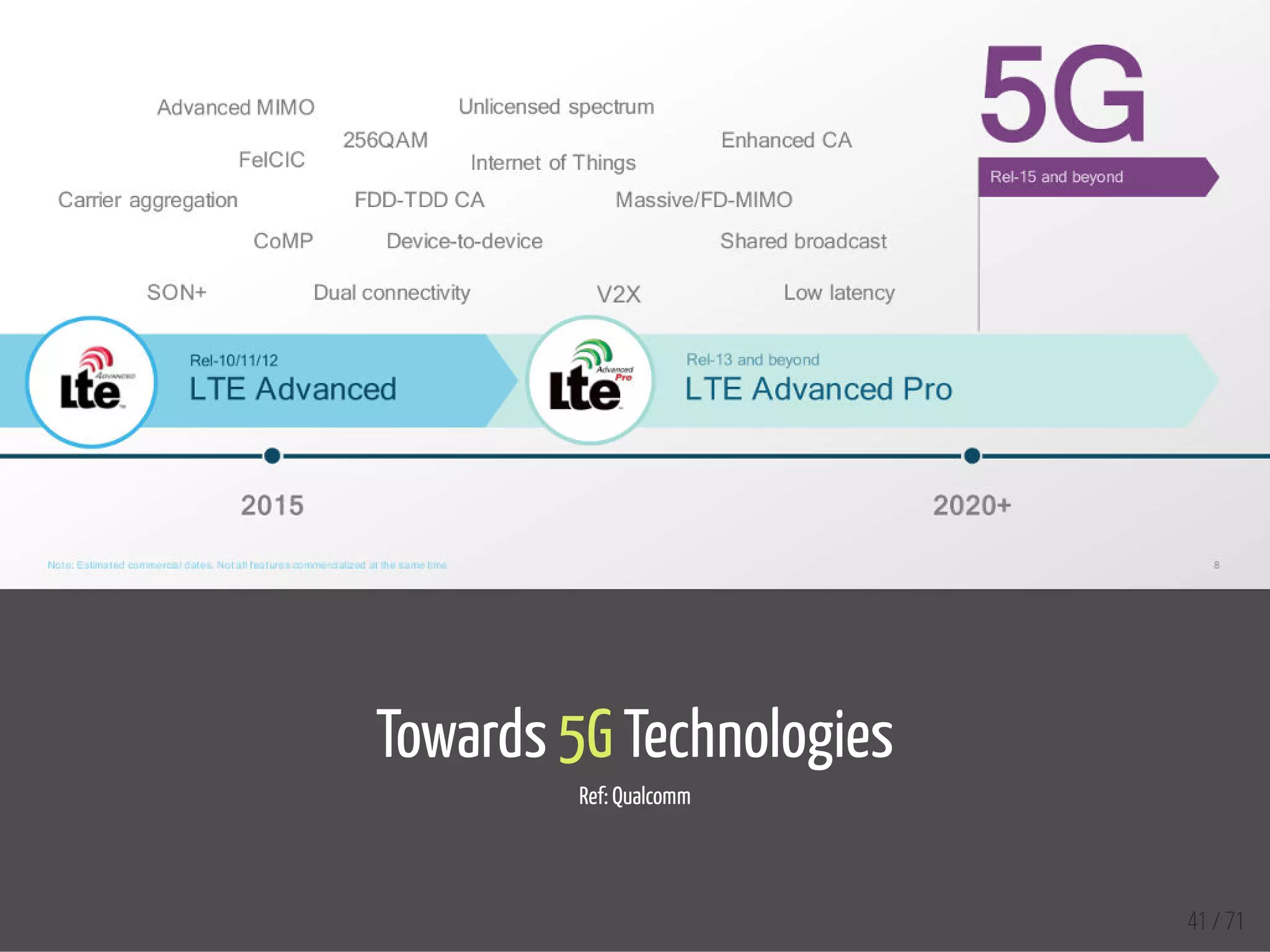
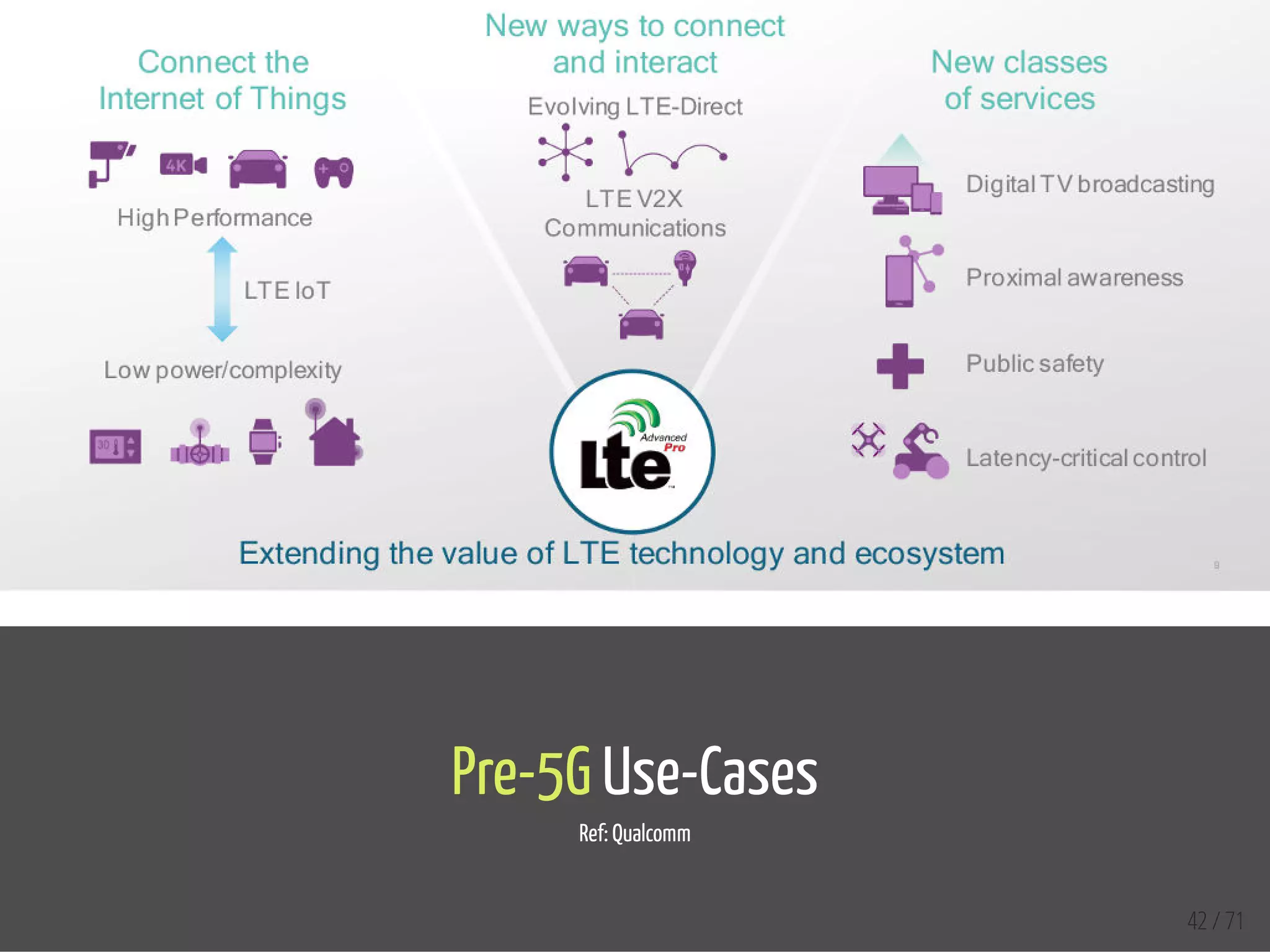
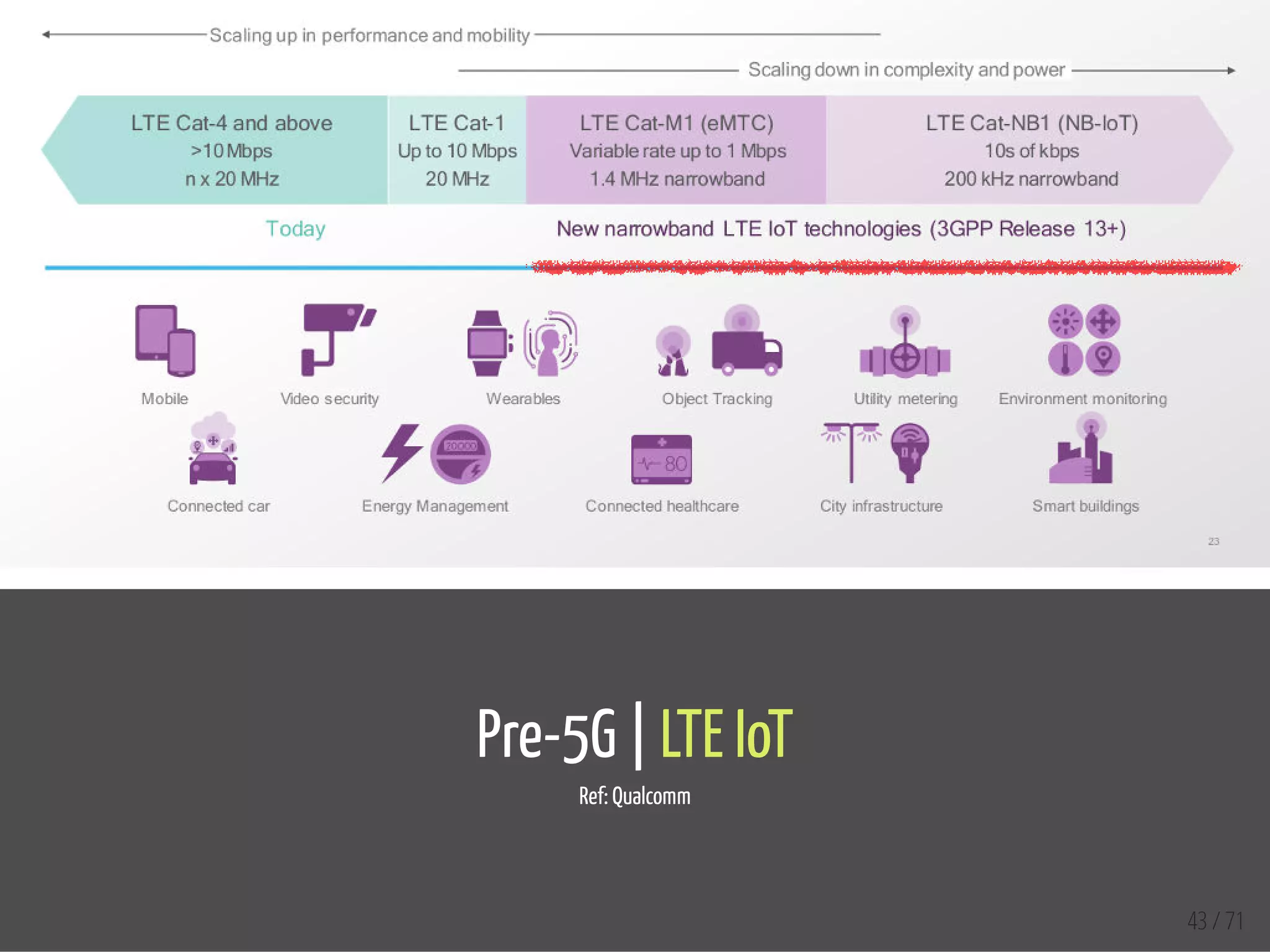
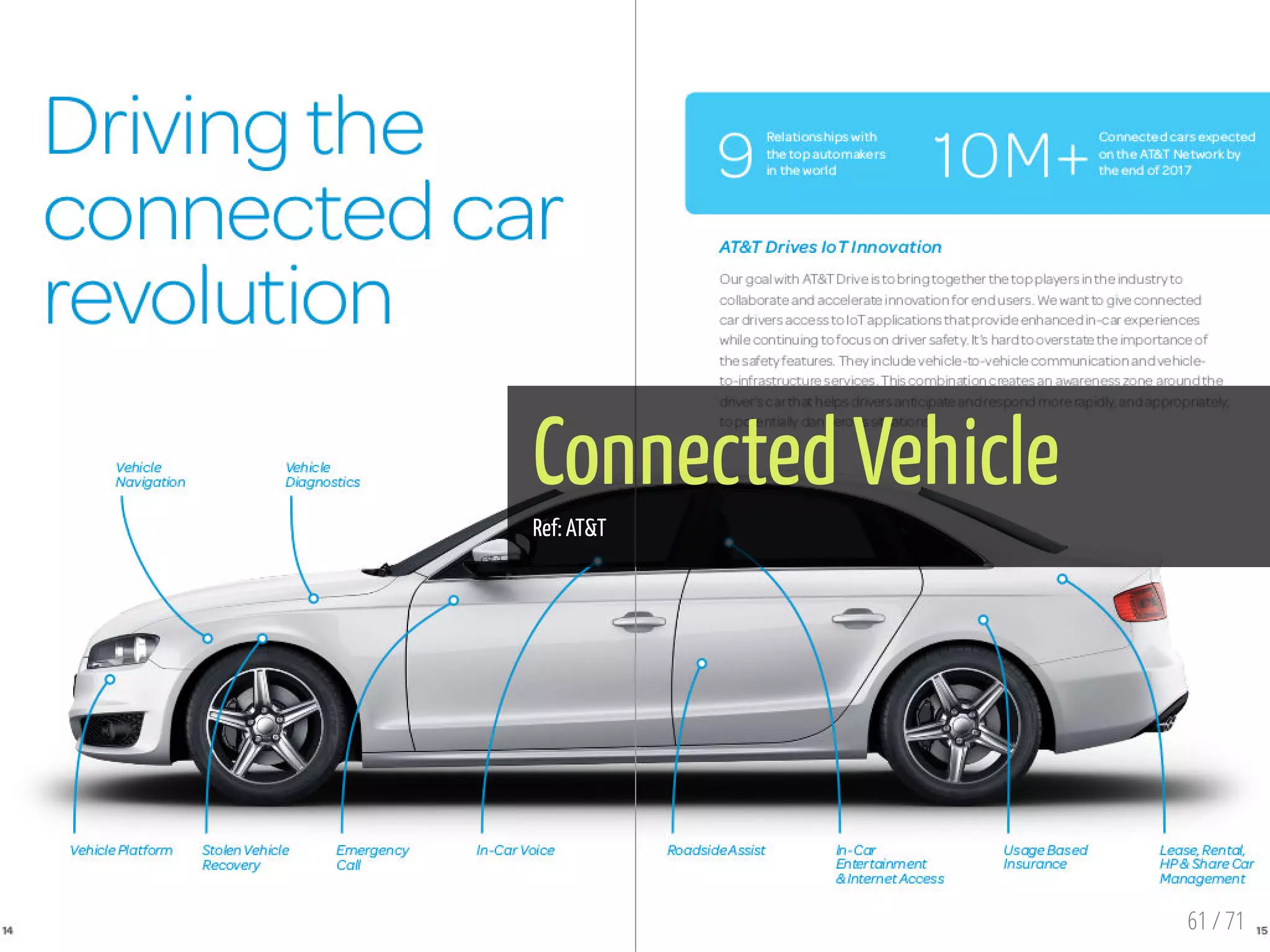
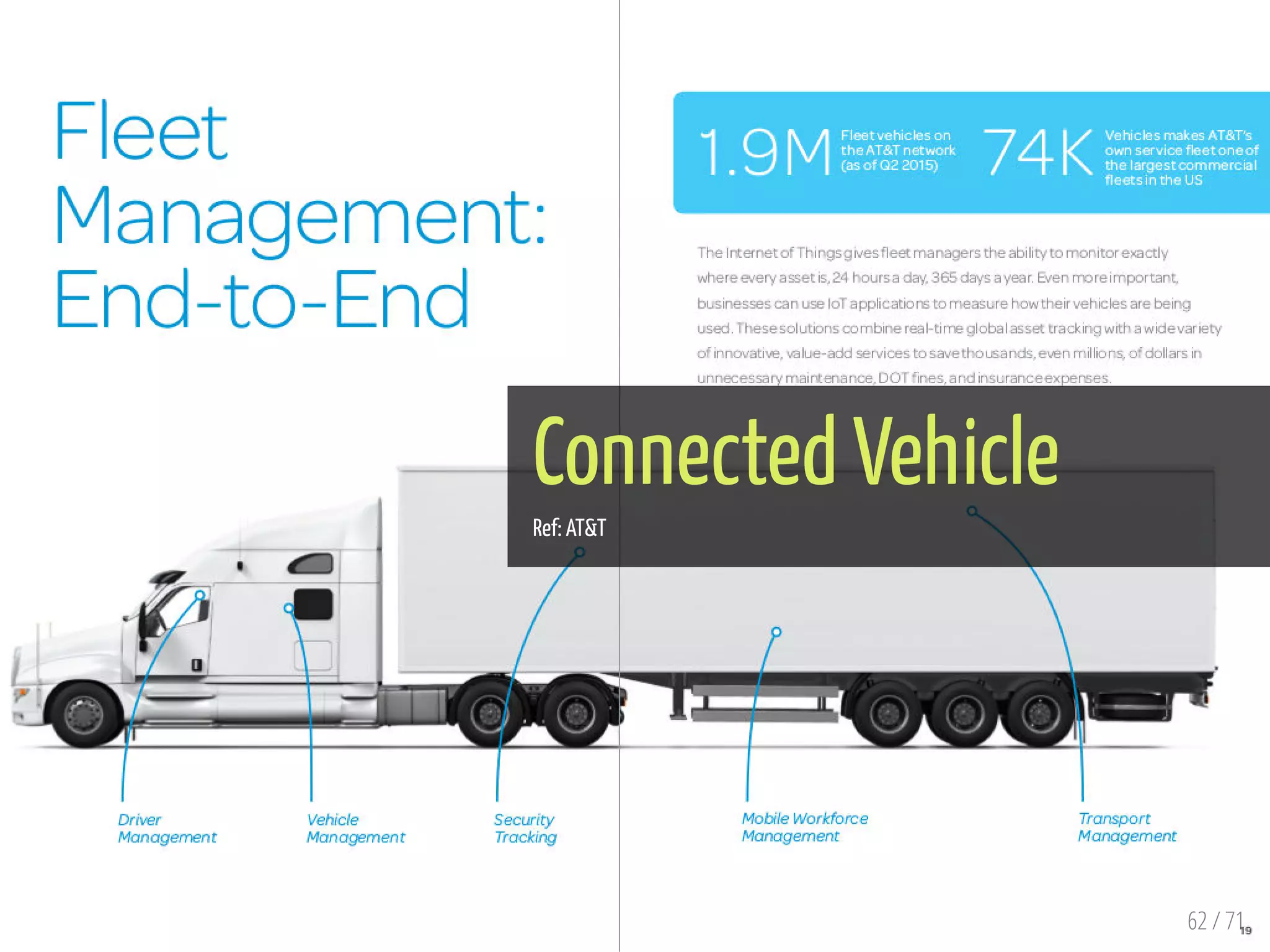
The document provides an overview of the Internet of Things (IoT) and its integration with 5G technology, highlighting key definitions, trends, and applications. It discusses both consumer and industrial IoT, detailing different architectures and the importance of data capture through connected devices. Additionally, it explores various use cases for IoT, including smart homes, connected vehicles, and smart cities, framing these technologies within the context of emerging trends in connectivity.