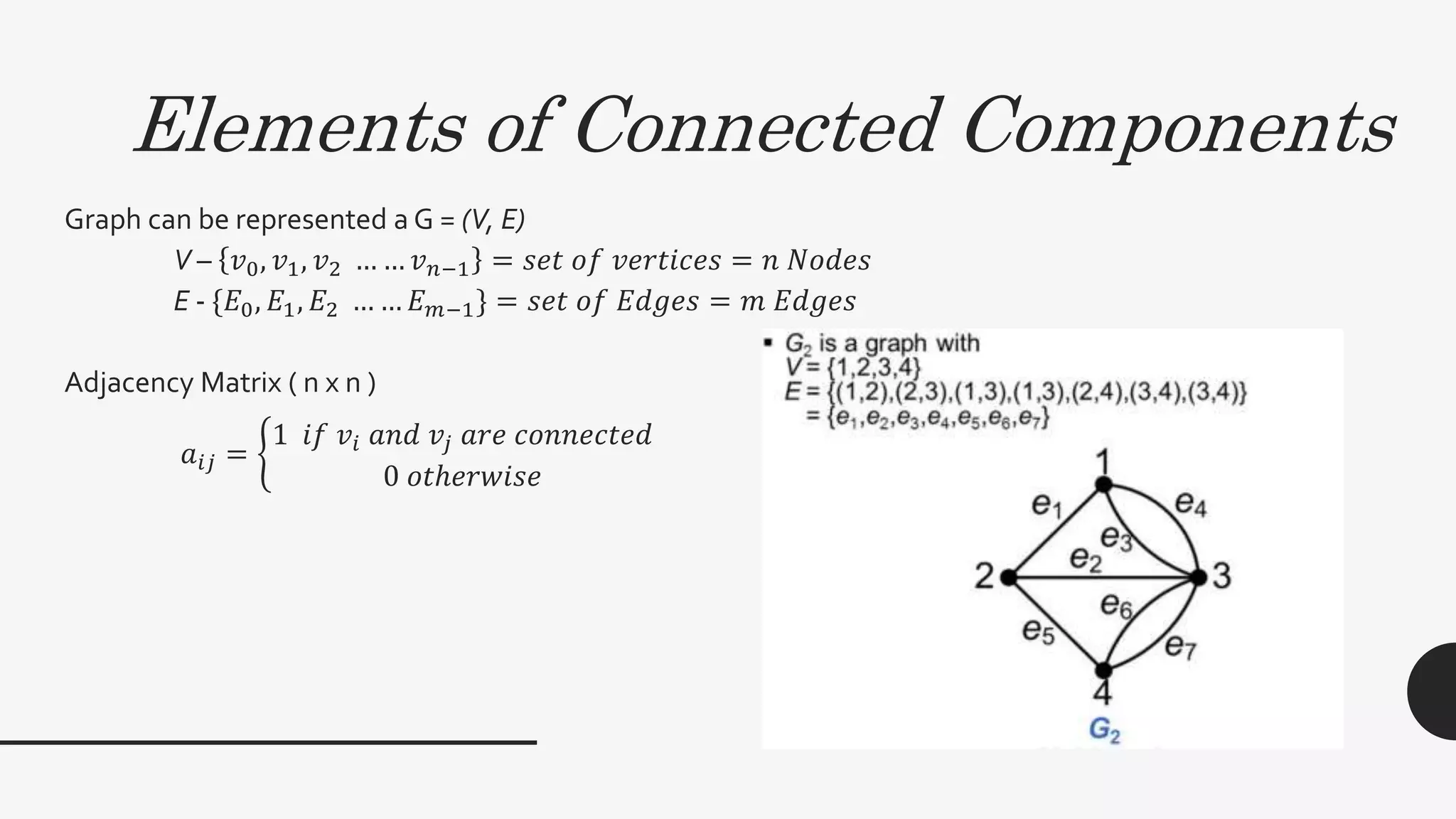
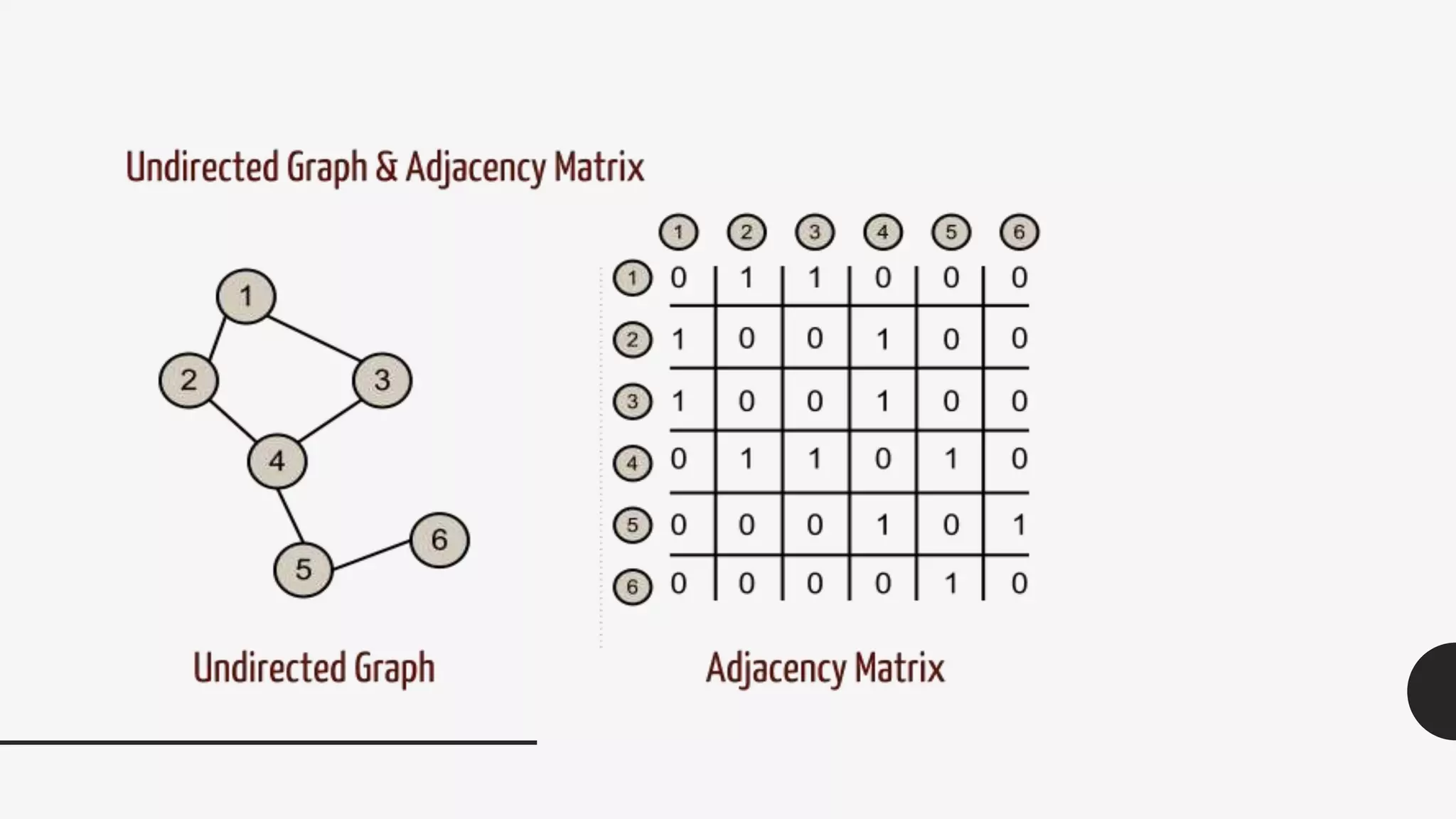
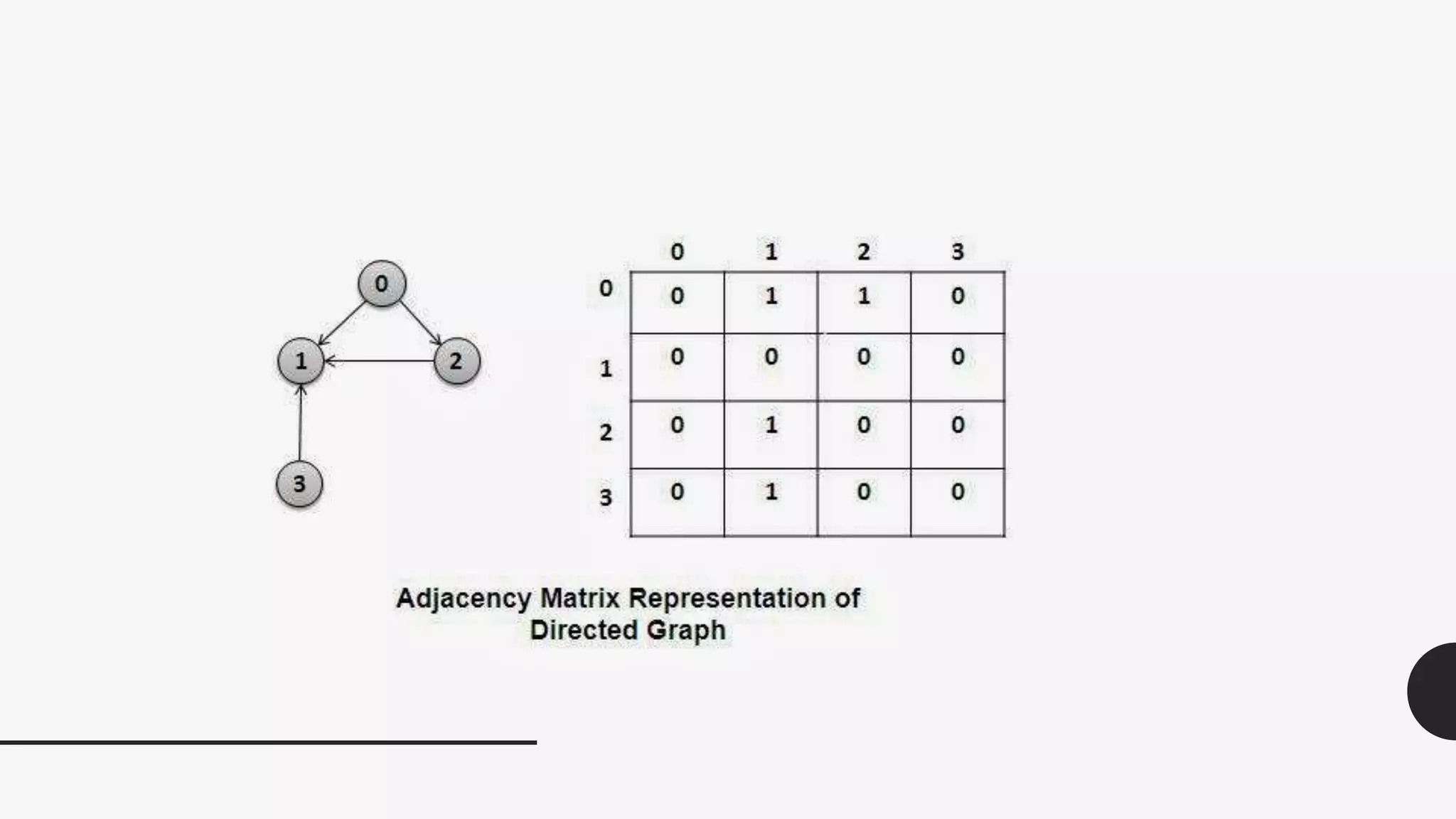
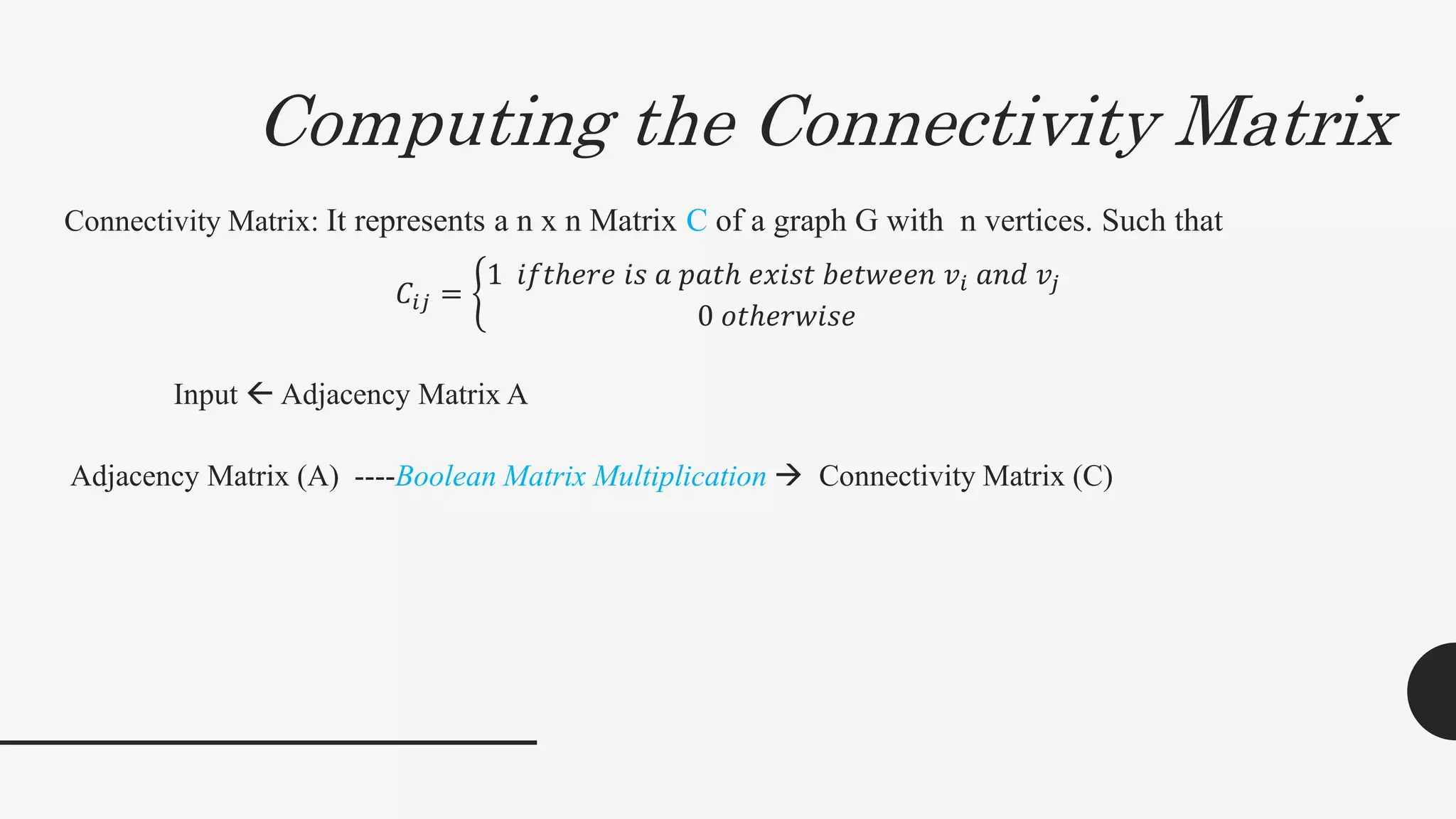
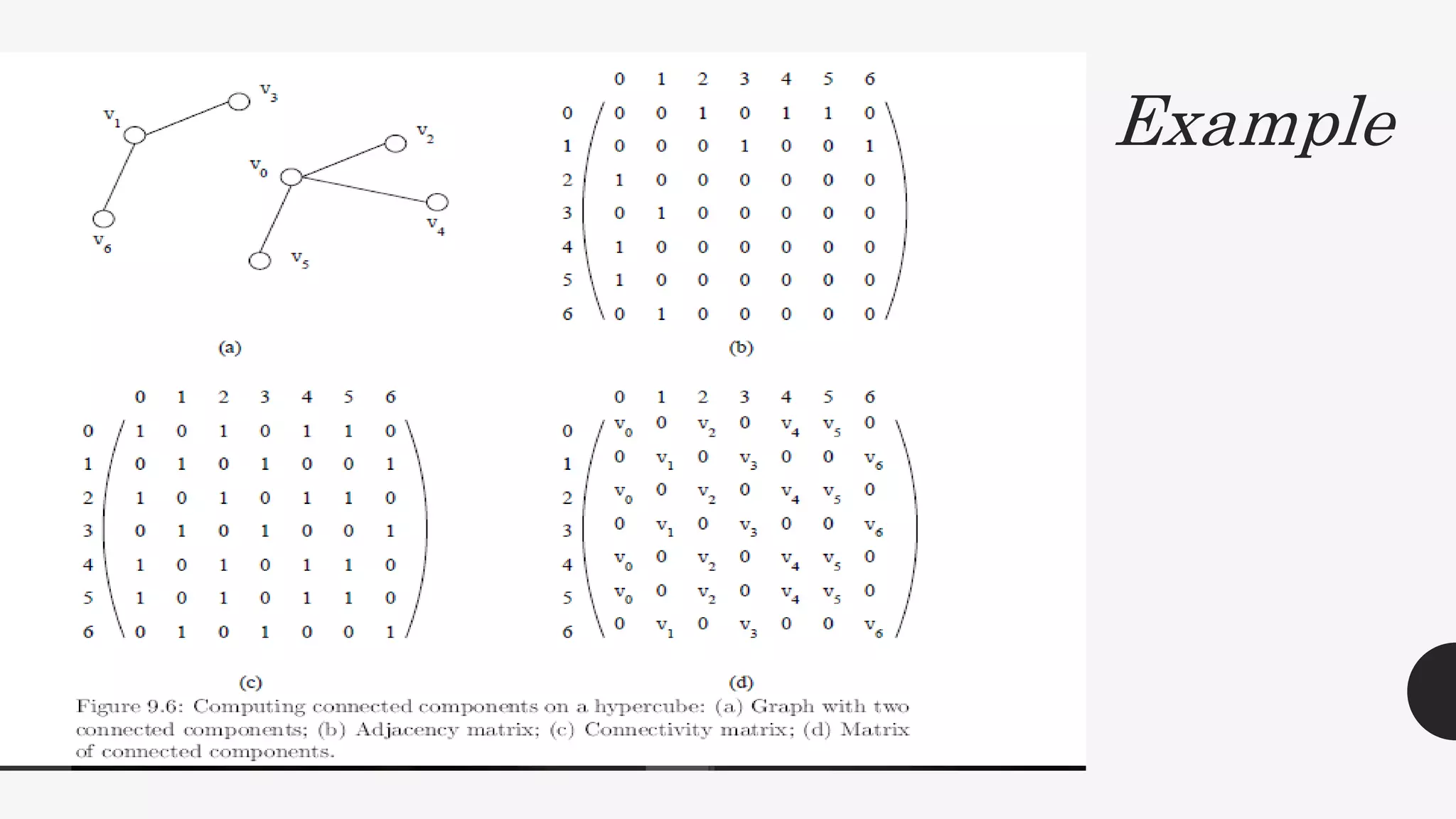
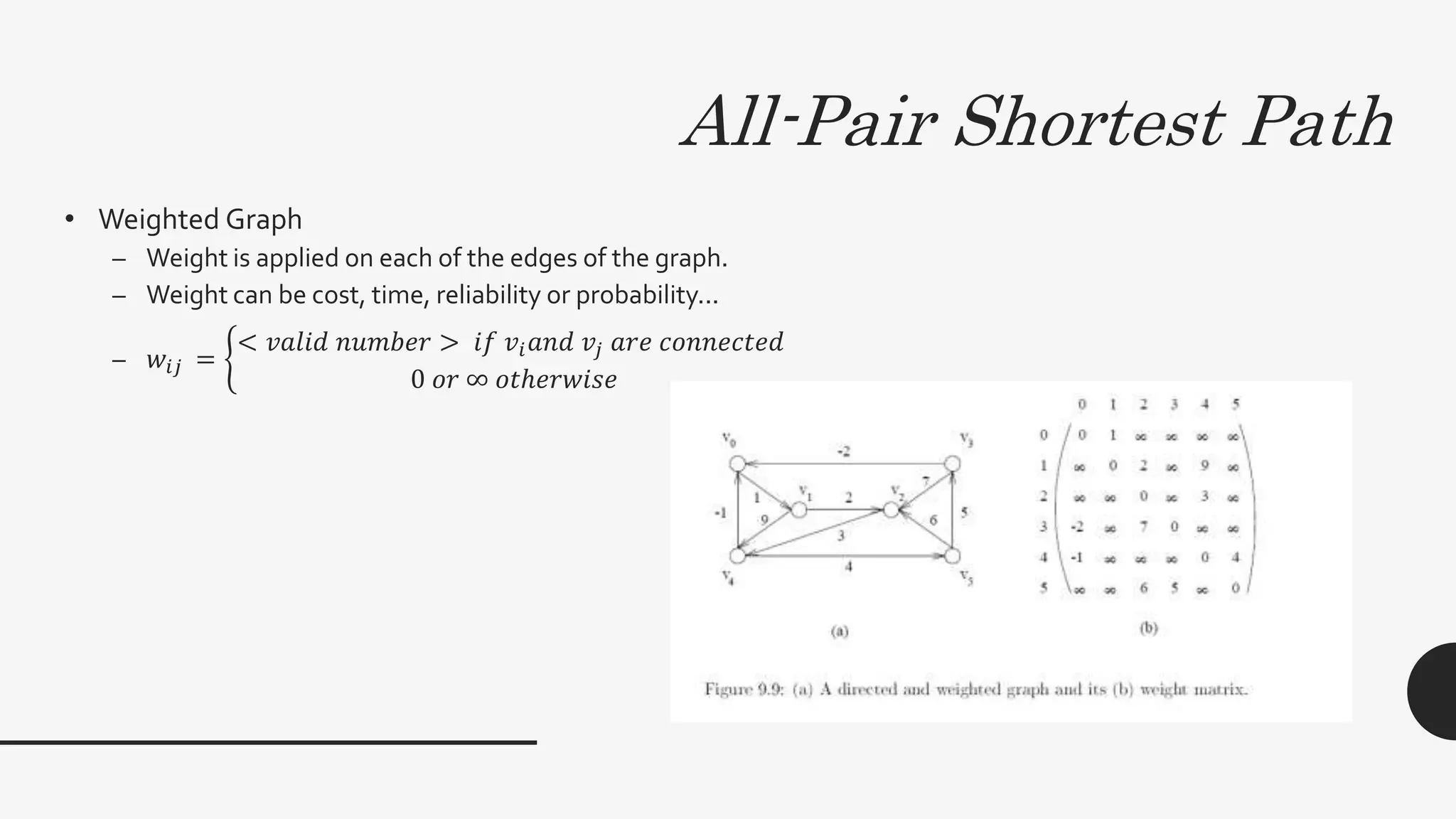
1. The document discusses connected components and shortest paths in graphs. It defines key concepts like adjacency matrix, connectivity matrix, and connected components.
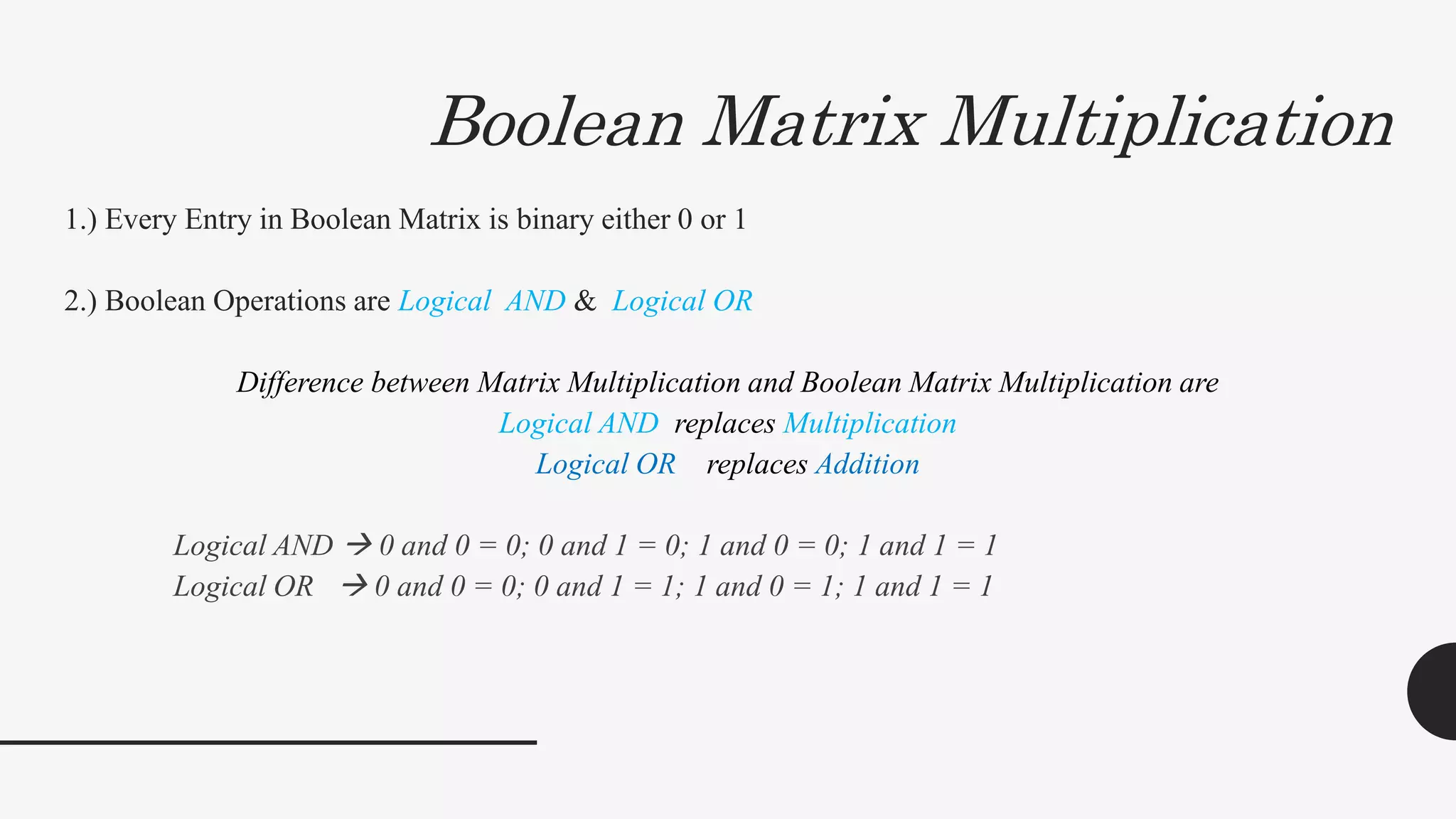
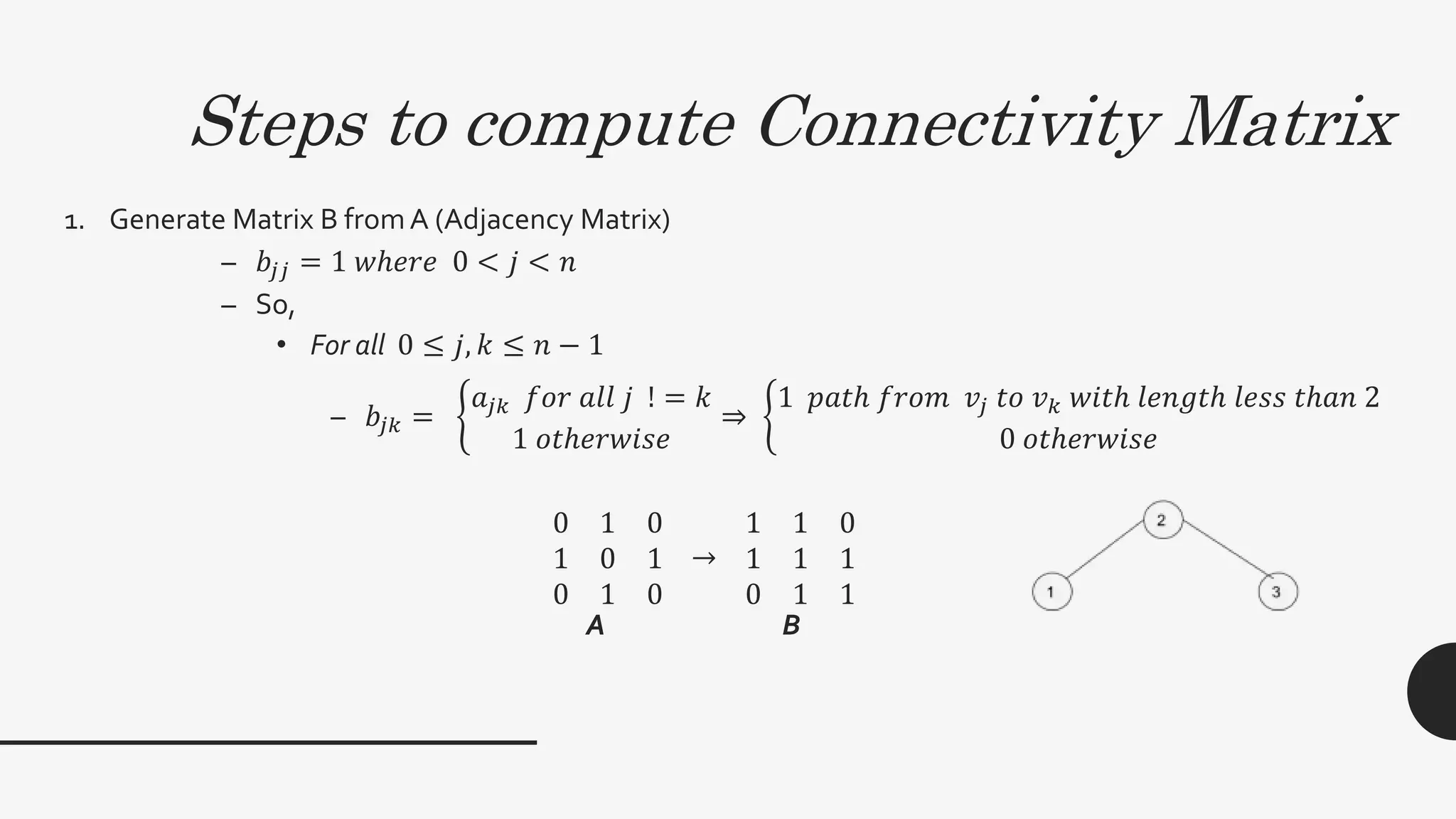
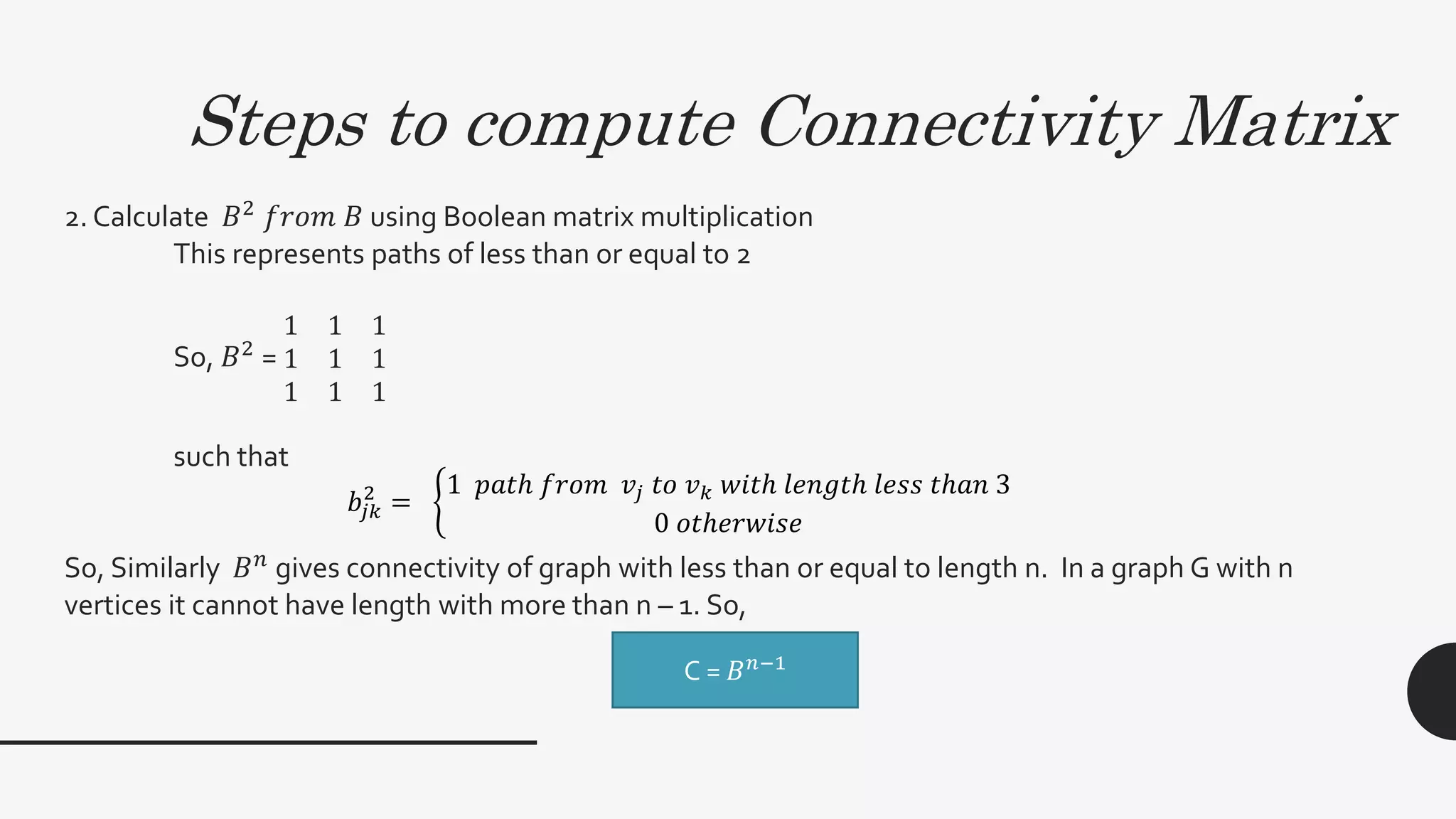
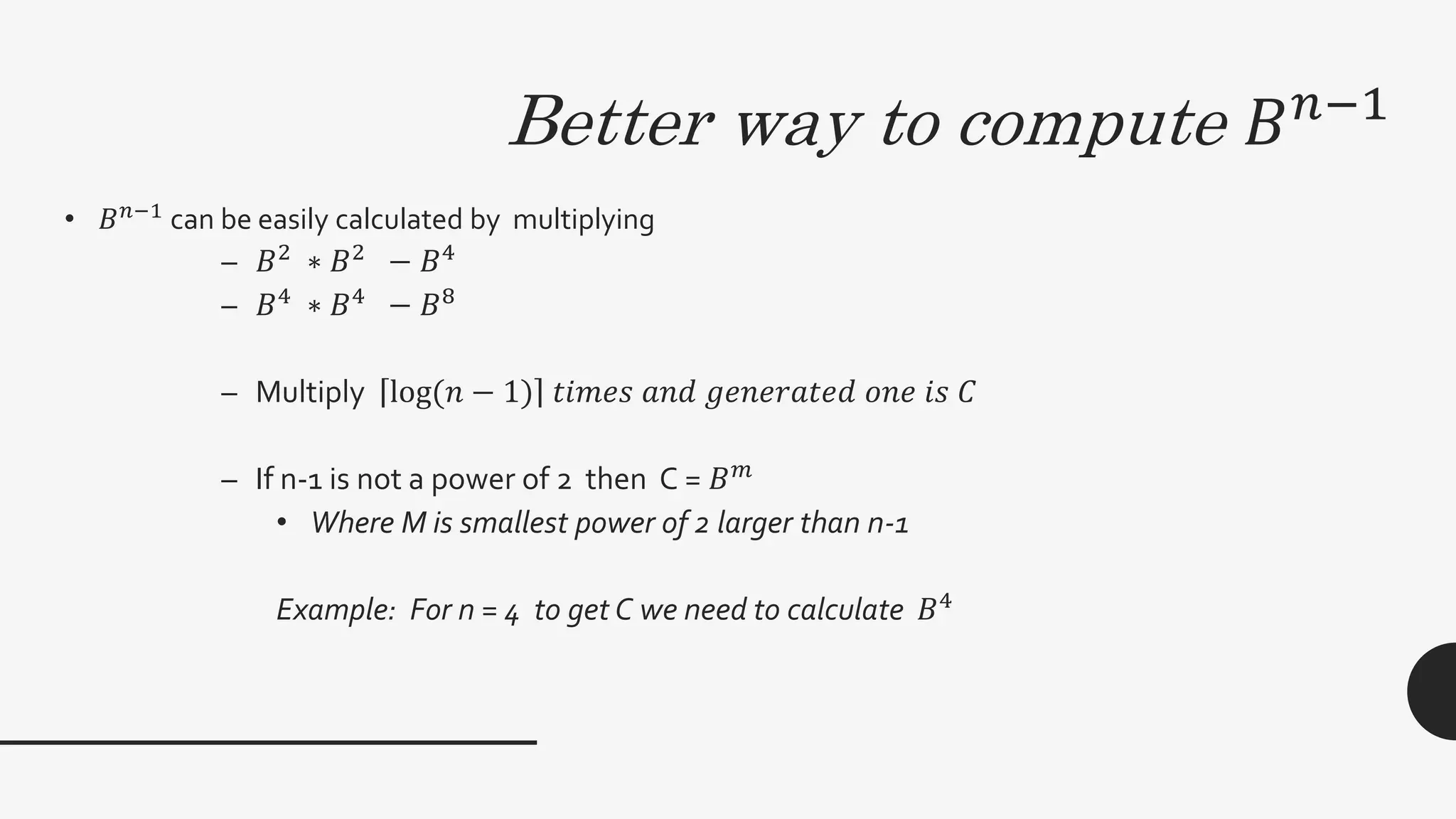
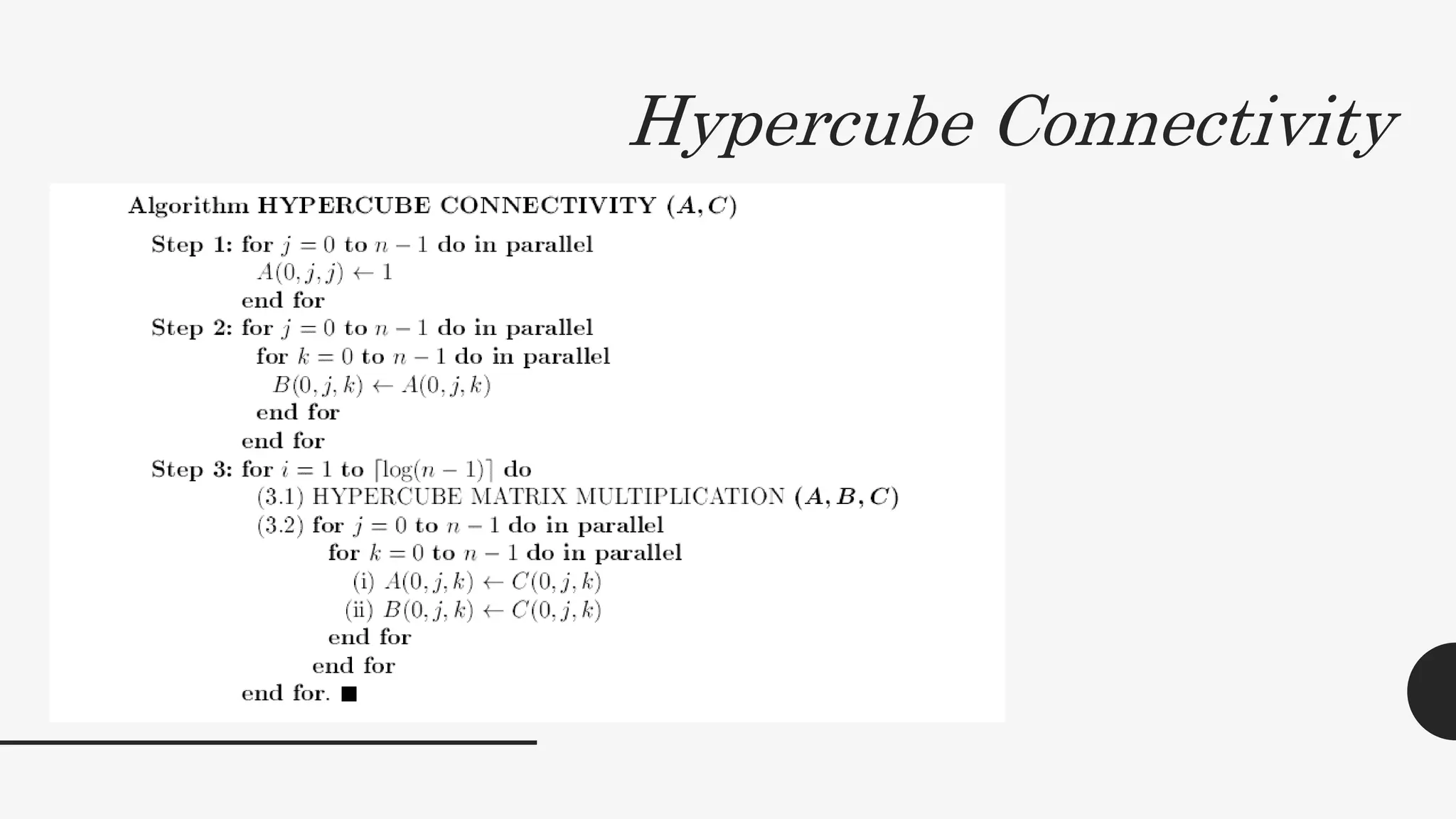
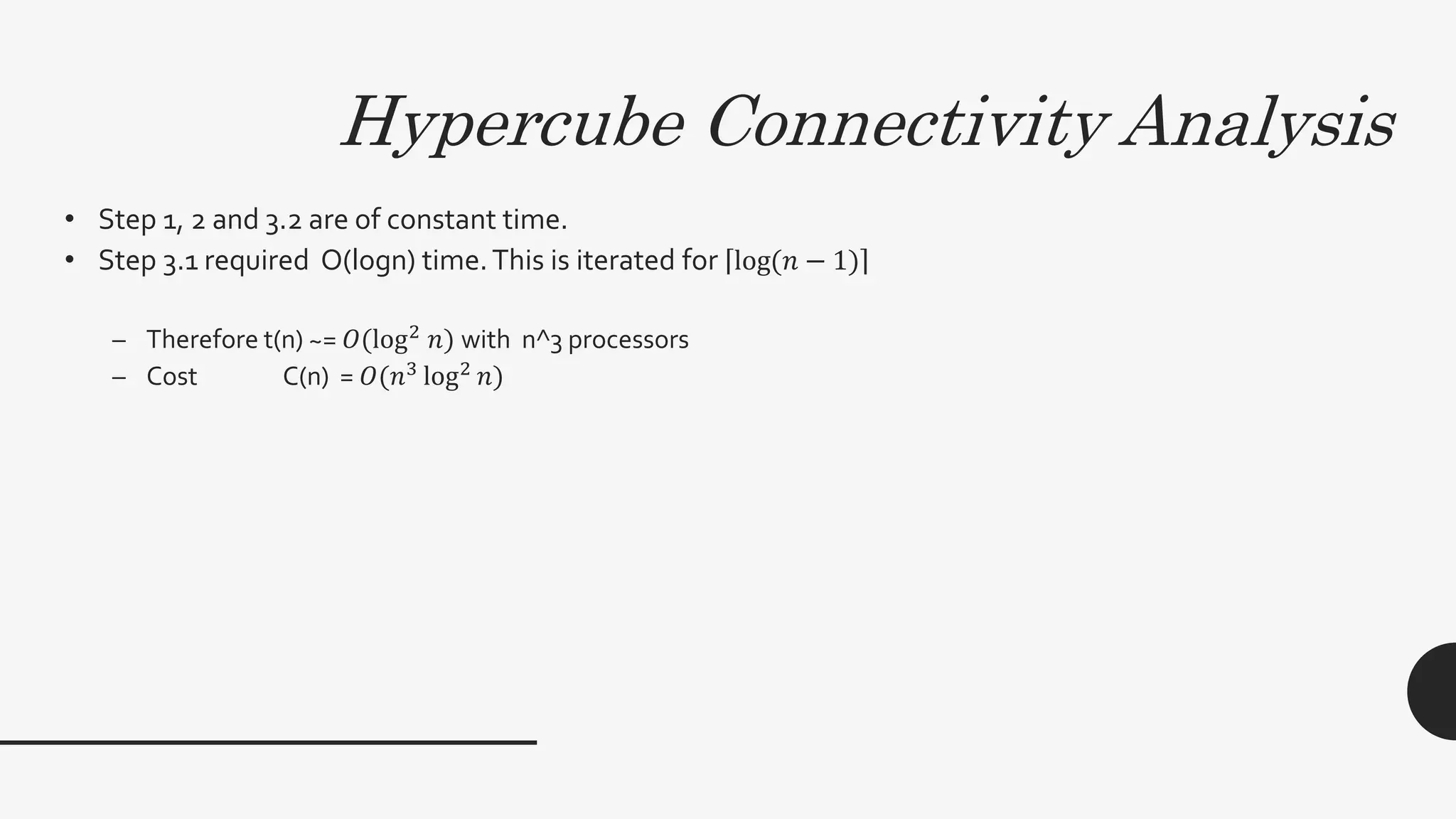
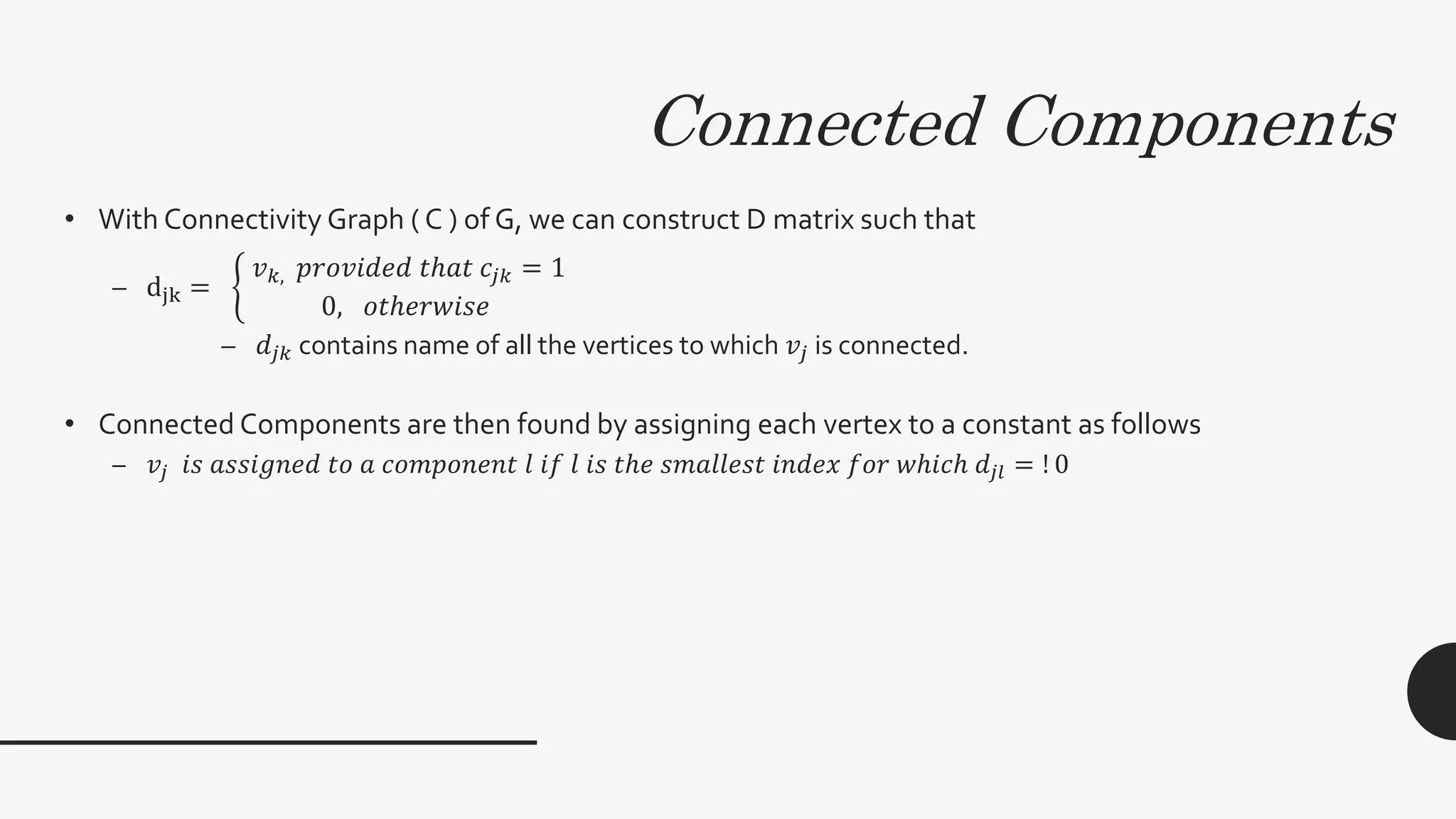
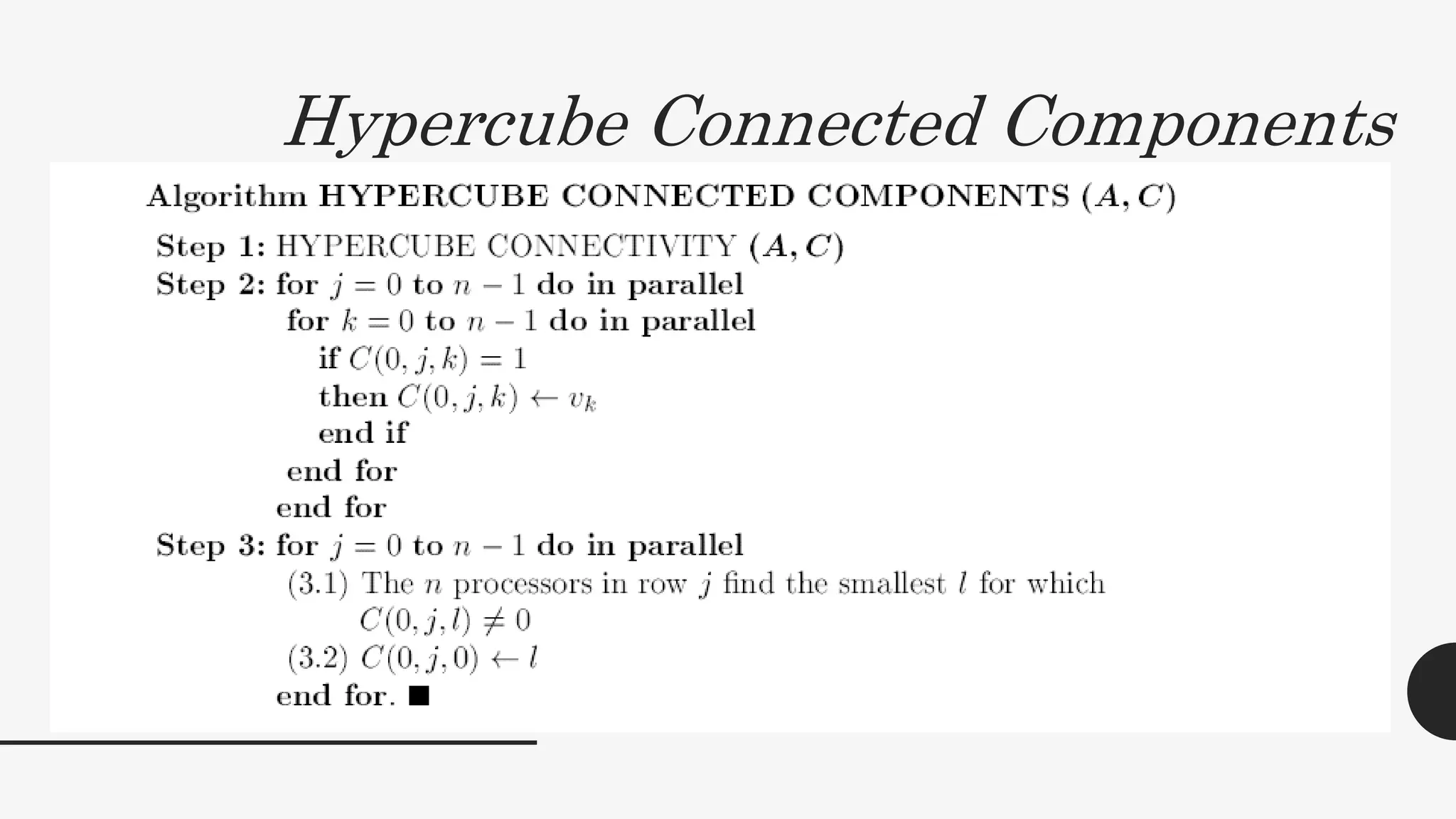
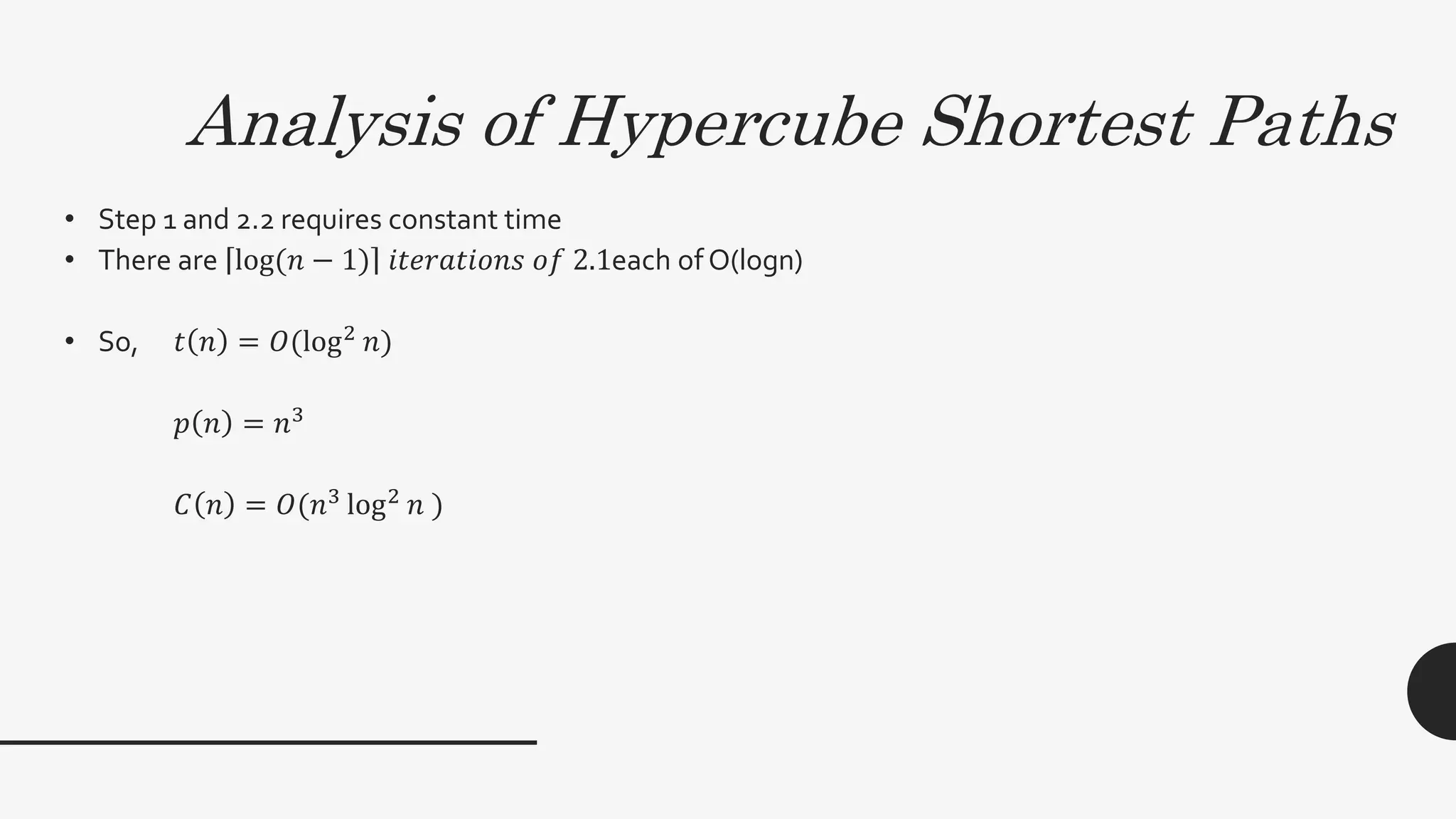
2. It provides algorithms to compute the connectivity matrix and connected components of a graph using boolean matrix multiplication. This takes O(log2n) time with n3 processors.
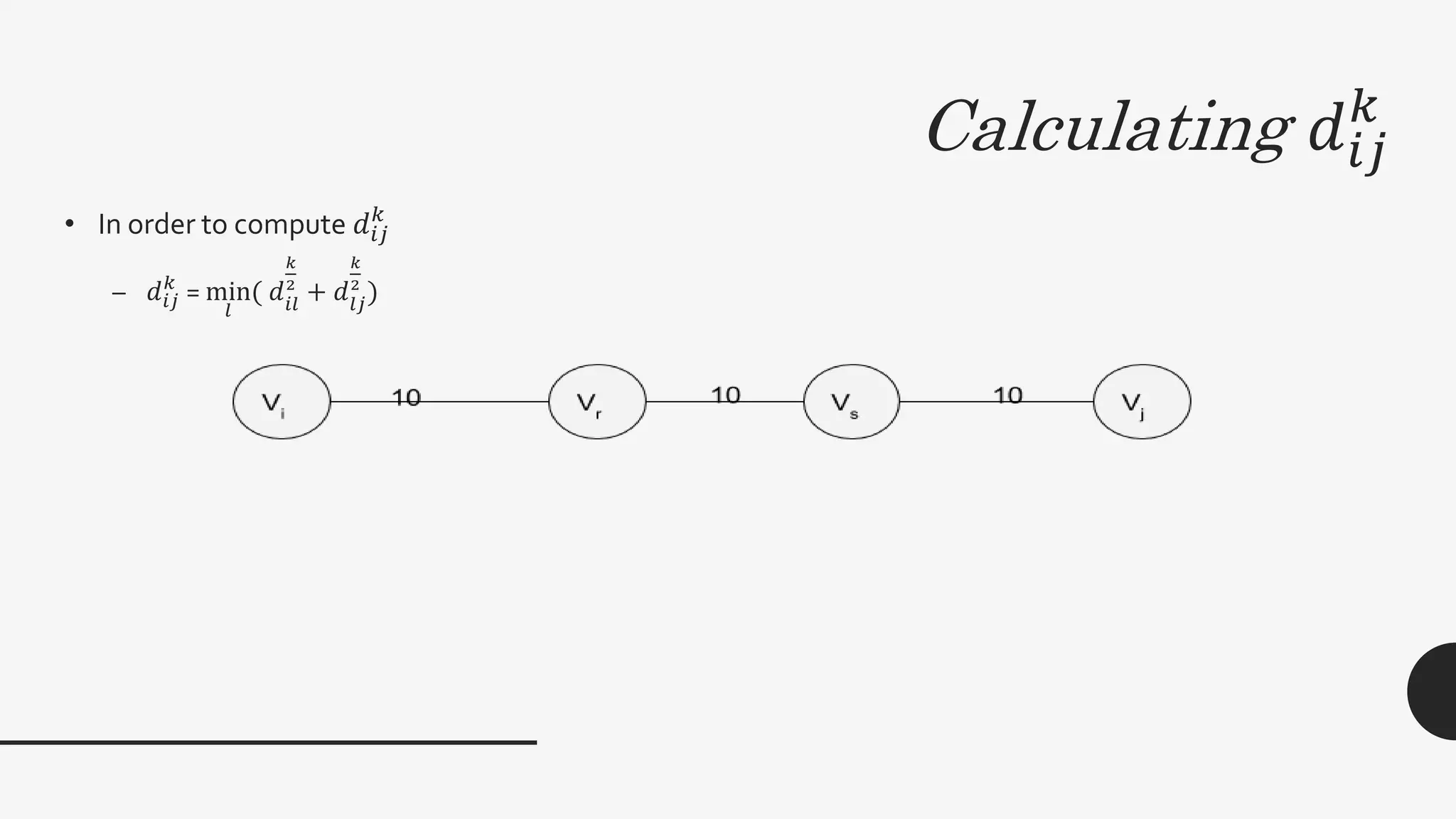
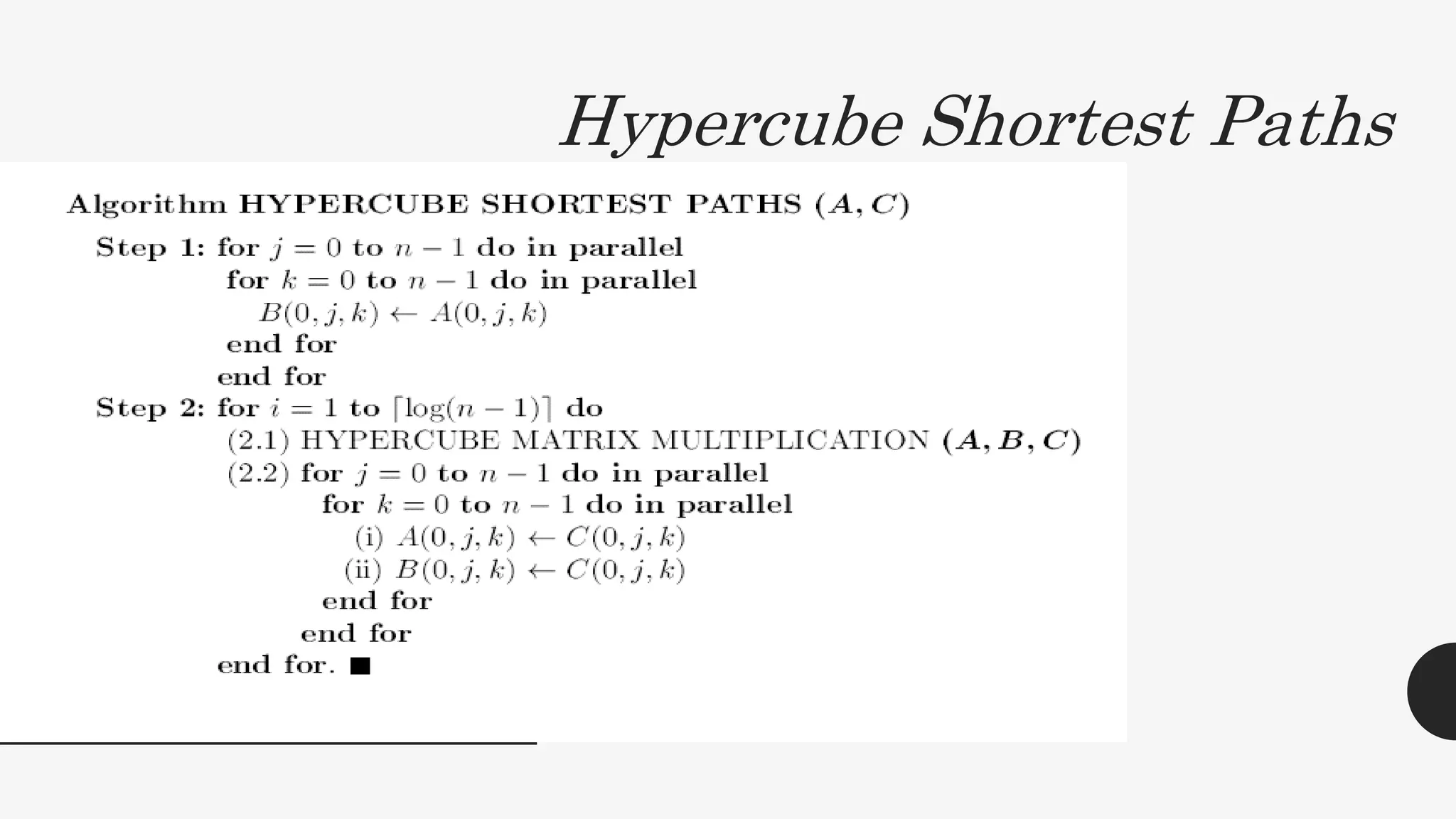
3. The document also discusses the all-pairs shortest path problem and provides an algorithm using matrix multiplication to compute shortest path distances between all pairs of vertices in a weighted graph. The runtime of this algorithm is also O(log2n) time with n3 processors.