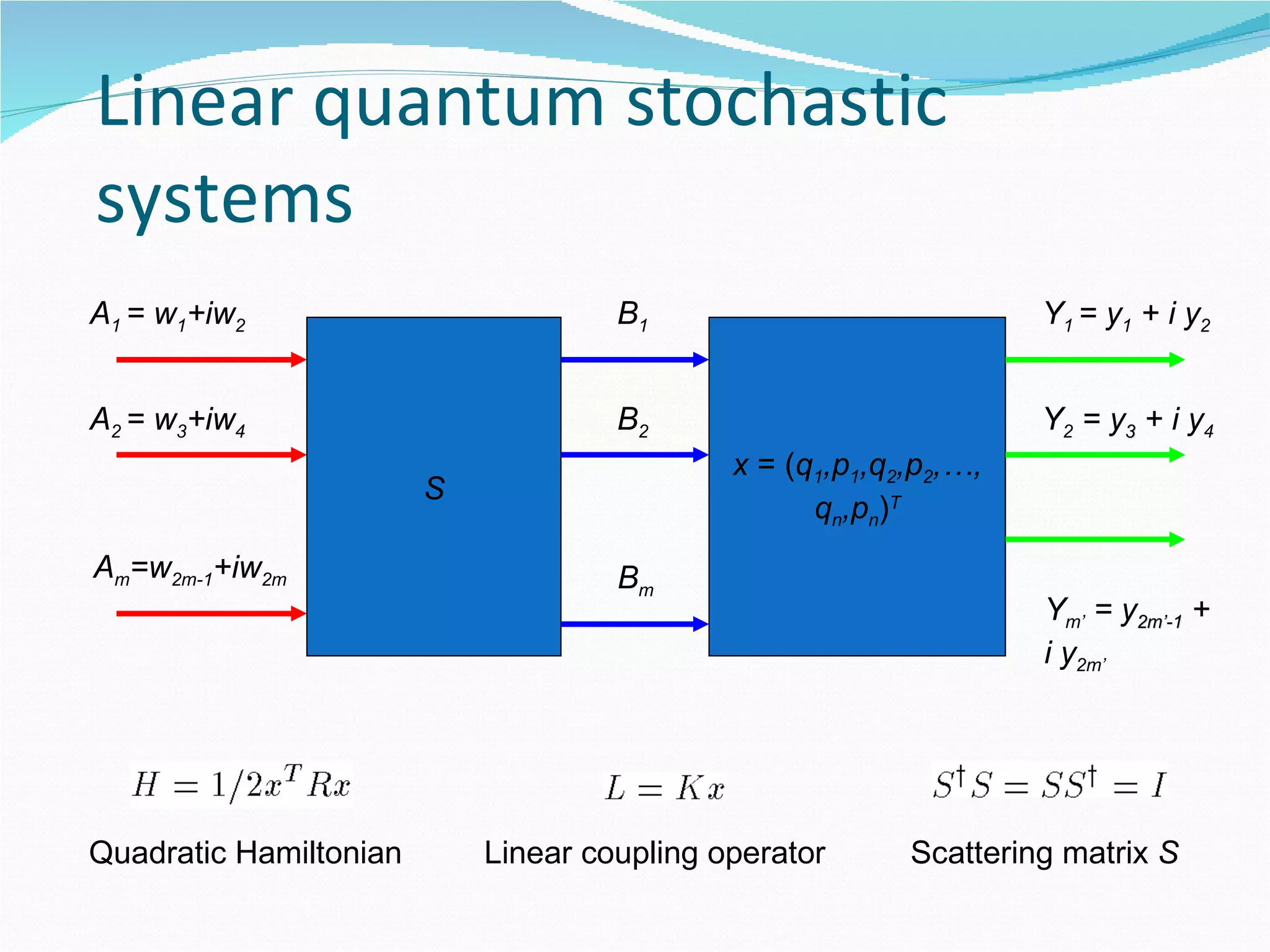
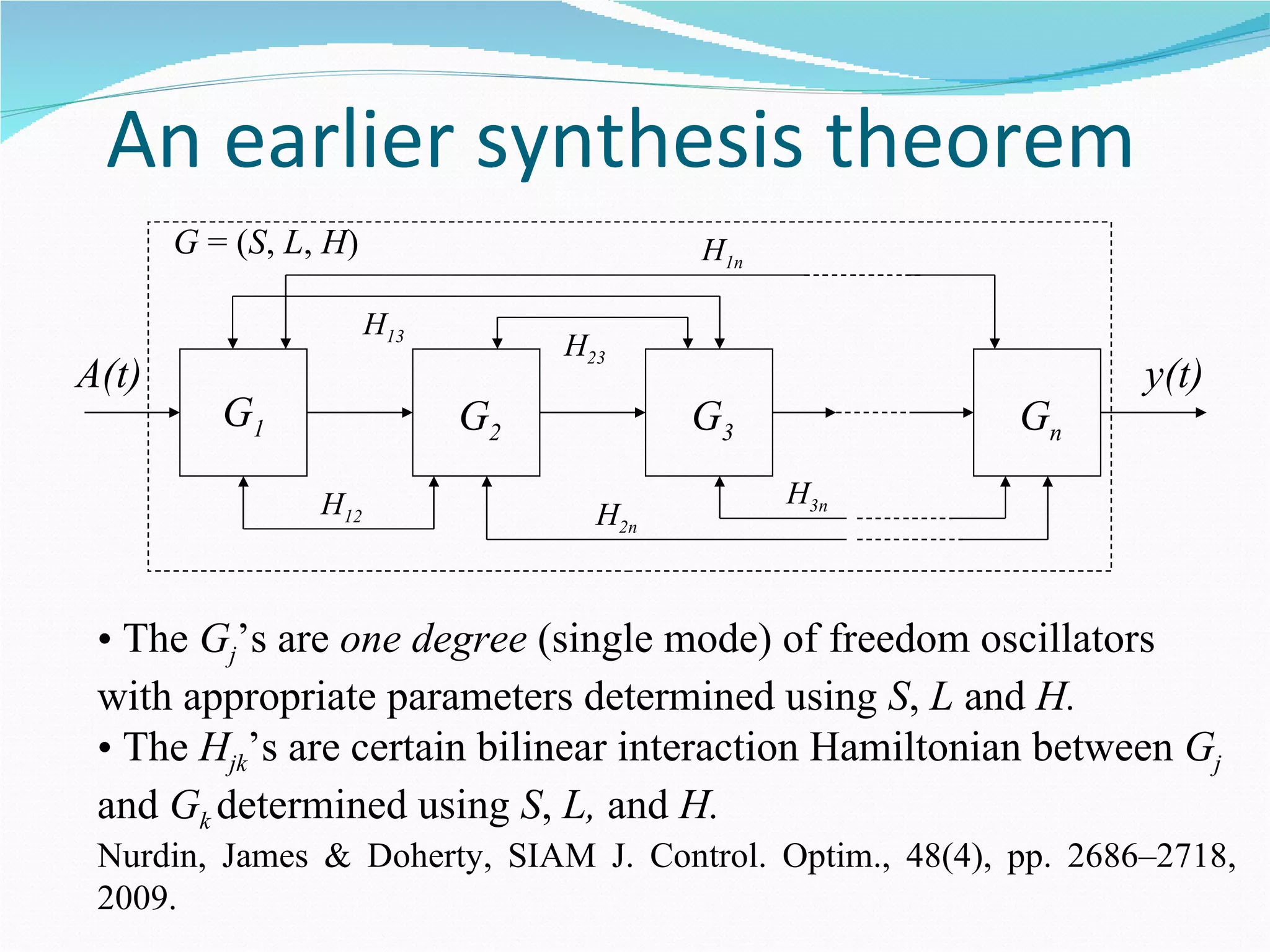
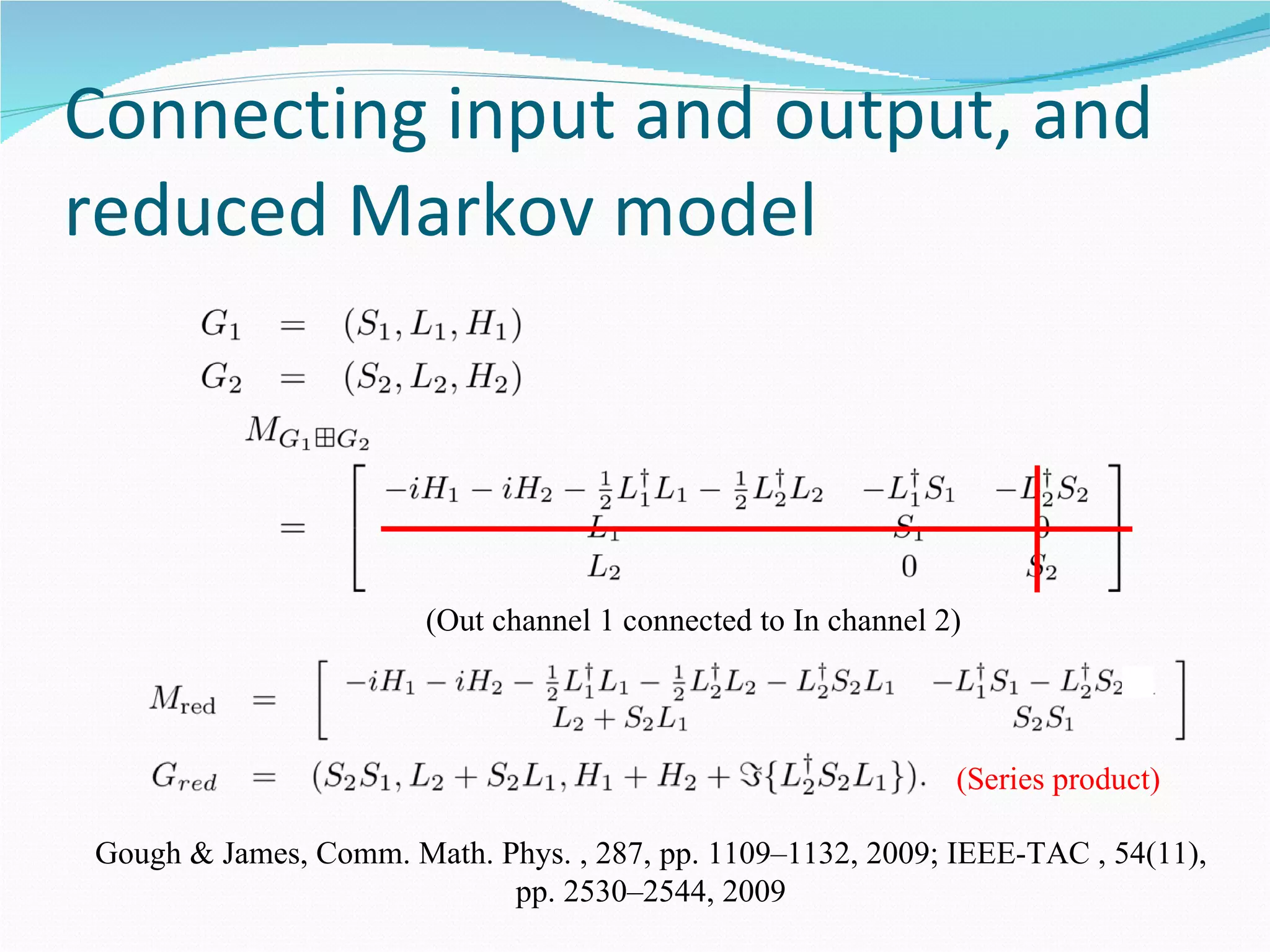
1. The document outlines a method for synthesizing linear quantum stochastic systems using quantum feedback networks. Small time delays allow approximating direct interactions with field-mediated interactions.
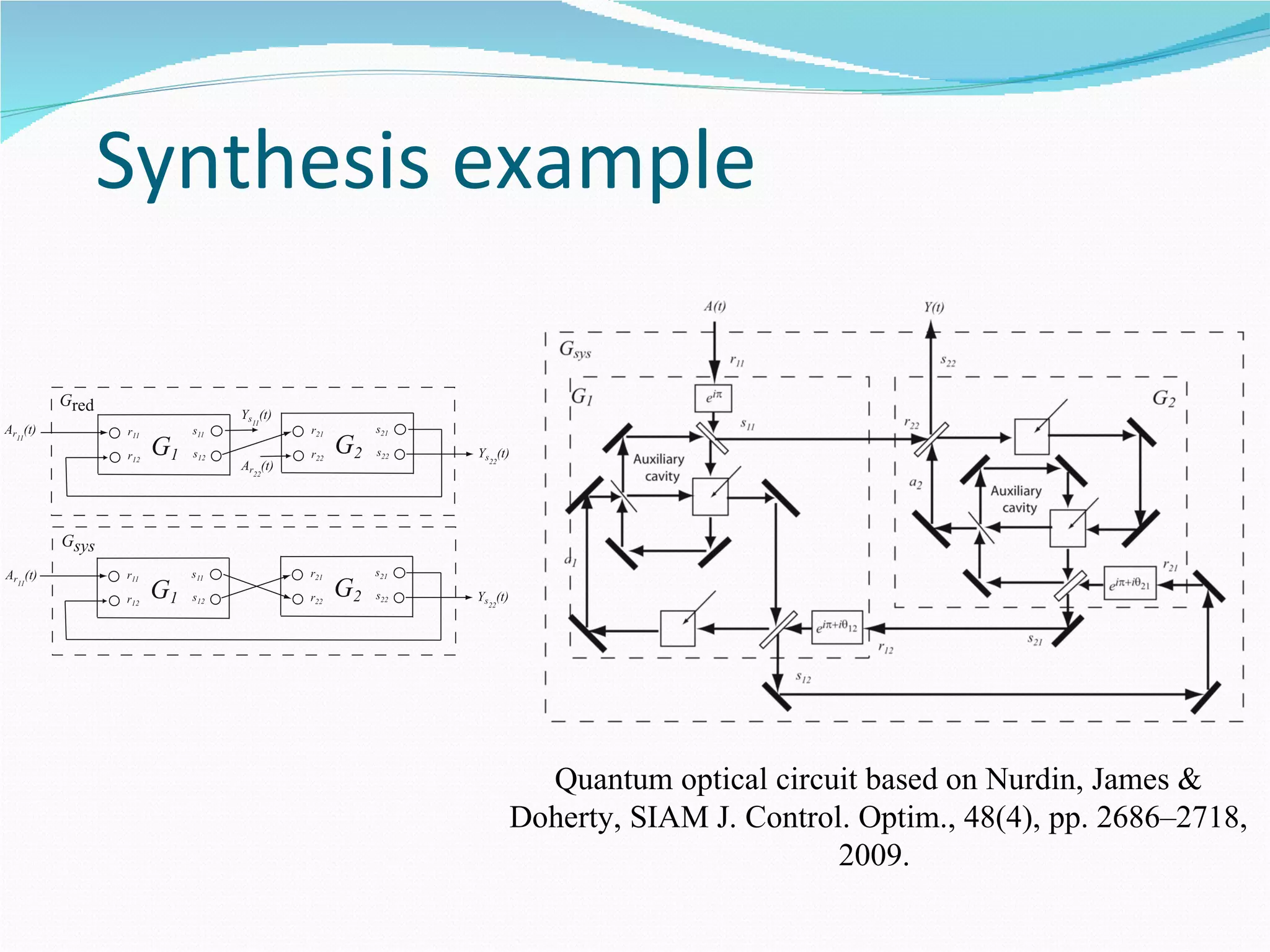
2. As an example, a quantum optical circuit is synthesized based on earlier work. Components are interconnected to approximate a desired system dynamics for small time delays.
3. In conclusion, linear quantum systems can be approximately synthesized by quantum feedback networks for small time delays, using field-mediated interactions to simulate direct interactions. Additional results are available in another paper.