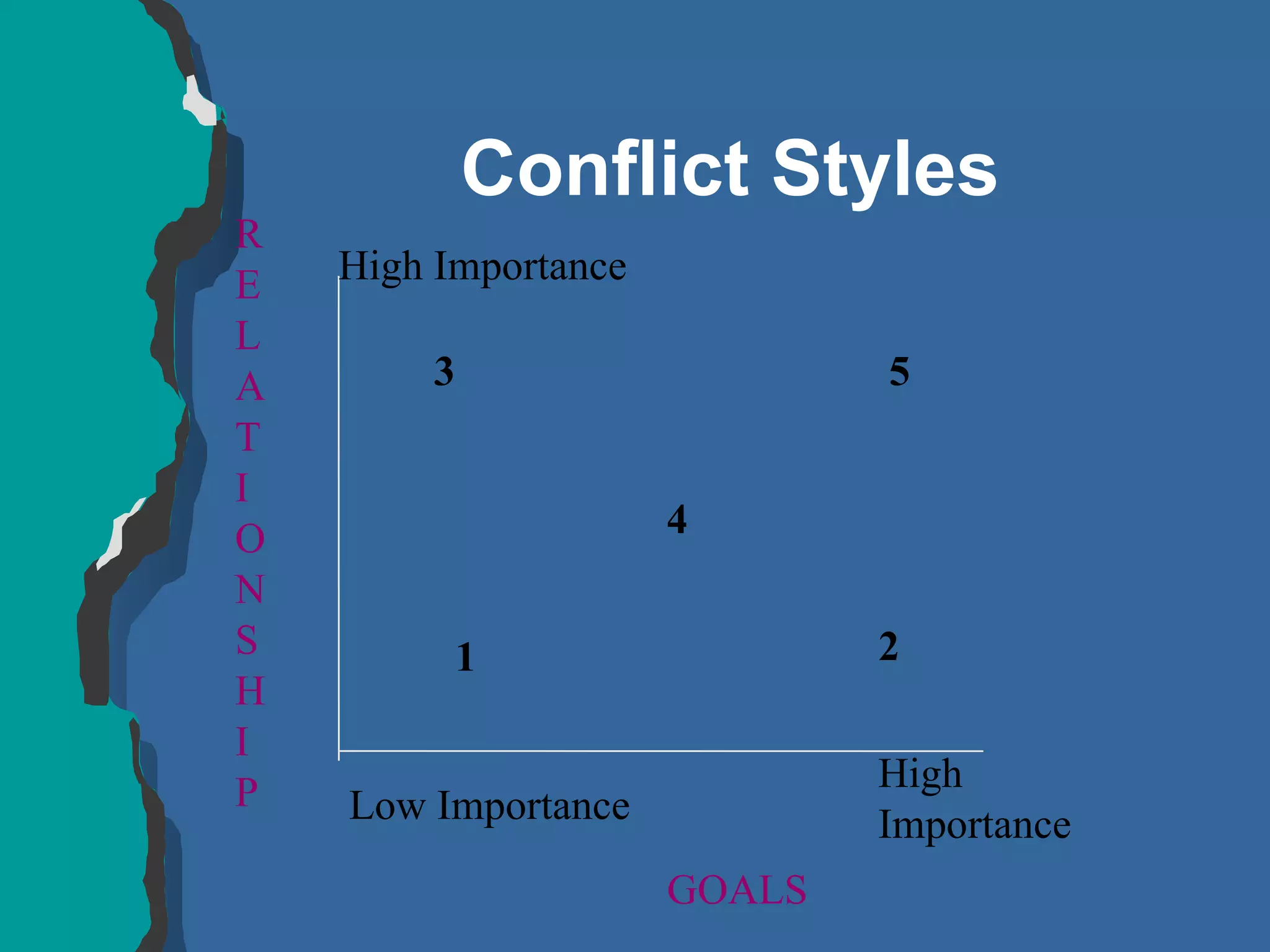
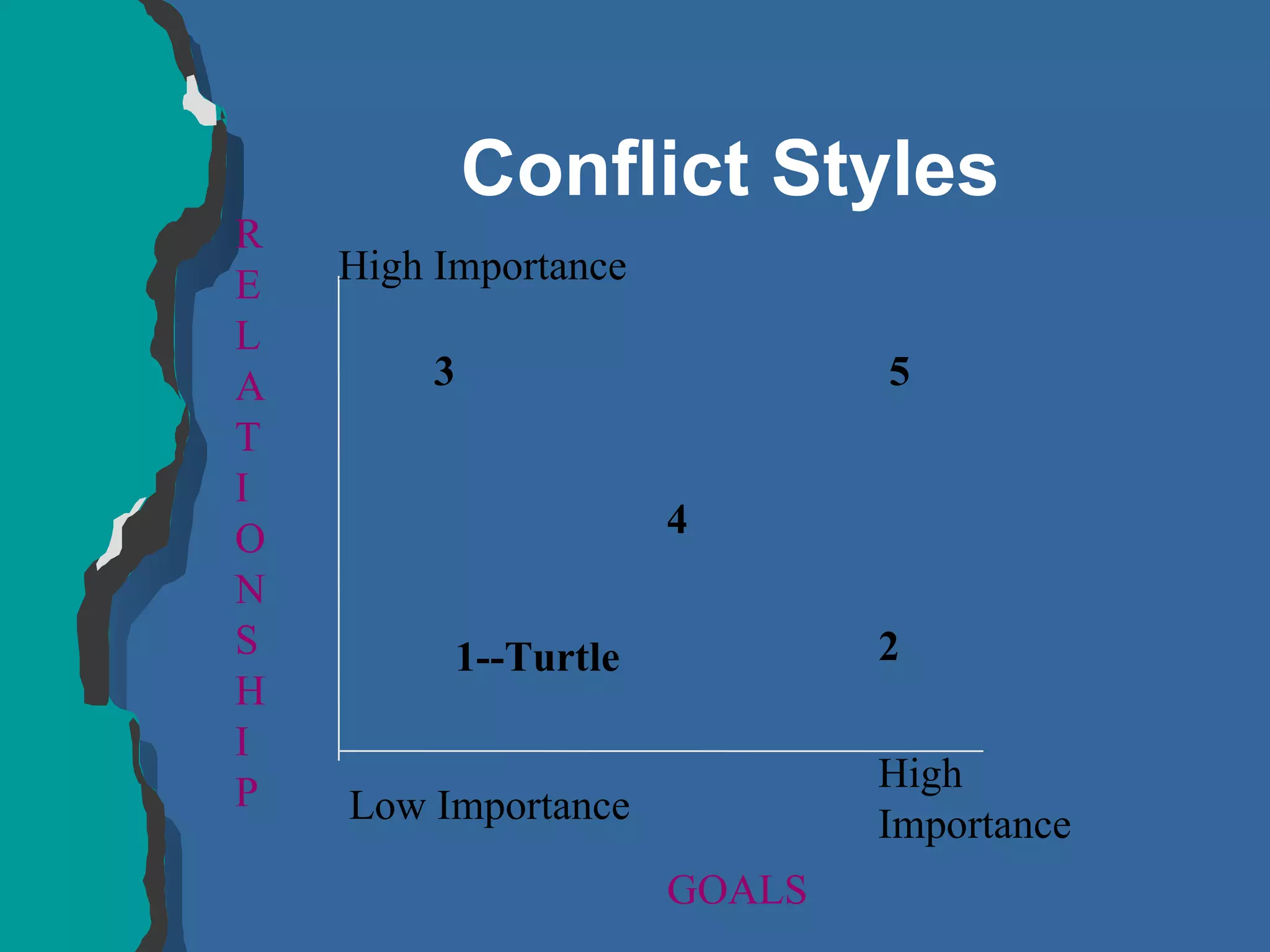
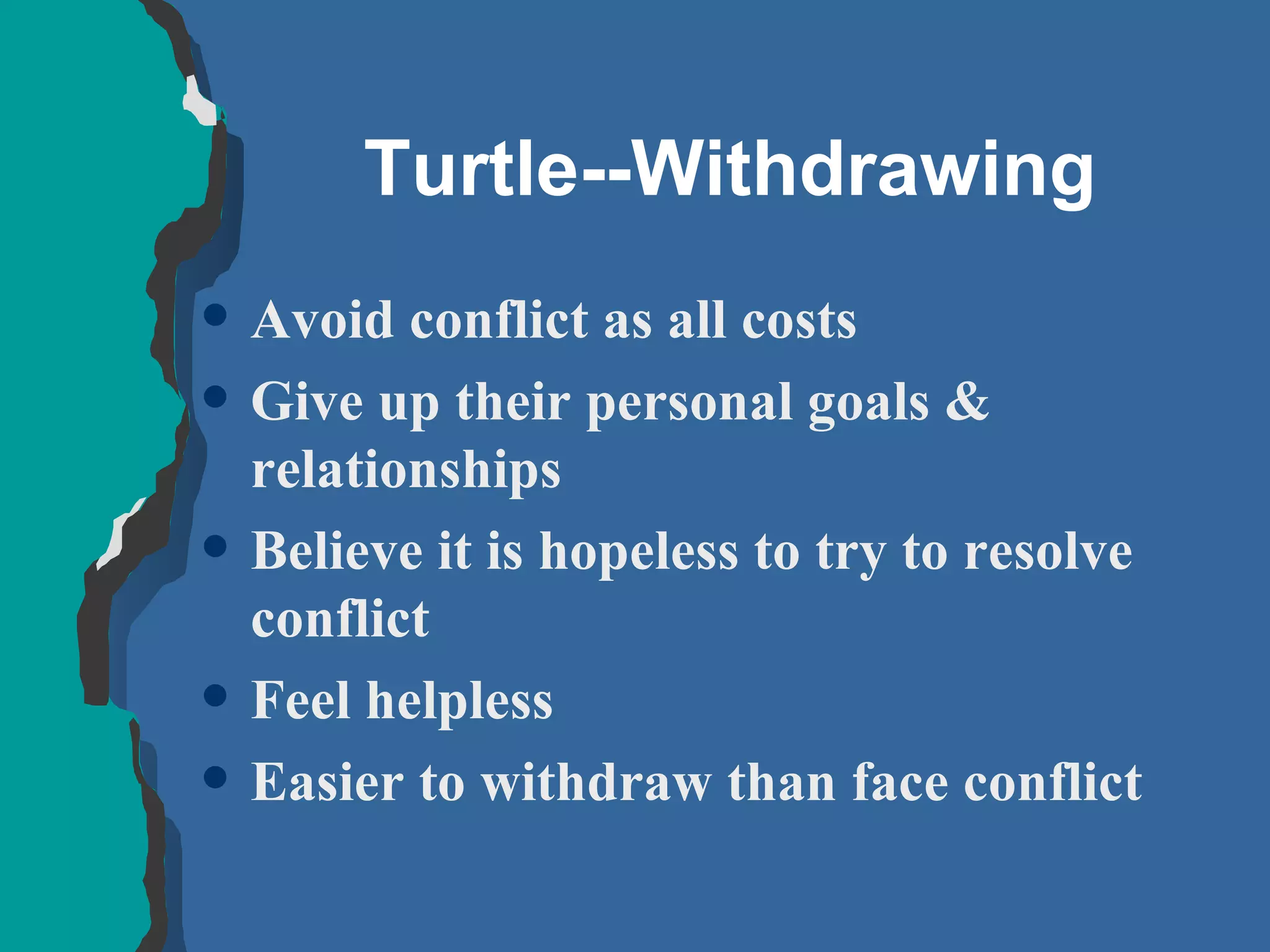
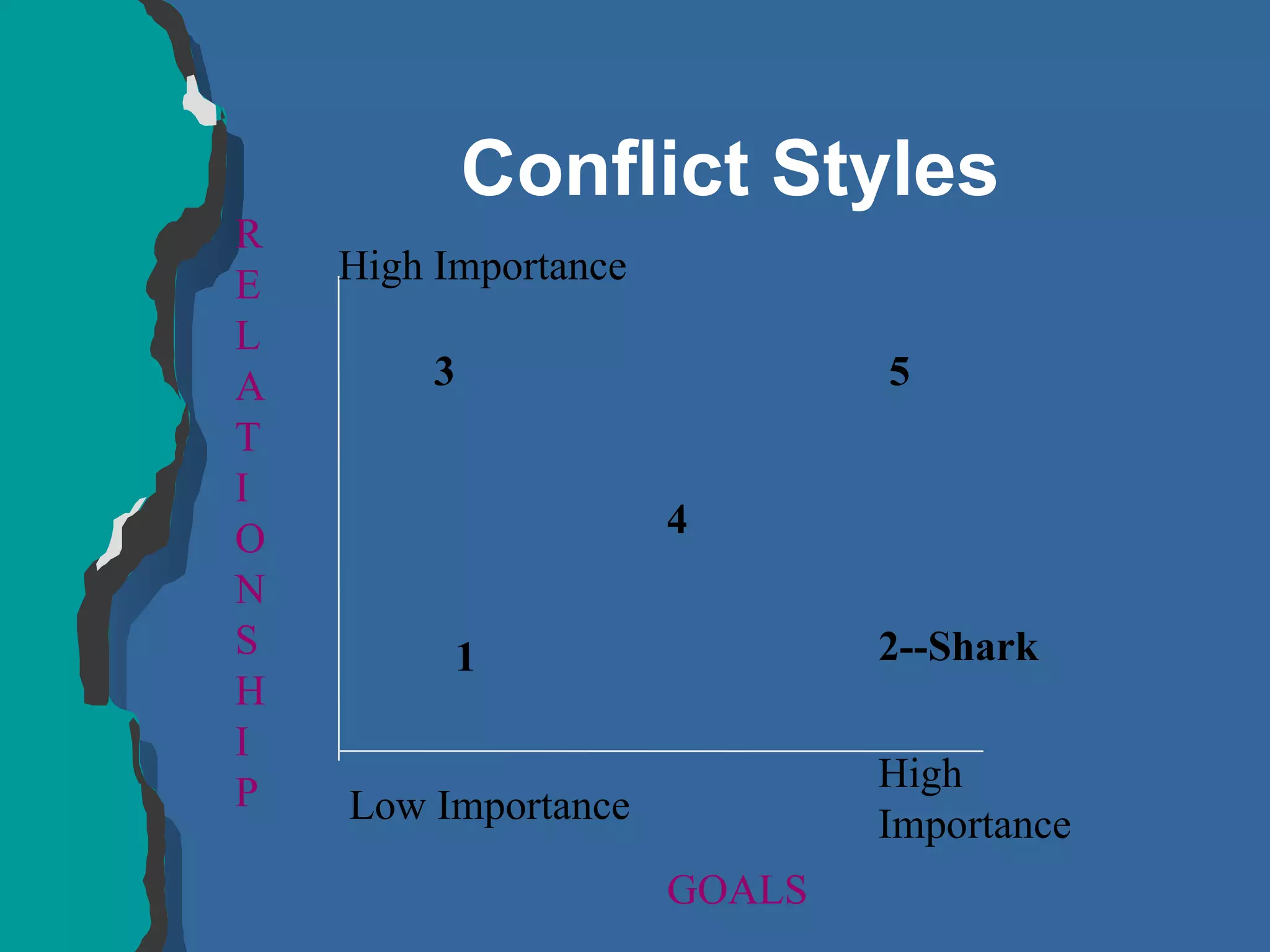
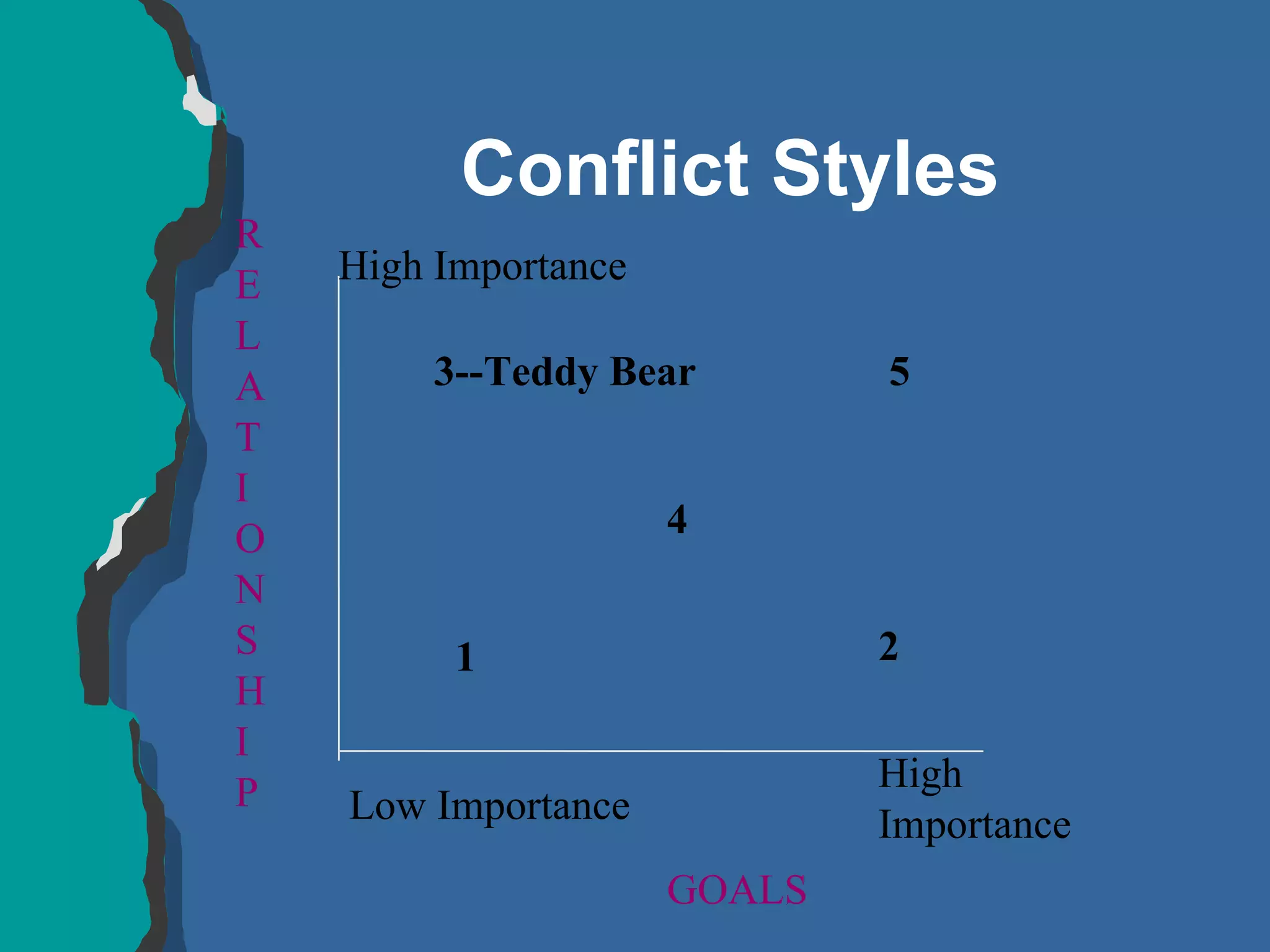
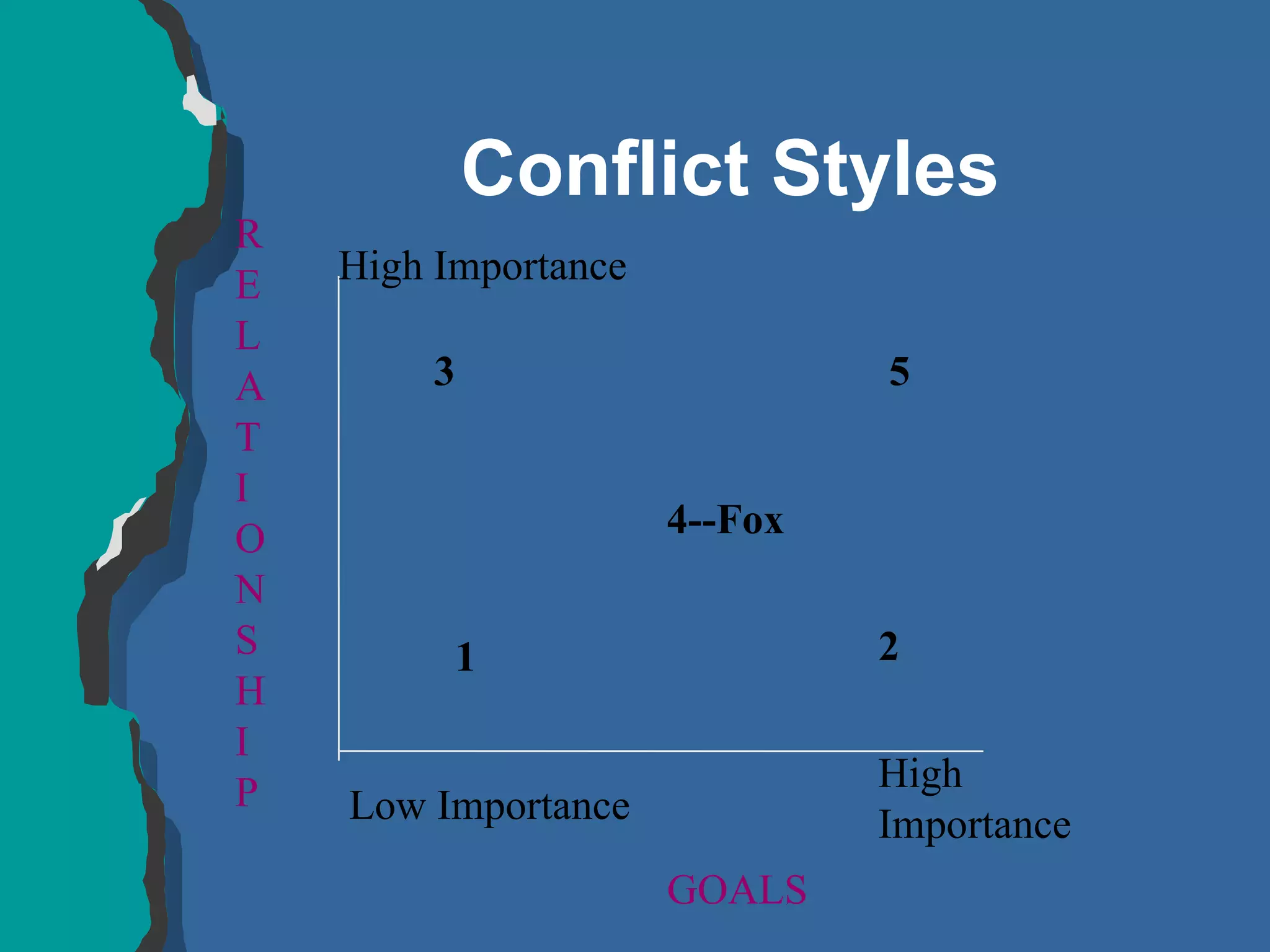
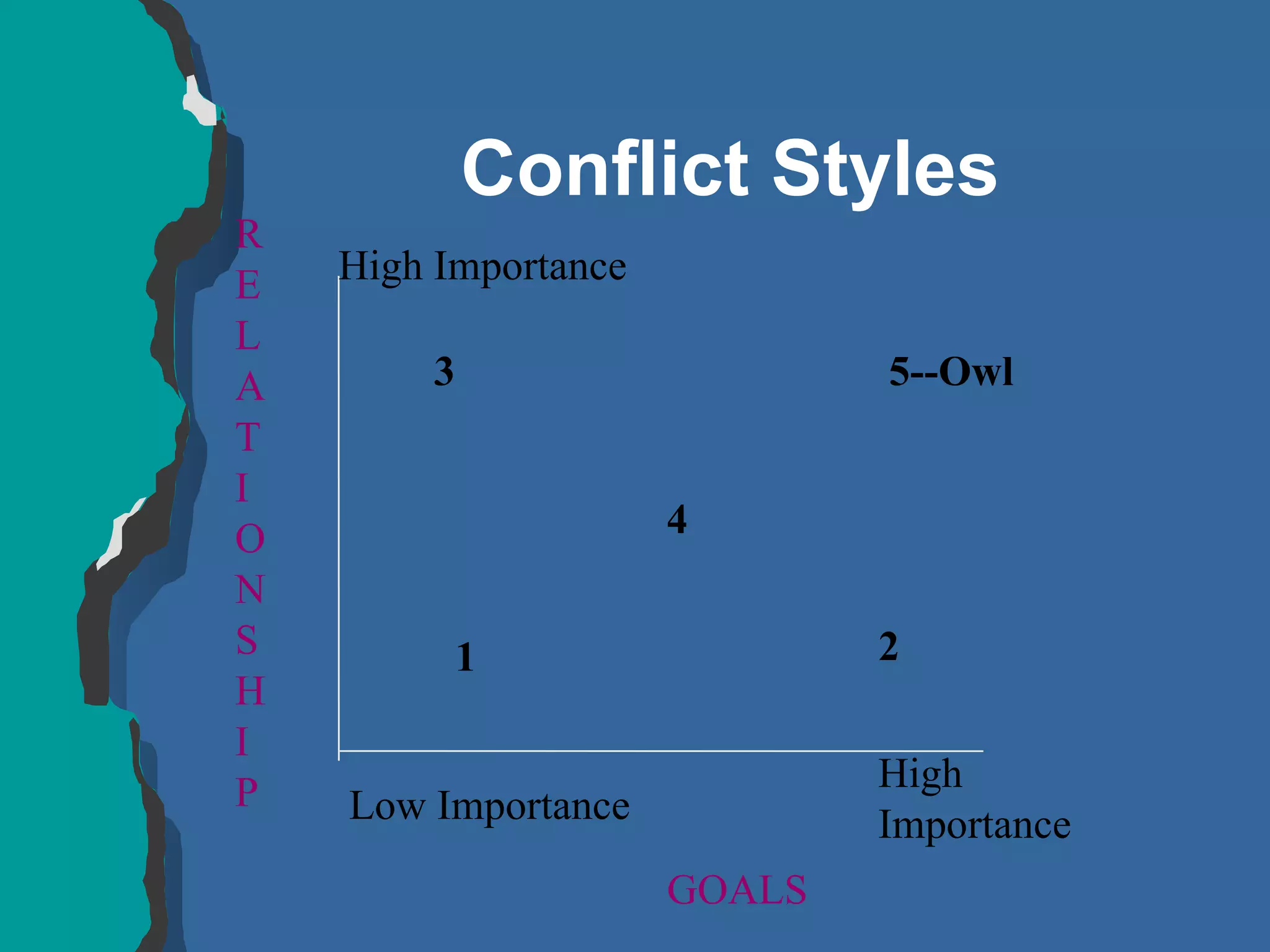
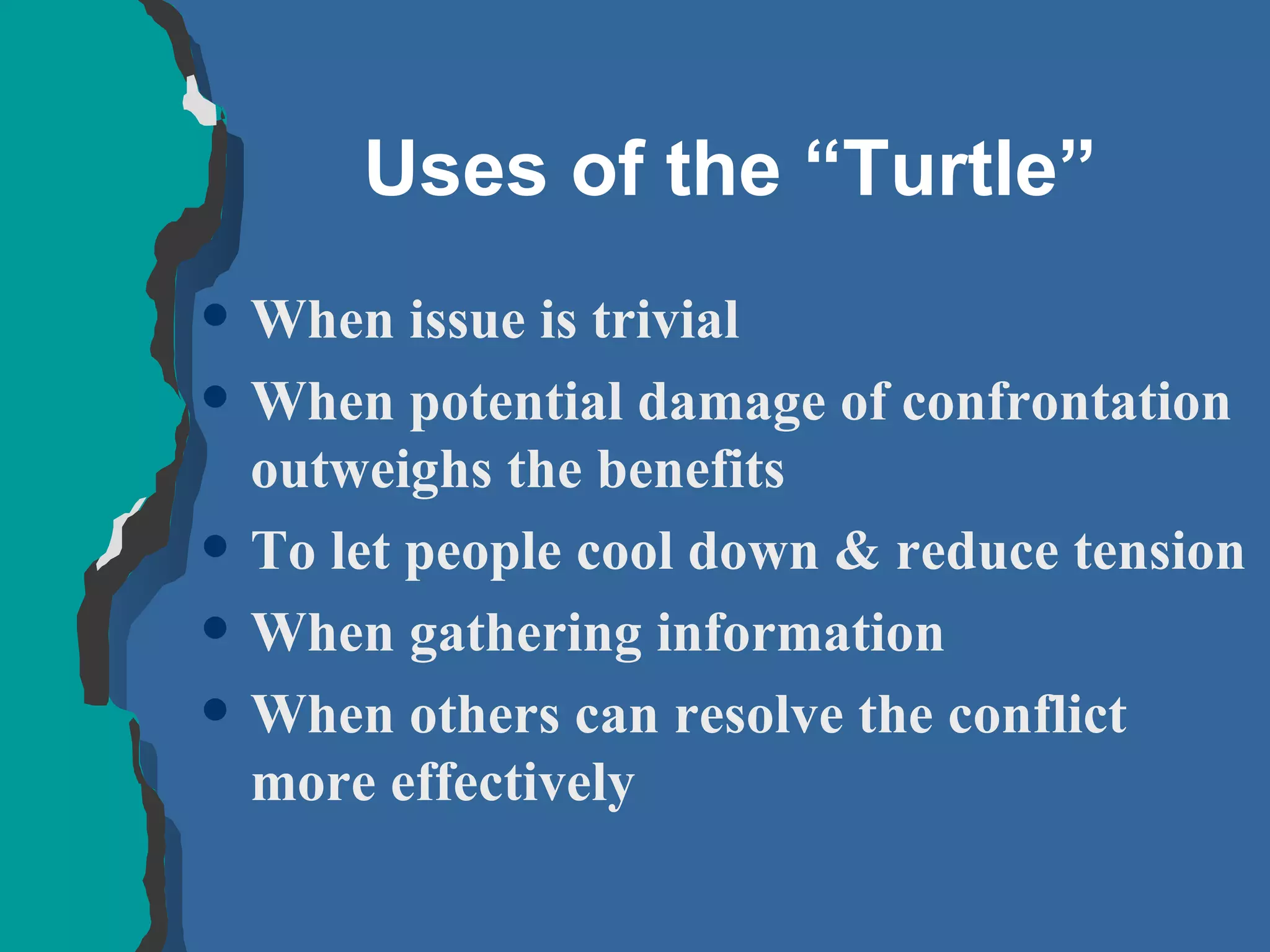
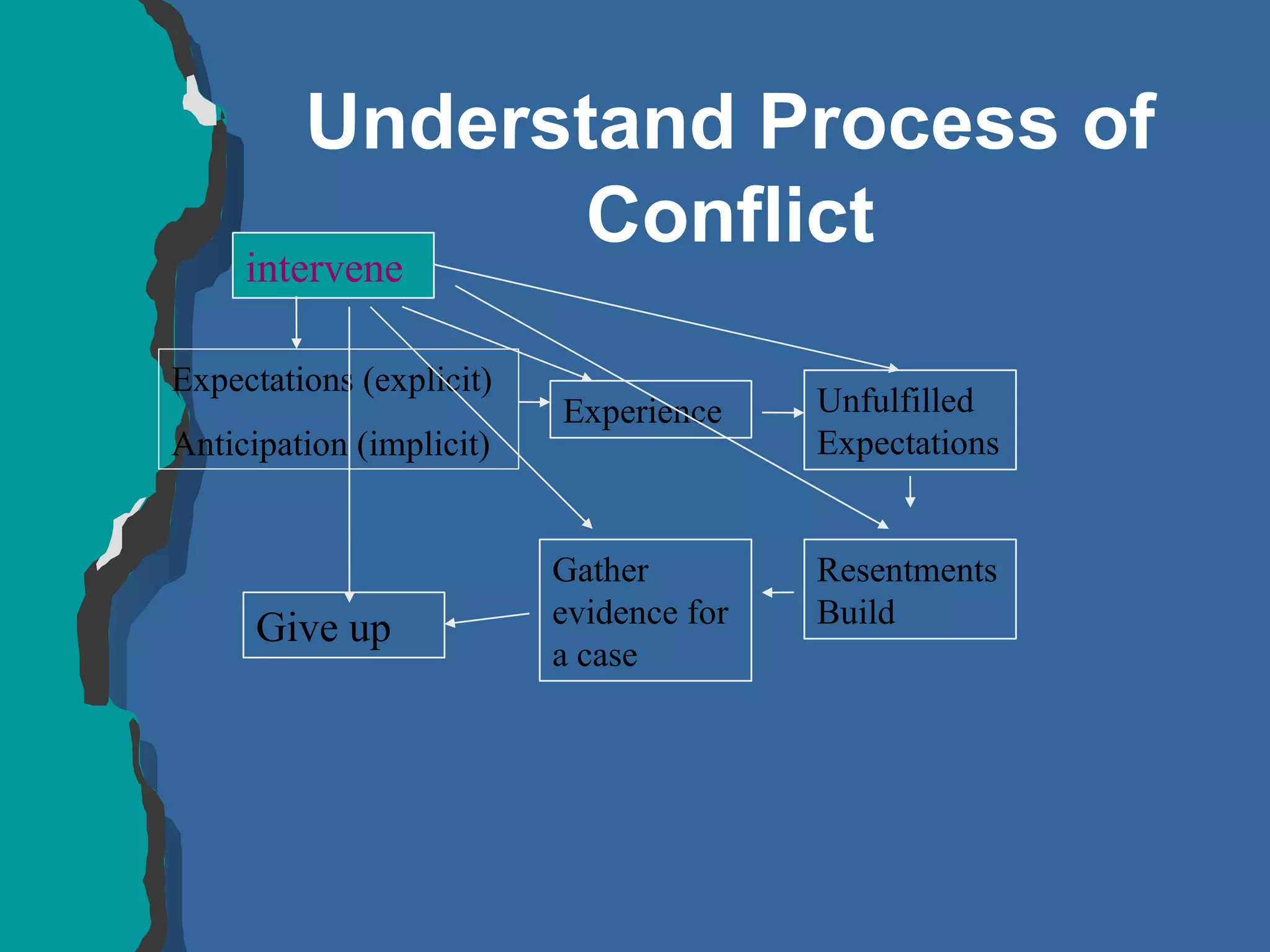
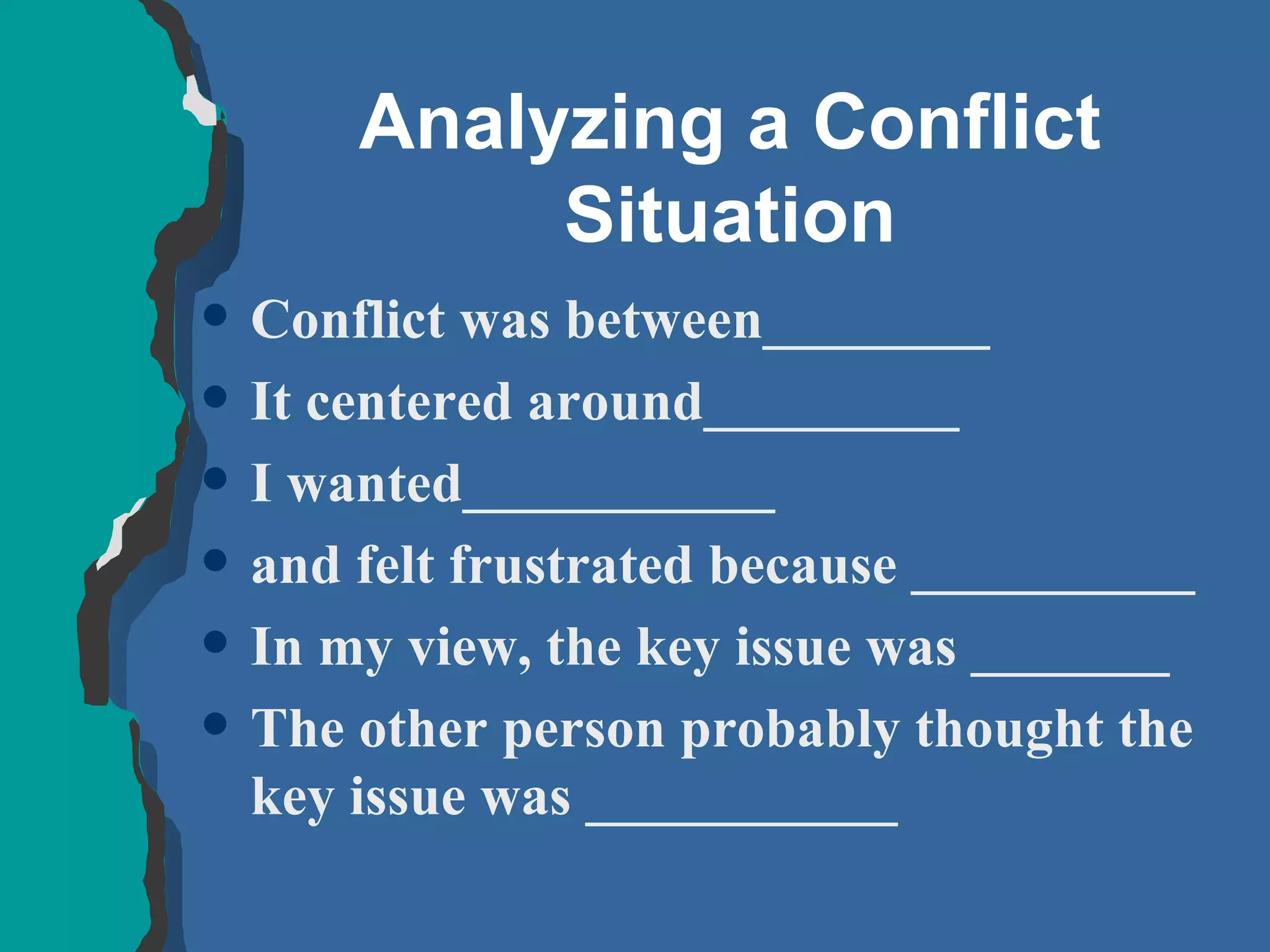
The document discusses conflict management and provides strategies for effectively dealing with conflict. It defines conflict as a disagreement between two or more parties with incompatible concerns. It notes that conflict is natural for humans and occurs when people have a stake in a relationship or outcome. The costs of unmanaged conflict can be high, but managed conflict can be productive. Effective conflict management involves understanding the different conflict styles, de-escalating tensions, and finding integrative solutions that satisfy all parties.