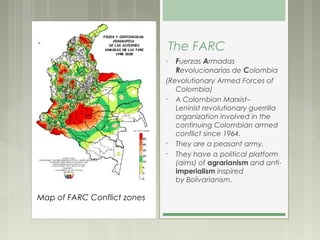
The document summarizes the ongoing conflict in Colombia between the government and peasant guerrilla groups like the FARC. It provides background on Colombia's independence from Spain in the early 19th century and later civil wars between Liberal and Conservative parties over inequality and land ownership. Disputes over coffee and agricultural lands between peasants and landowners have contributed to the conflict. The FARC was formed in 1964 as the military wing of the Communist party and funds operations through kidnapping, drugs, and mining, though it has recently released some prisoners. The conflict has led to displacement of farmers and mental and physical health impacts on communities.