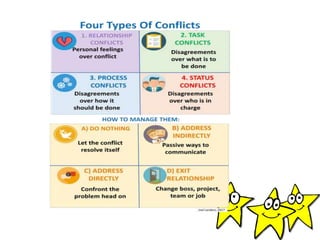
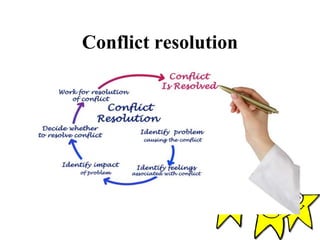
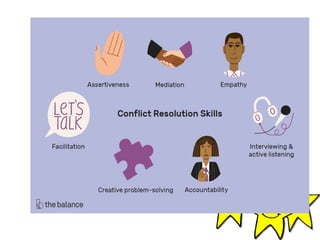
The document discusses conflict as a painful emotional state arising from contradictory desires and presents various types of conflict, including approach-approach, avoidance-avoidance, approach-avoidance, and multiple approach-avoidance conflicts. It highlights the nature of internal conflicts, which can be conscious or unconscious, and outlines steps for conflict resolution such as identifying causes, adjusting goals, and seeking advice. Overall, the focus is on understanding and managing conflict in both personal and interpersonal contexts.