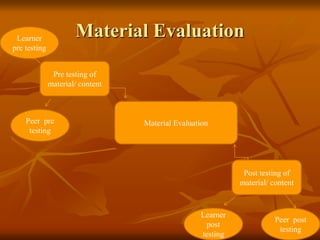
The document discusses conducting material evaluation for educational purposes. It outlines the objectives of material evaluation as assessing whether the material's objectives and contents achieve the curriculum's goals and are relevant and appropriate for learners. Key aspects to evaluate include the material's achievement of objectives, relevance, visuals, language level, and teaching-learning process. The evaluation process involves pre-testing the material with learners and peers, revising it based on feedback, and post-testing the finalized material. Formative evaluation aids development, while summative evaluation assesses the material's suitability for dissemination.