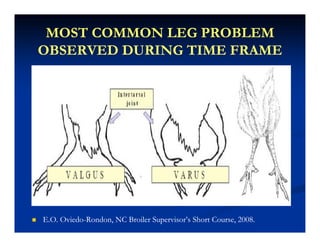
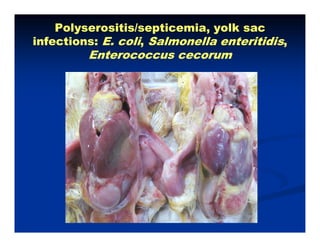
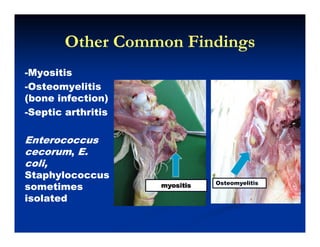
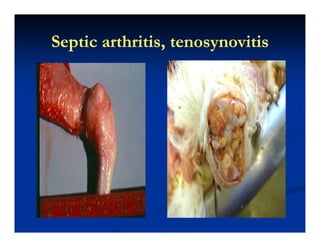
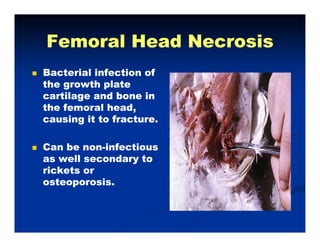
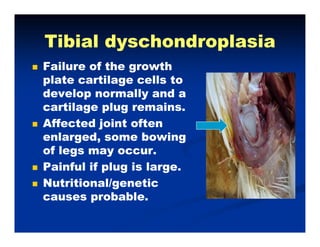
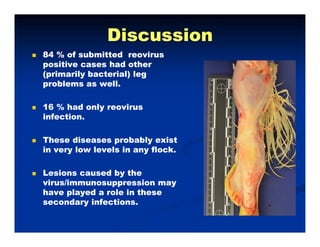
- Broiler chickens submitted to the Animal Diagnostic Laboratory between February and May 2012 showed problems with leg weakness and lameness.
- The majority of cases had concurrent bacterial infections like E. coli, Enterococcus cecorum, and Salmonella enteritidis along with reovirus infection. Only 16% had solely reovirus.
- The bacterial infections were causing issues like polyserositis, septicemia, osteomyelitis, and septic arthritis in the legs at different ages of the broilers. Reovirus infection may have contributed to immunosuppression and secondary bacterial infections in the legs.