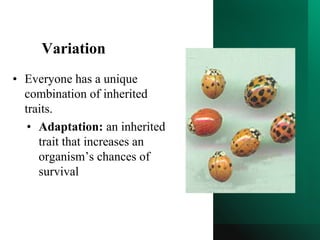
Evolution is the process of change over generations in a population's inherited traits due to natural selection, where individuals with traits better suited to the environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their beneficial genes. Key concepts include: variation within populations provides different traits for natural selection to act upon; competition for limited resources means not all individuals survive to reproduce; and over many generations, beneficial traits accumulate while harmful traits are eliminated from the gene pool. Mutation introduces new variation that natural selection can then act on.