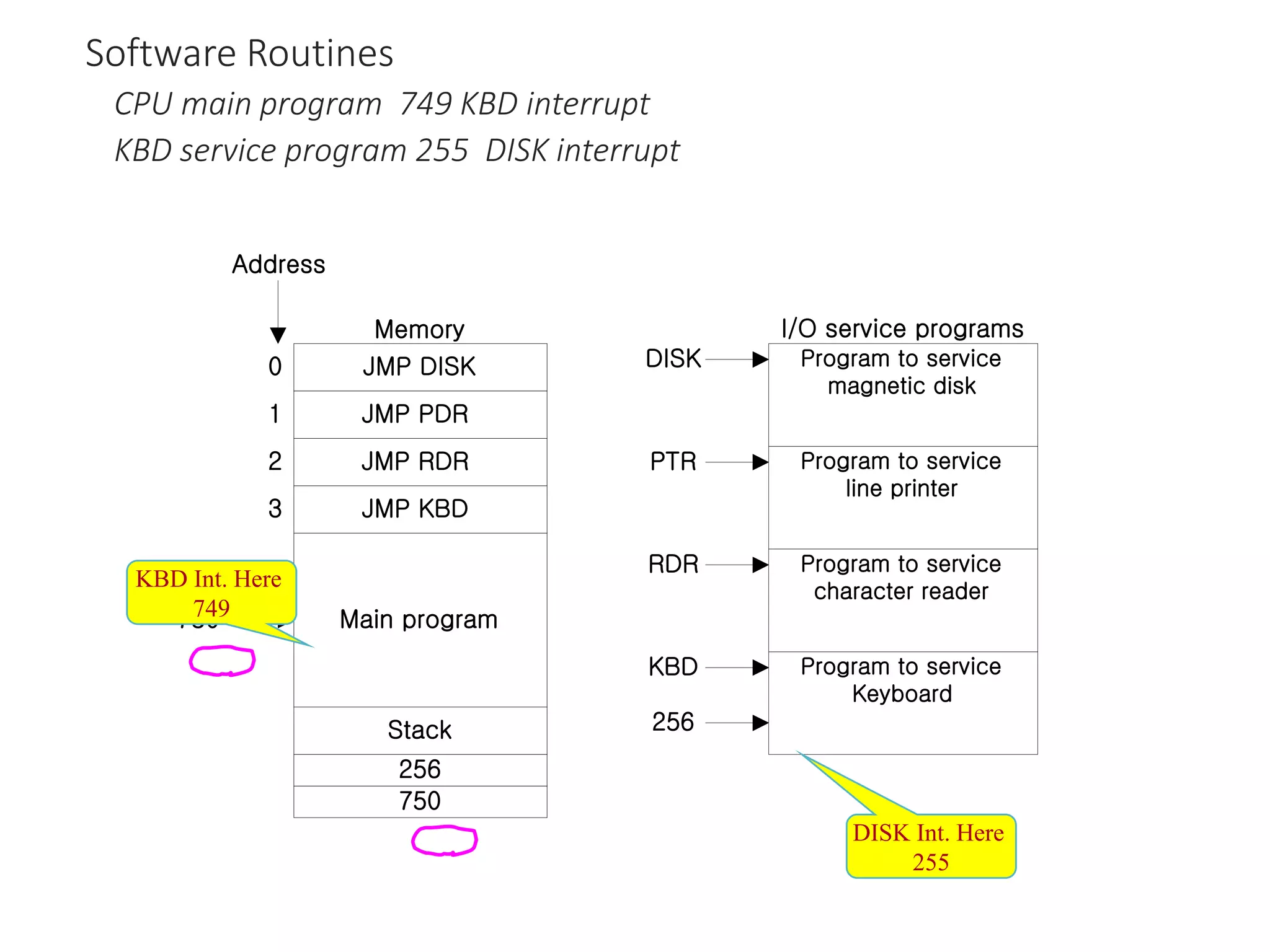
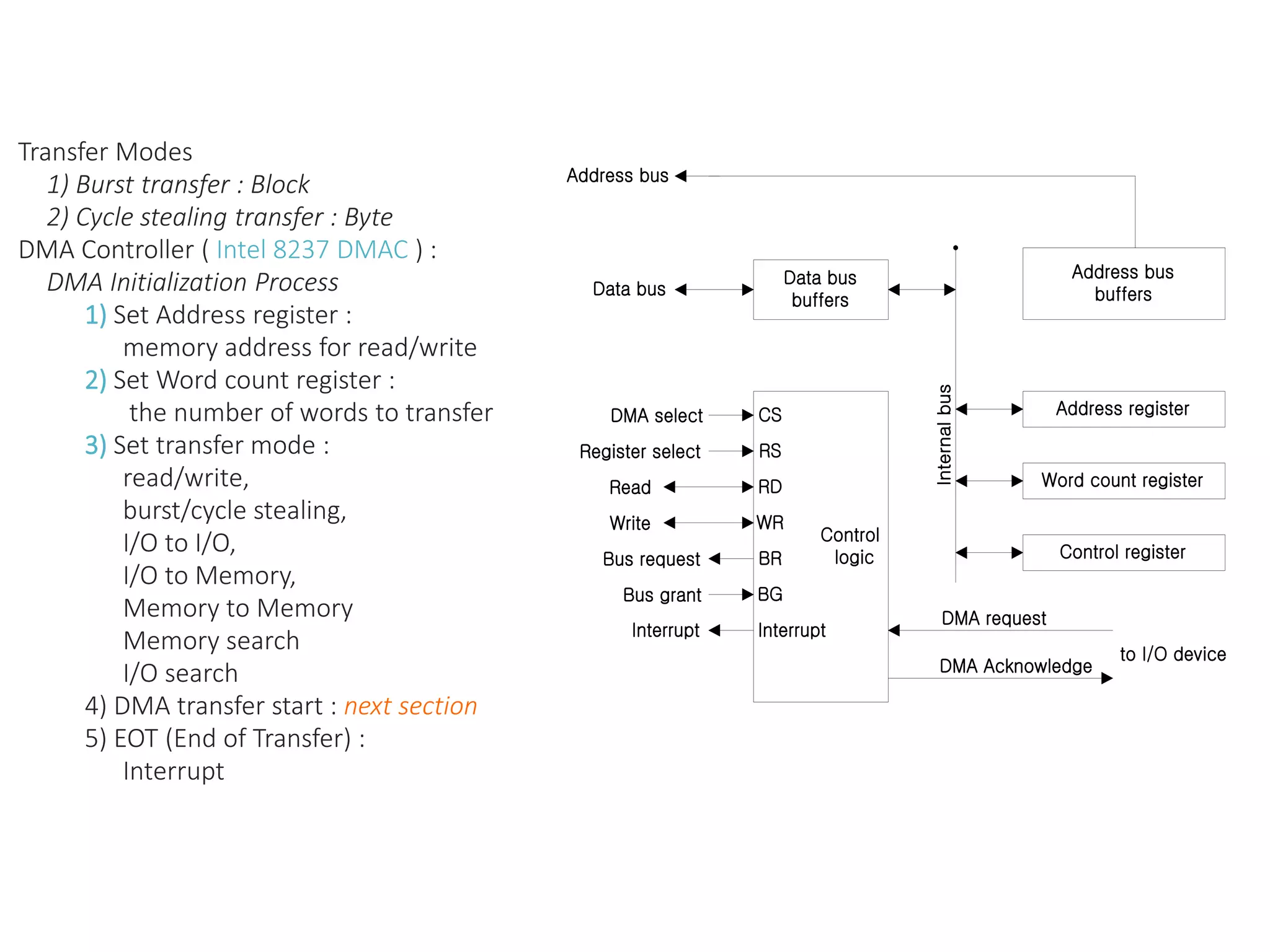
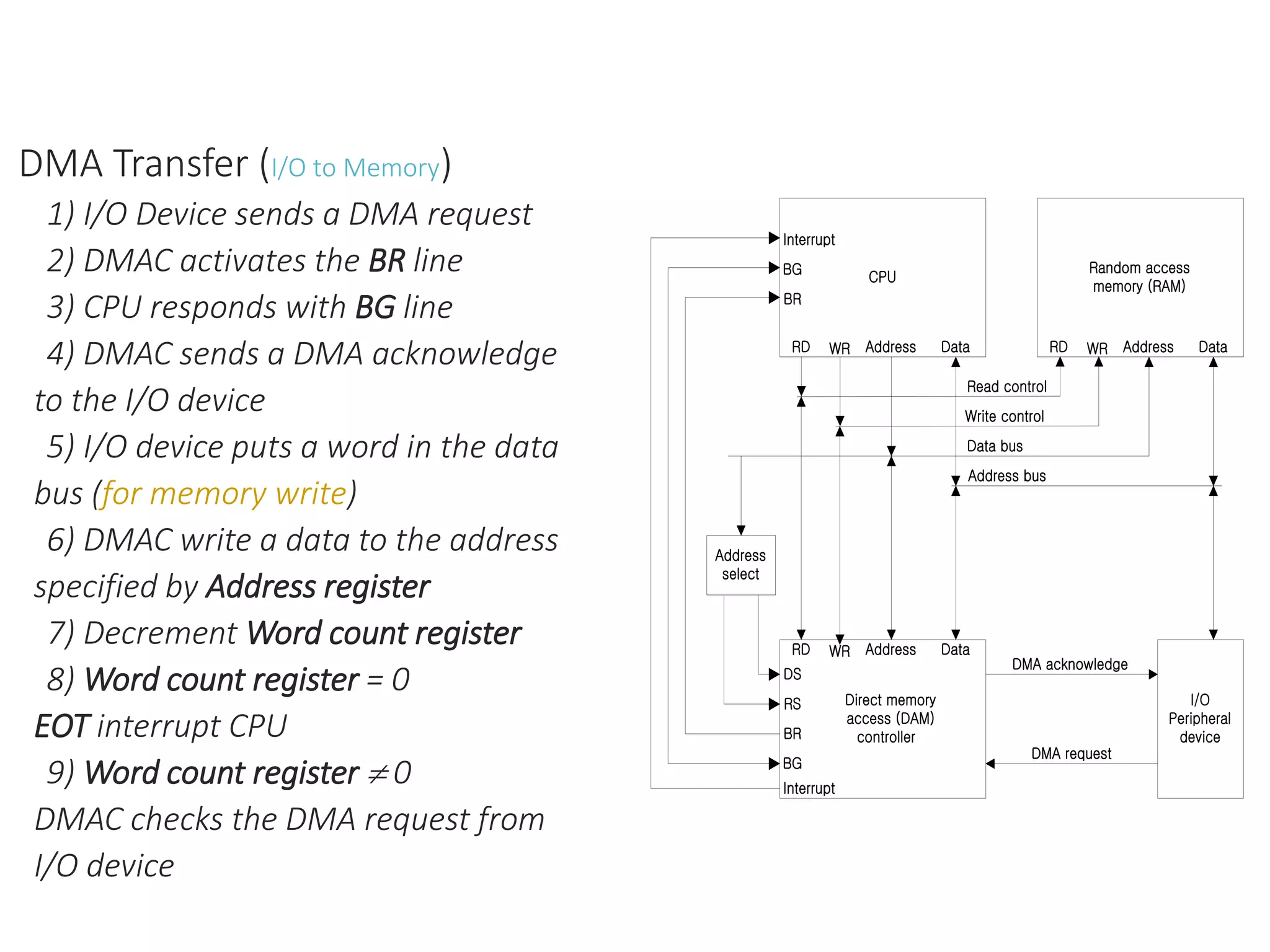
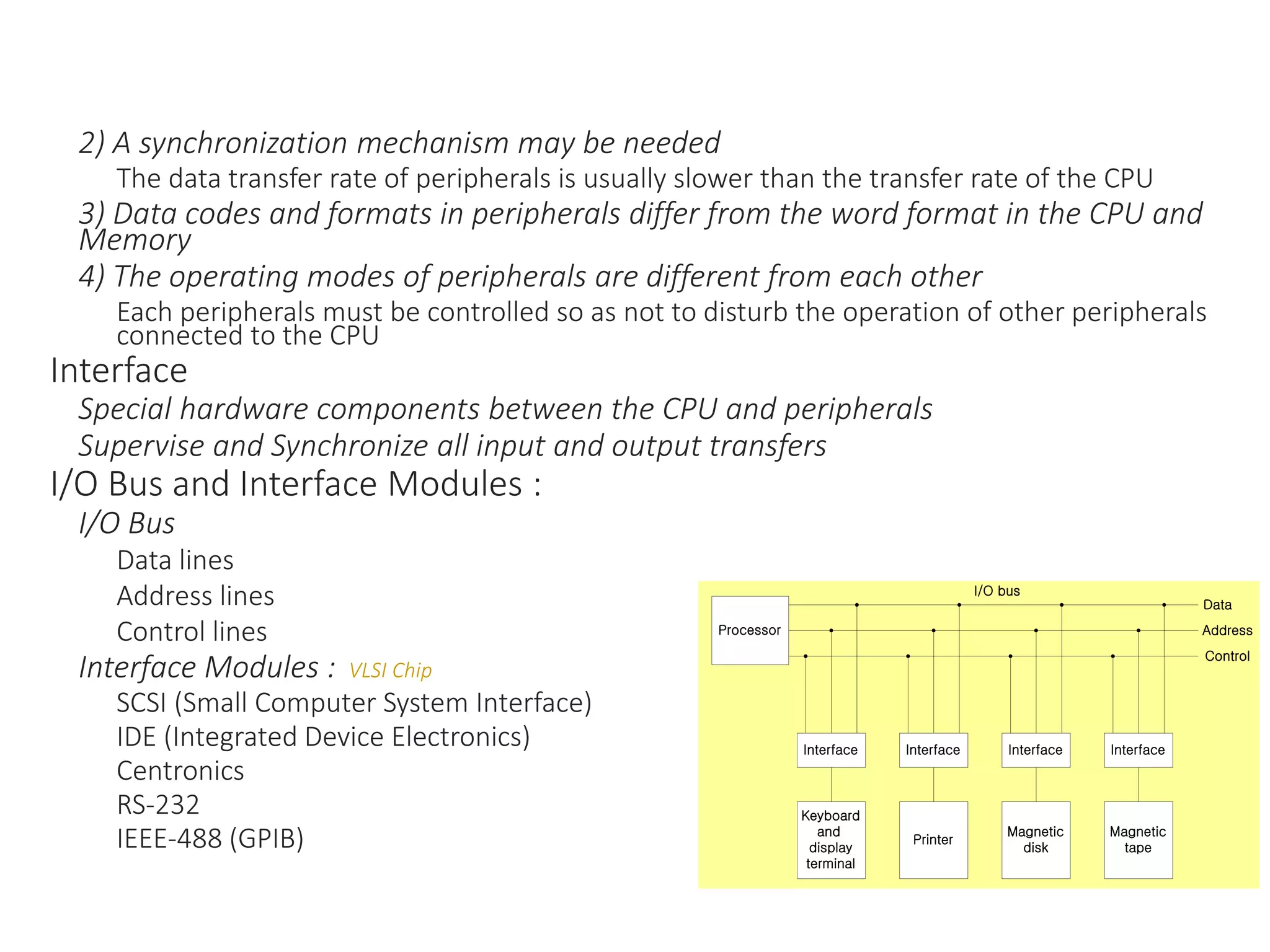
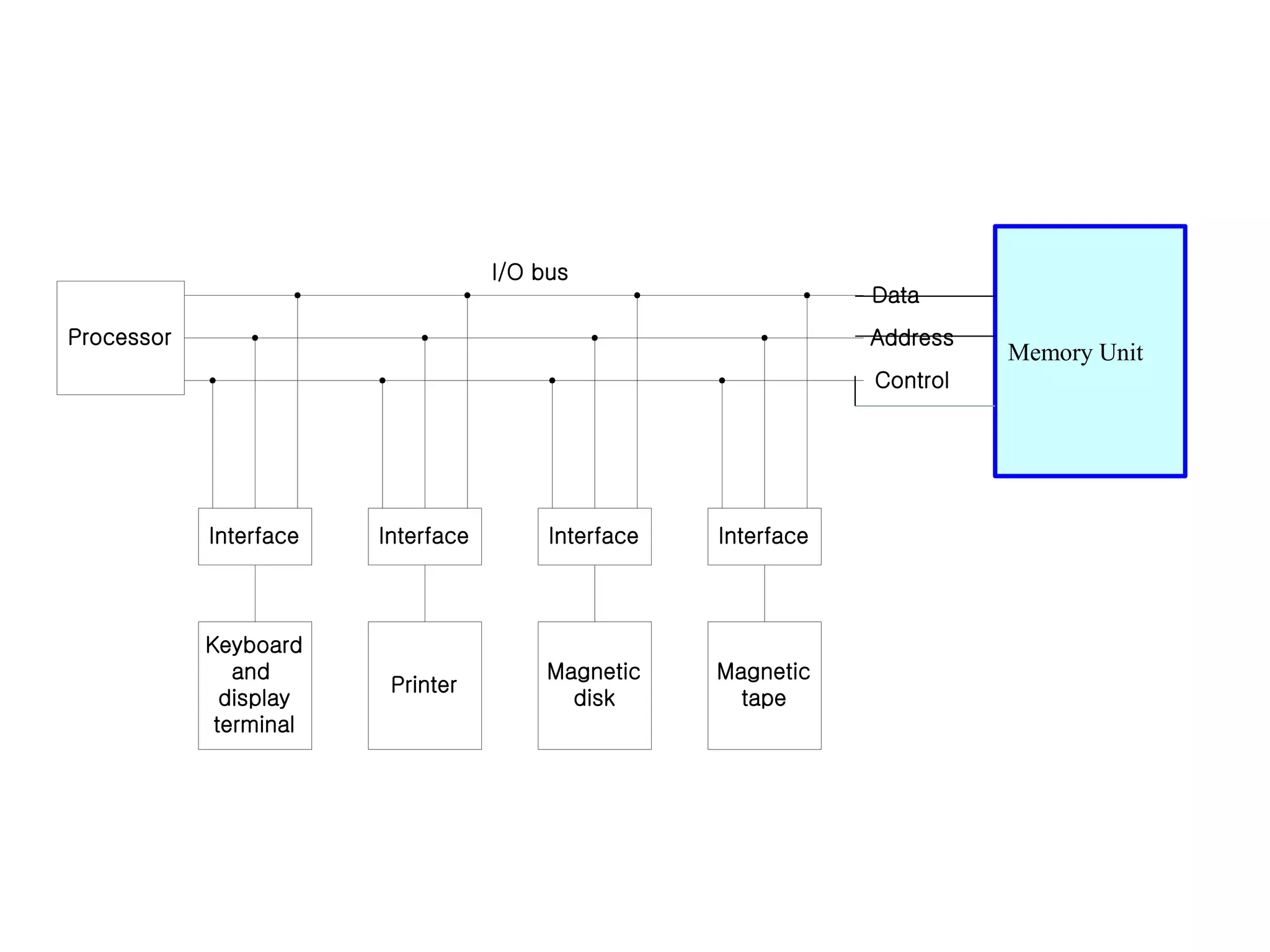
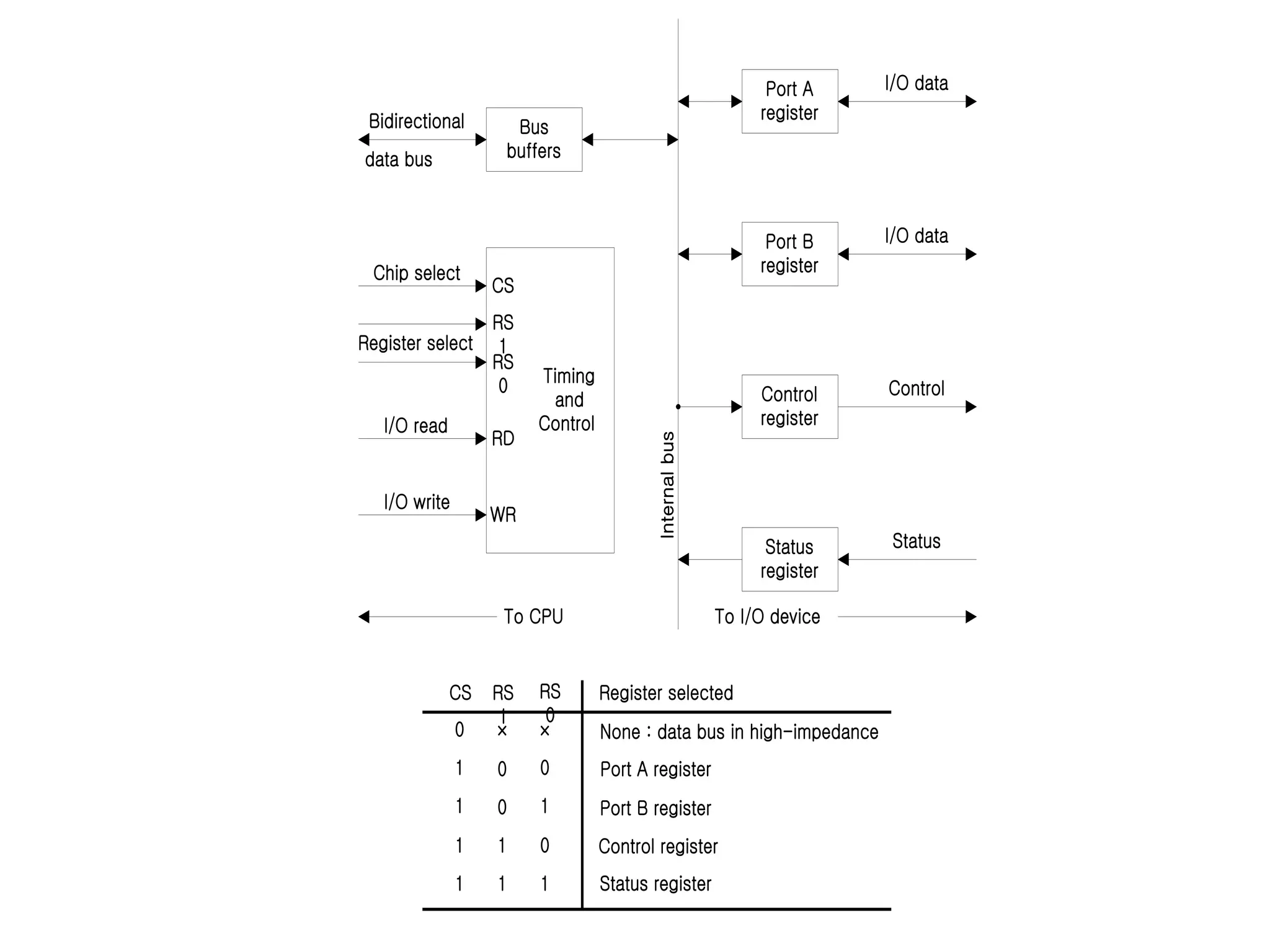
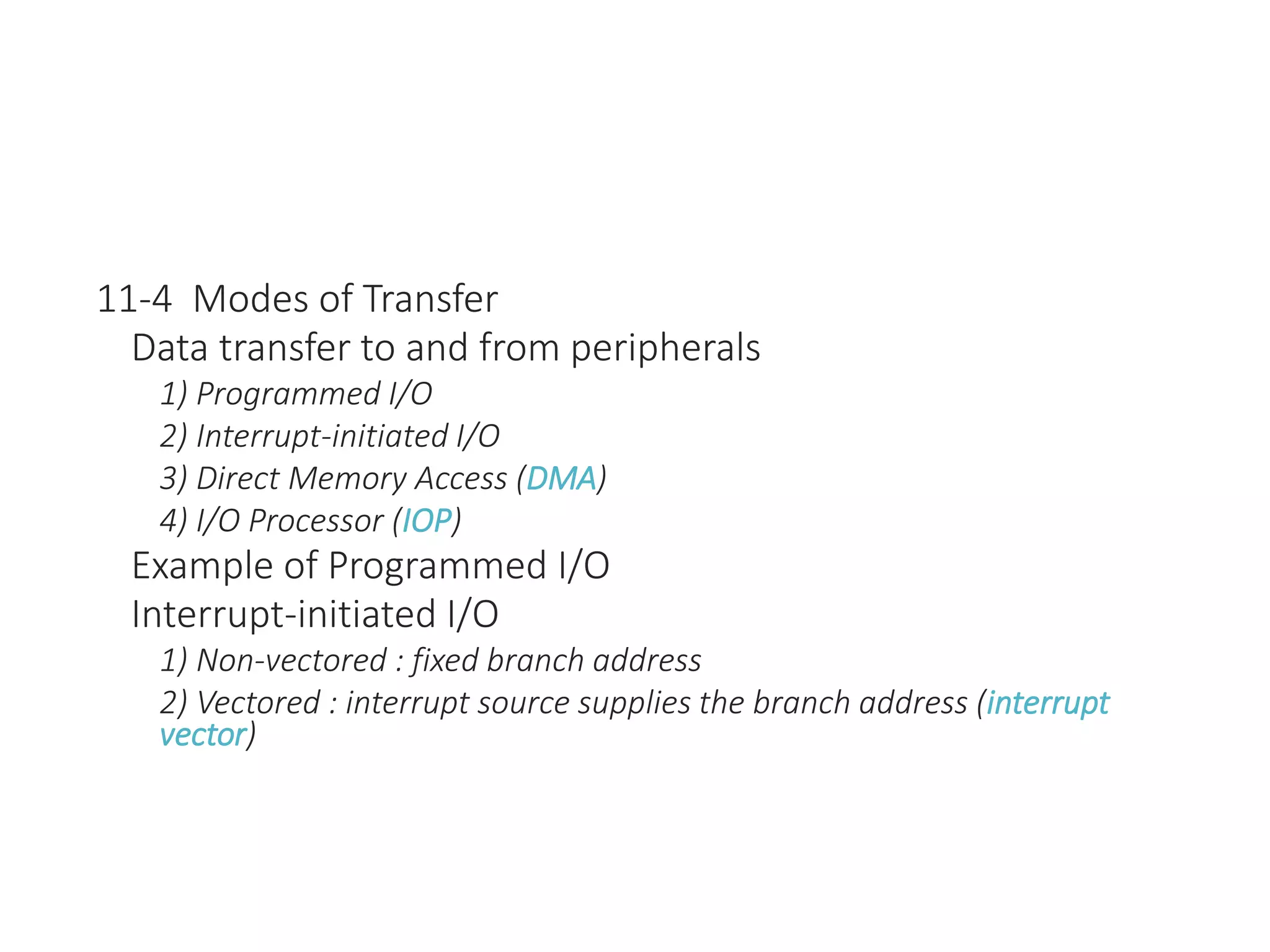
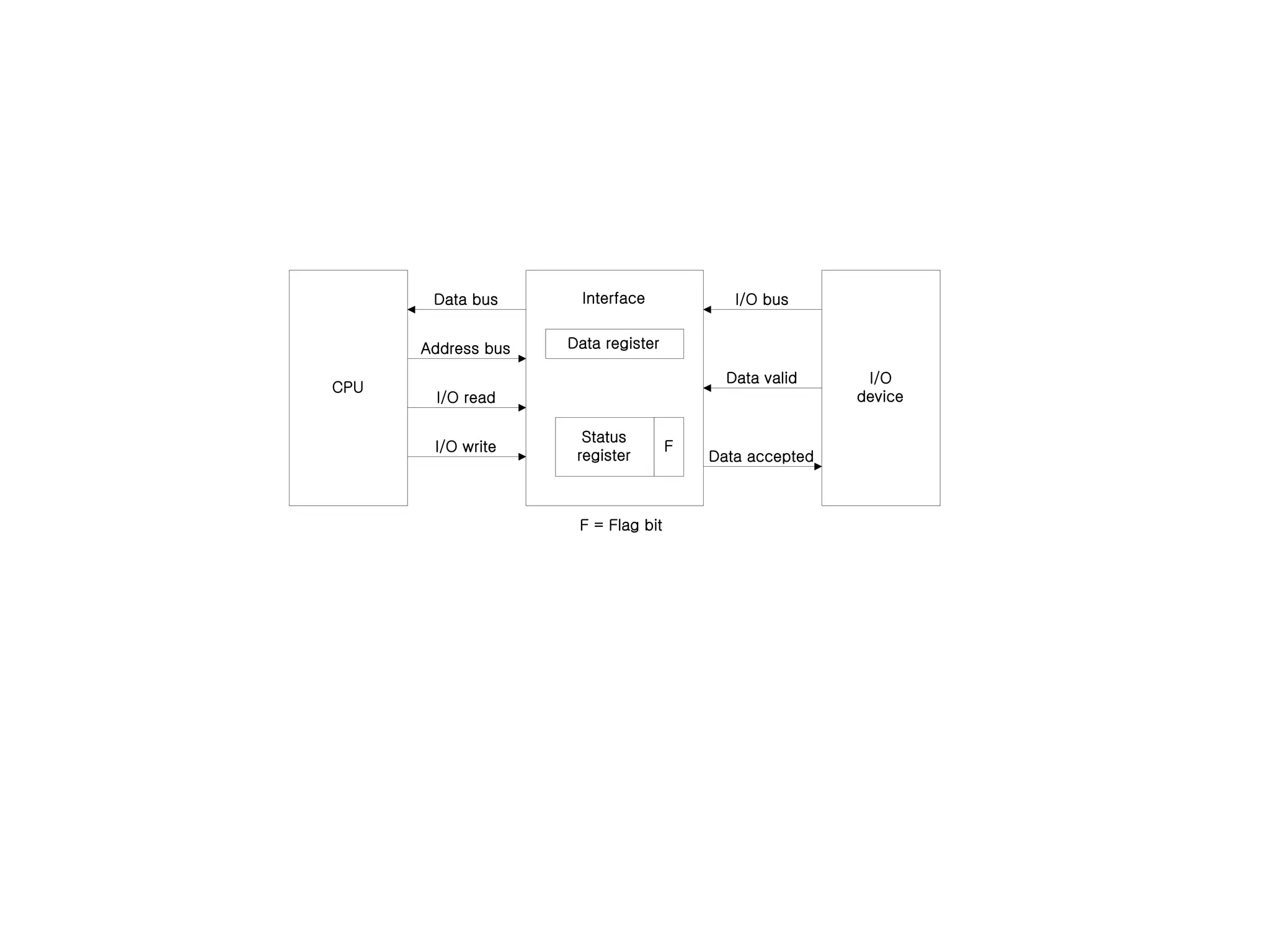
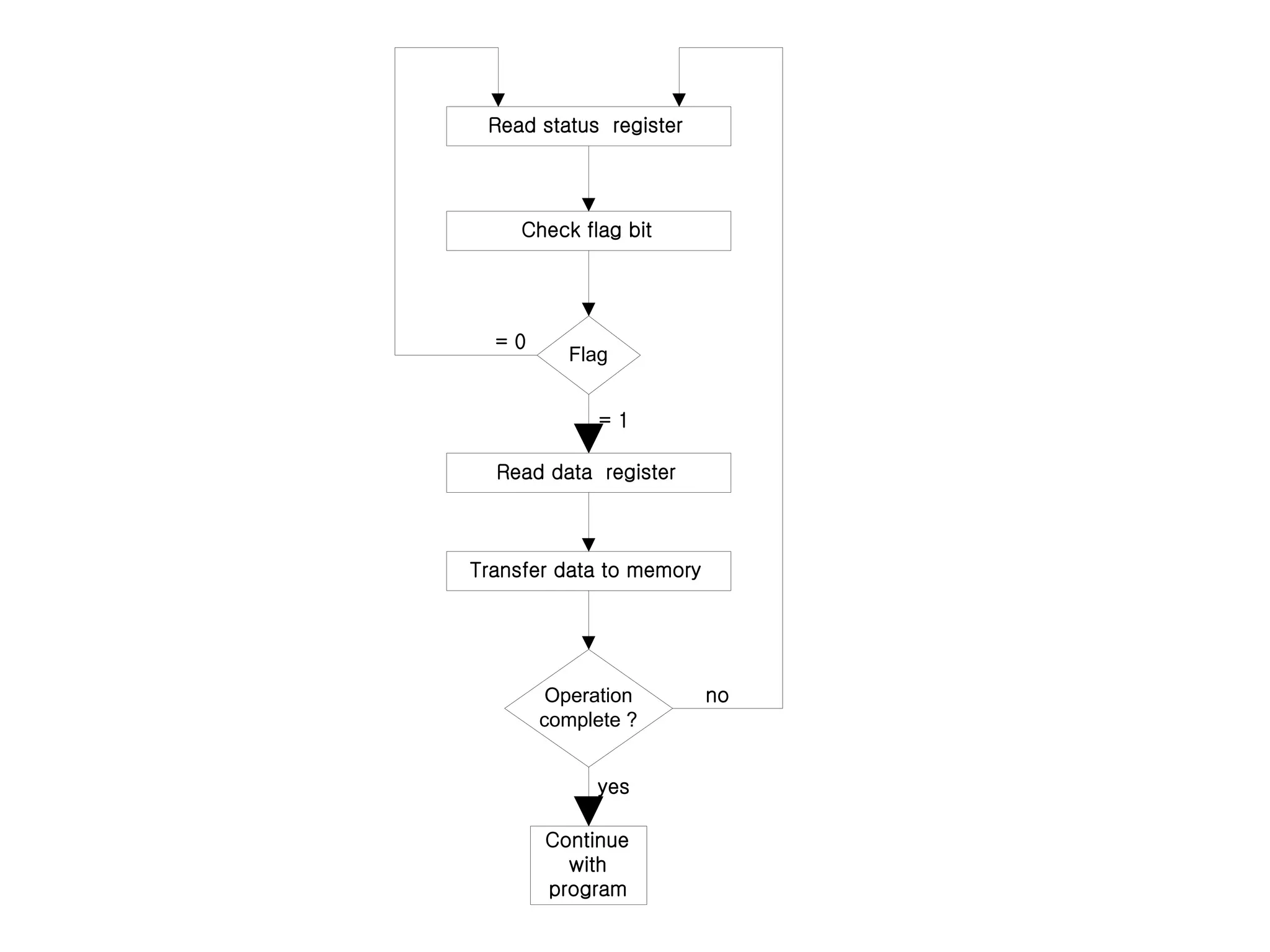
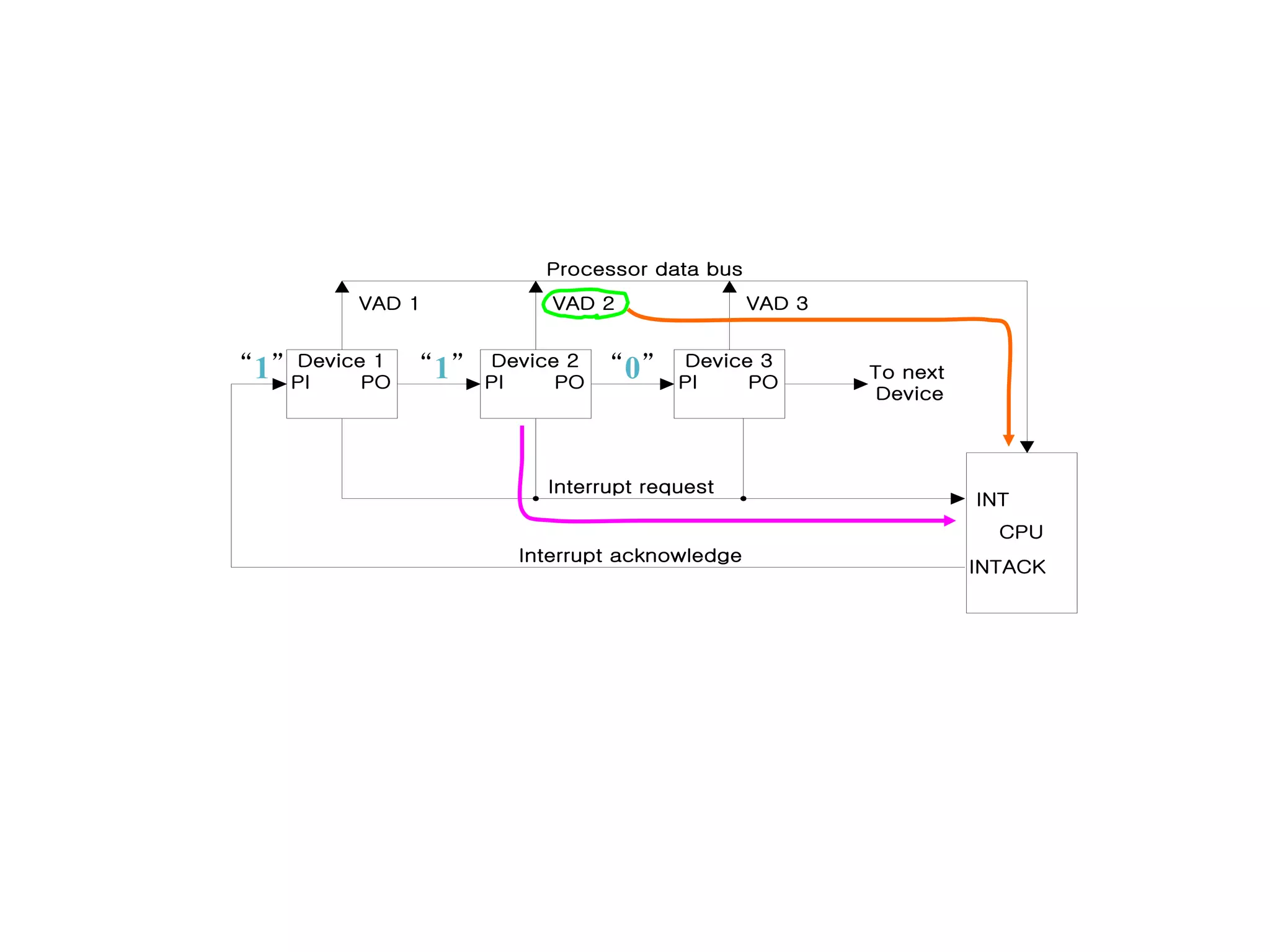
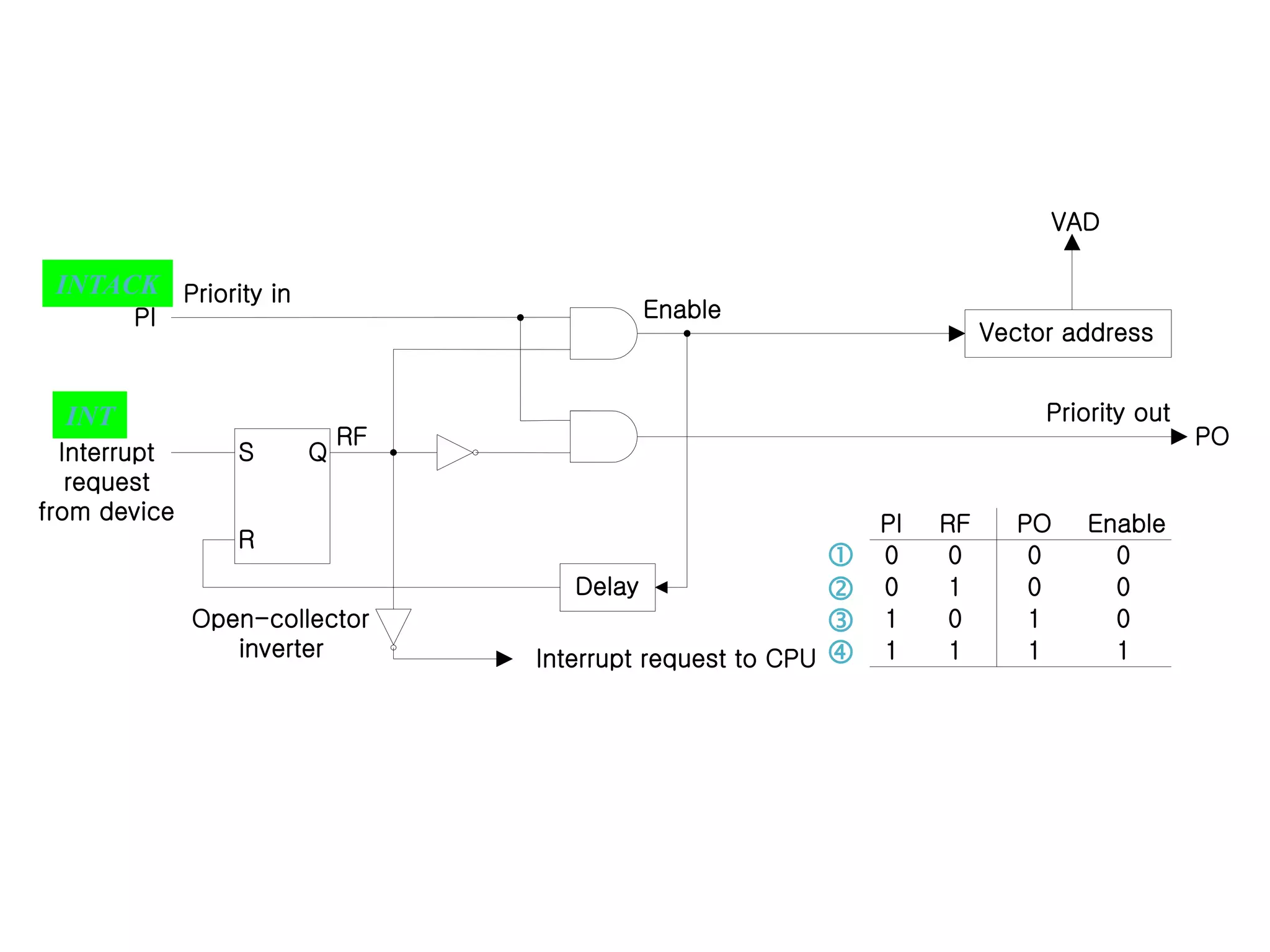
The document discusses input-output organization and direct memory access. It describes how I/O devices are connected to computers through interfaces that handle synchronization and conversion between the CPU and peripherals. It also explains different I/O transfer modes like programmed I/O, interrupt-driven I/O, and direct memory access (DMA). DMA allows high-speed transfer of data directly between memory and an I/O device without CPU involvement by using bus request/grant signals to gain control of the buses.







![0
3
2
1
0
3
2
1
Priority
encoder
I0
I2
I3
I1
disk
Keyboard
Reade
r
Printer
Interrupt
register
y
0
0
0
0
0
0
x
IST
IEN
VAD
to CPU
Enable
Interrupt
to CPU
INTACK
from CPU
Mask
register
n
instructio
next
Fetch
to
0
1
]
[
1
Go
IEN
VAD
PC
INTACK
PC
SP
M
SP
SP
−
: Decrement stack point
: Push PC into stack
: Enable INTACK
: Transfer VAD to PC
: Disable further interrupts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerorganizationpart2-211220113939/75/Computer-organization-part-2-17-2048.jpg)