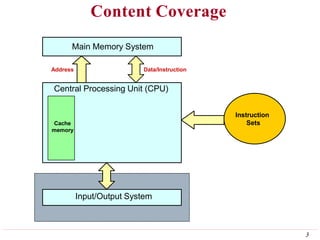
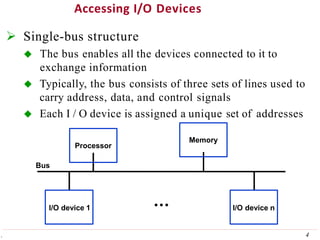
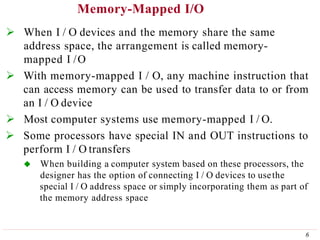
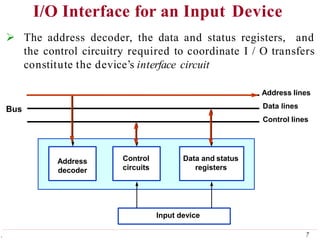
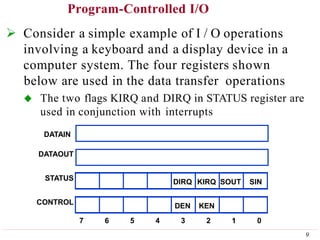
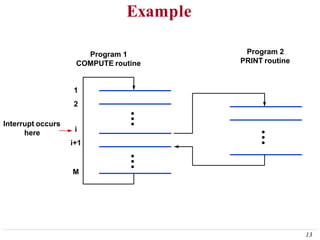
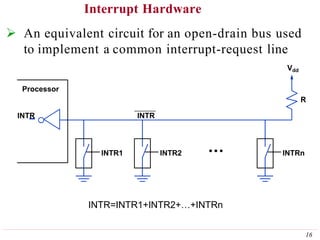
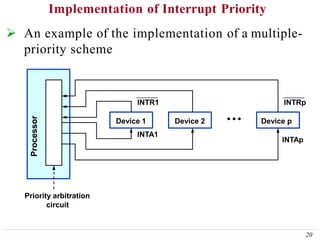
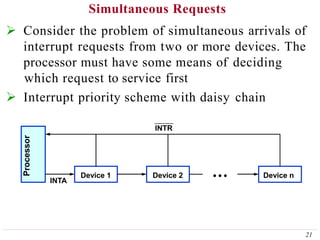
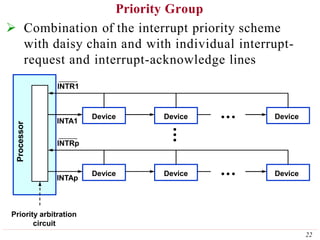
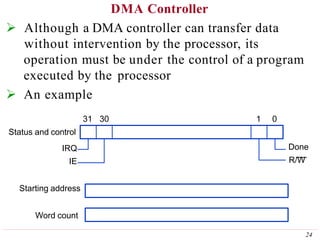
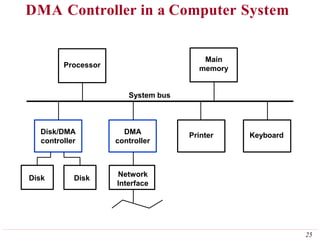
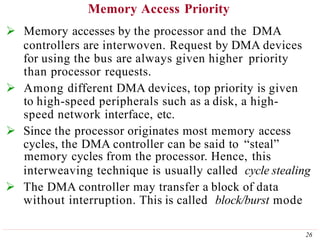
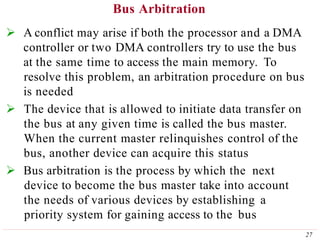
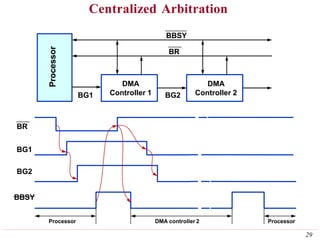
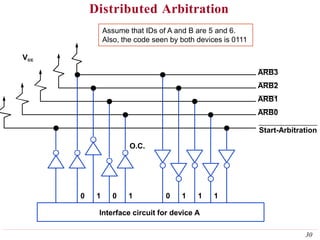
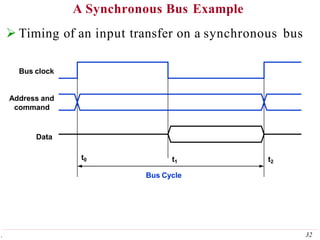
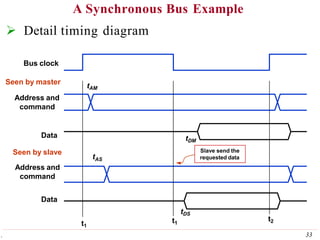
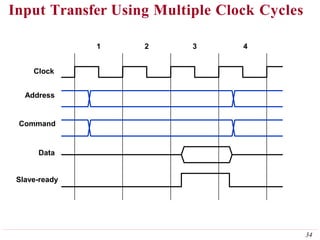
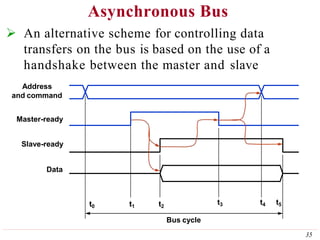
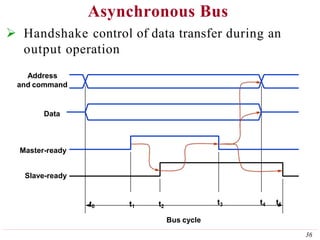
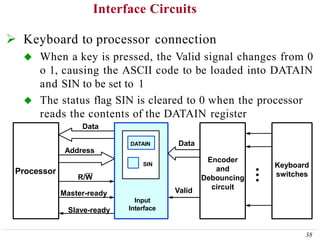
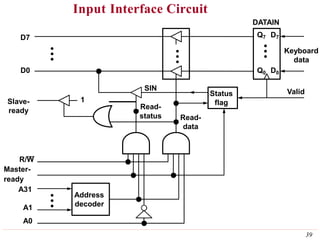
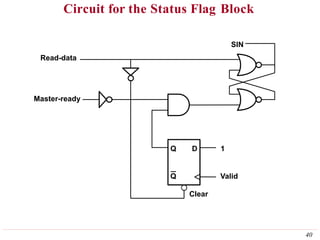
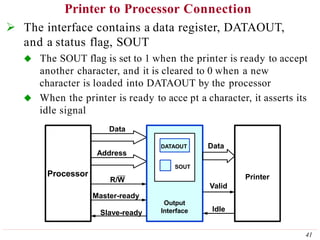
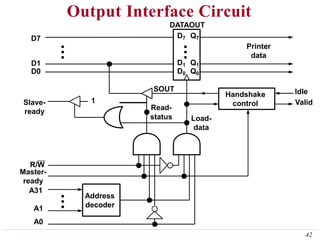
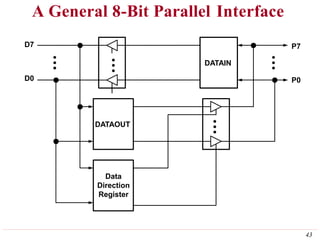
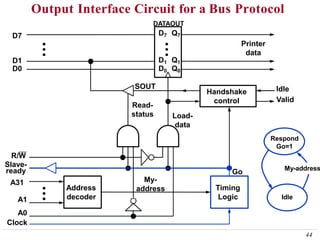
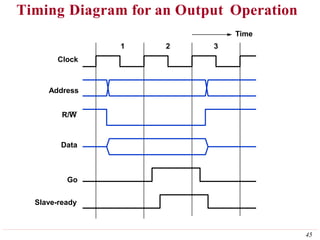
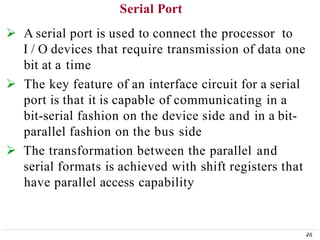
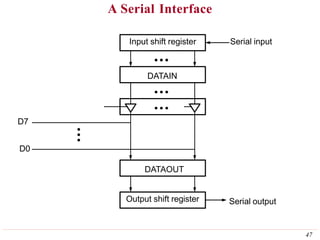
This document discusses input/output (I/O) organization in computer systems. It covers various I/O techniques including programmed I/O, interrupts, direct memory access (DMA), and I/O interfaces. Memory-mapped I/O allows I/O devices to use the same address space as memory. Interrupts allow I/O devices to signal the processor when they need service. DMA controllers can transfer data directly between I/O devices and memory without processor intervention. Buses and interface circuits are used to connect I/O devices to the processor and main memory.