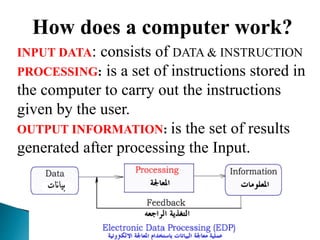
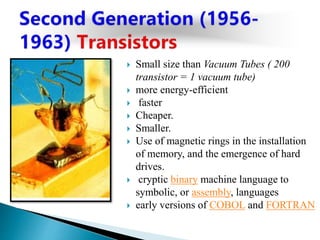
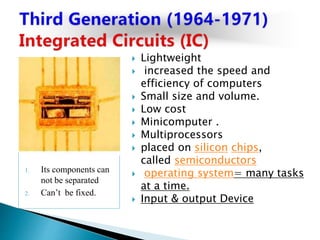
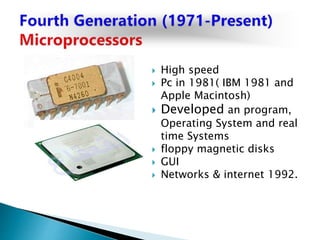
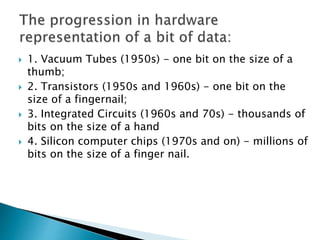
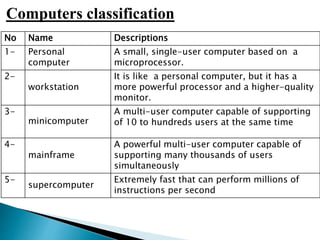
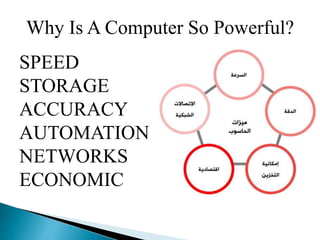
The lecture introduces fundamental concepts of computers, including their capabilities in processing data through arithmetic and logical operations. It outlines the evolution of computer generations from vacuum tubes to silicon chips and discusses various types of computers and classifications based on users. The importance of speed, accuracy, and storage in enhancing computer power is highlighted, along with the significance of data and information processing.