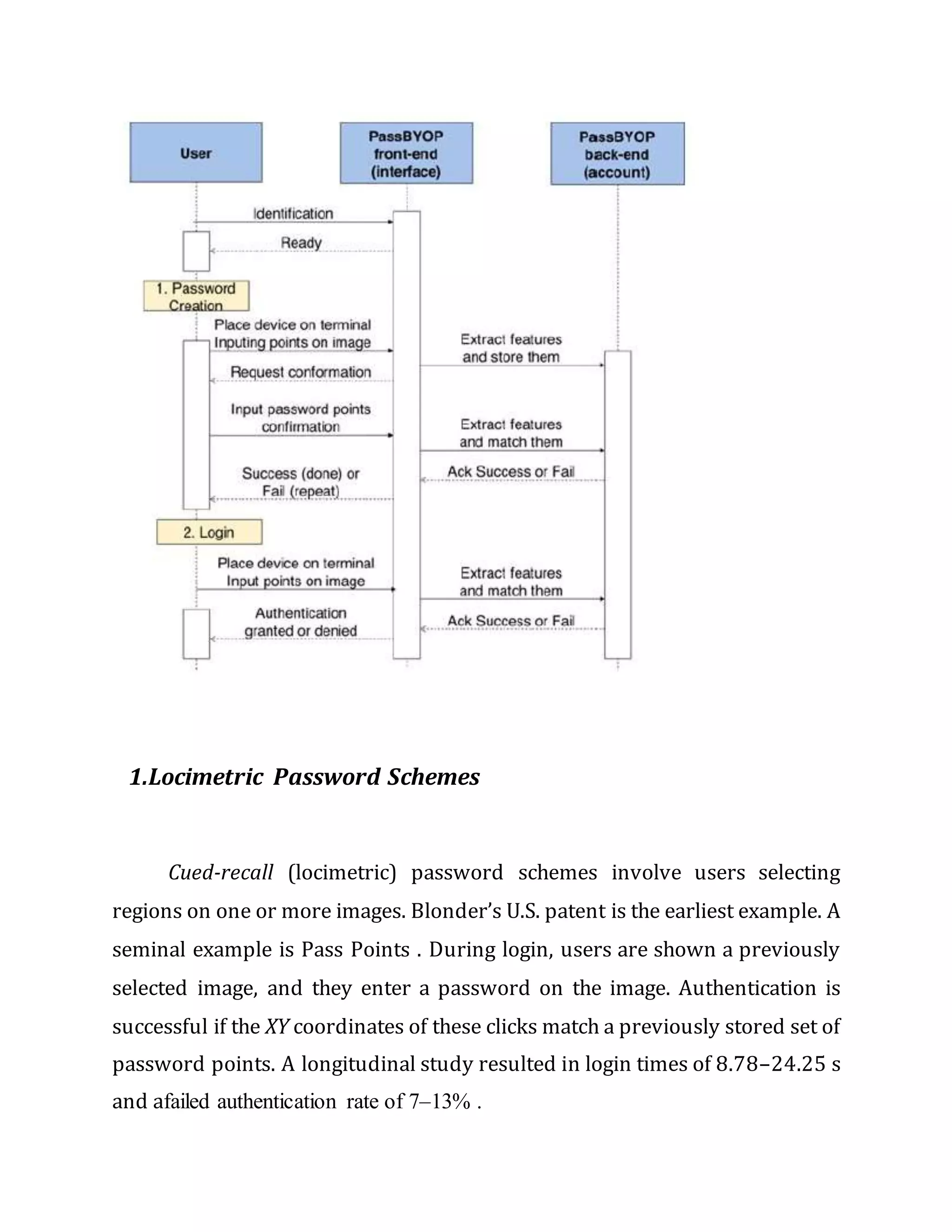
The document presents passbyop, a graphical password scheme using personalized digital images displayed on users' devices to enhance security against observation attacks. Feasibility studies demonstrate passbyop's reliability, usability, and resistance to observation, suggesting advantages over traditional textual passwords. The proposed pass matrix authentication system offers improved security and usability, allowing users to log in safely while mitigating shoulder surfing risks.