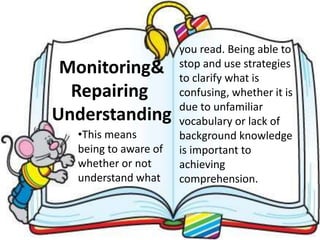
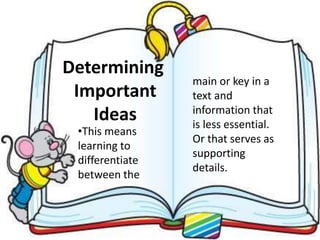
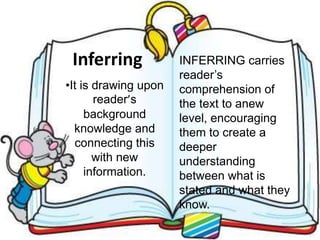
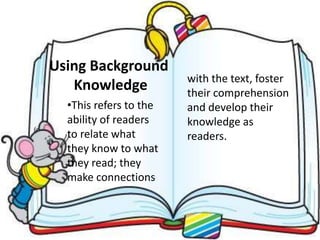
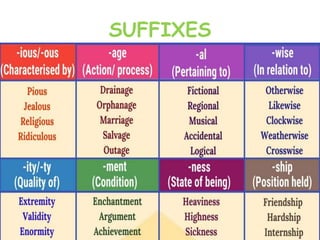
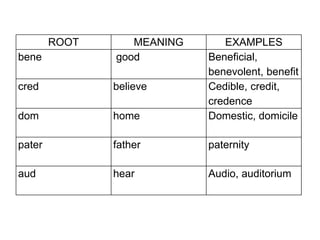
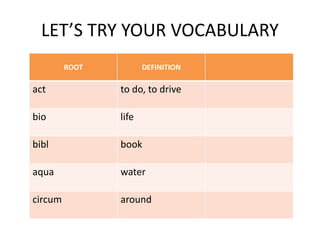
Here are potential prefixes, suffixes, and new words to complete the activity:
Group 1:
Prefix/suffix: un
Word: happy
New word: unhappy
Group 2:
Prefix: dis
Word: satisfy
New word: dissatisfy
Group 1:
Prefix: tele
Word: scope
New word: telescope
Group 2:
Suffix: ion
Word: valid
New word: validation
Group 1:
Prefix: a
Word: sexual
New word: asexual
Group 2:
Suffix: ity
Word: scope
New word: scopeity
Group 1:
Prefix: re
Word: valid
New word