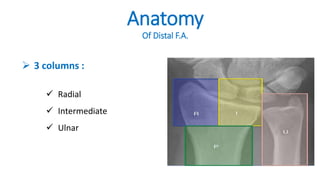
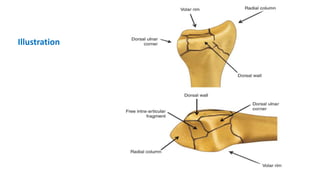
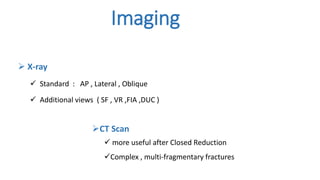
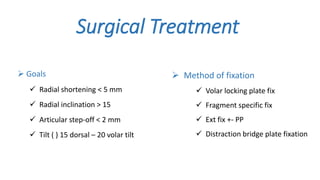
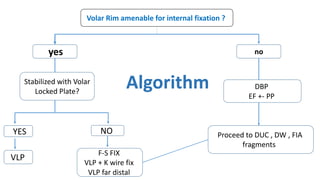
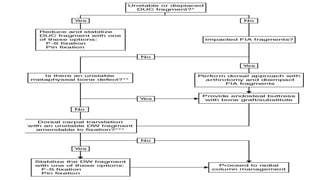
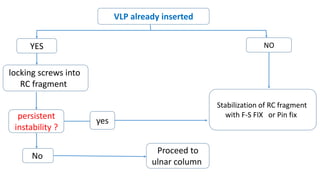
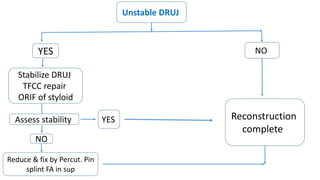
The document presents a journal club discussion on the management of complex distal radius fractures, highlighting anatomy, imaging, and surgical treatment options. Key goals of surgery include achieving proper radial shortening, inclination, and articular alignment through various fixation methods. Understanding the anatomy and reconstruction goals is essential for effective preoperative planning and decision making in these challenging cases.