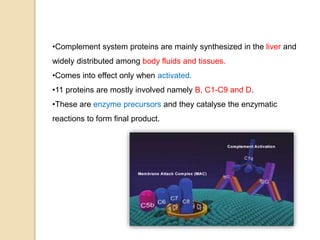
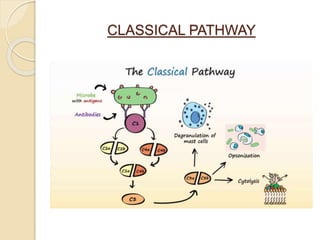
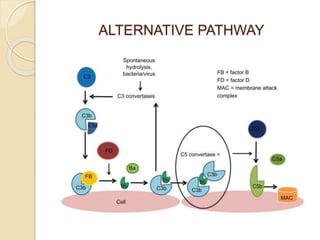
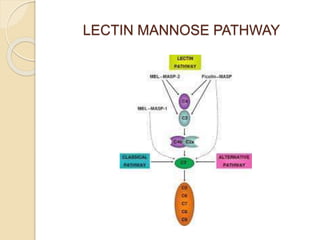
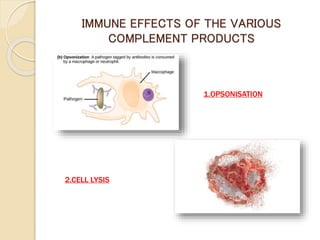
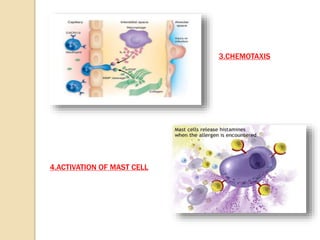
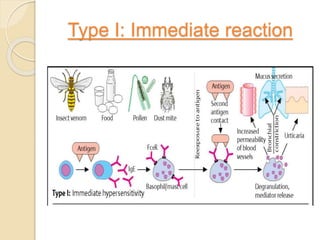
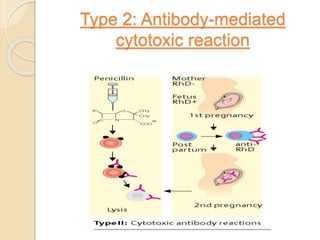
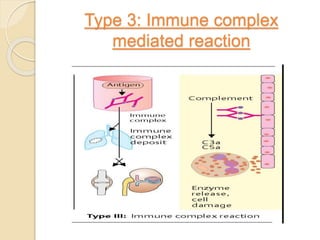
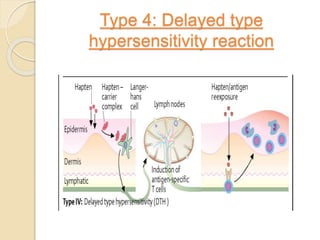
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on the complement system and hypersensitivity of the immune response. It provides an overview of the complement system, including that it is comprised of 20 plasma proteins that form an essential part of innate immunity. It describes the three pathways of complement system activation - the classical, alternative, and lectin pathways. It also outlines the four types of hypersensitivity reactions classified by Gell and Coombs.