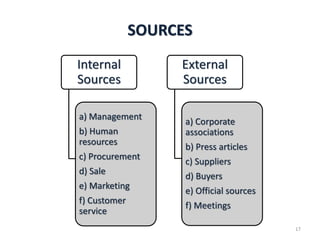
Competitor analysis involves evaluating a company's objectives, strategies, strengths, and weaknesses compared to current and potential competitors. It involves identifying who the competitors are and understanding their objectives, strategies, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Competitor analysis provides advantages like helping determine strategic decisions, reducing costs, increasing sales and profits, and minimizing risks.

![COMPETITOR
ANALYSIS
IDENTIFYING
COMPETITORS
[OBJECTIVES AND
STRATEGIES]
ANALYZING
COMPETITORS
[STRENGTHS AND
WEAKNESSES]
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitoranalysis-200119072009/85/Competitor-analysis-2-320.jpg)

![A] FIVE MATTERS
1) Who are our competitors?
2) What are their objectives?
3) What are their vision and mission?
4) How is the approach of their reaction?
5) What is their strategy?
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitoranalysis-200119072009/85/Competitor-analysis-4-320.jpg)
![B] TWO VIEWPOINTS
Identifying competitors at
industrial concept
Number of sellers [pure
monopoly, pure oligopoly,
differentiated oligopoly, monopolistic
competition, perfect competition]
Entry and mobility barriers
Exit and shrinking barriers
Cost structure
Vertical integration
Global reach
Price
Identifying competitors at
market concept
In context of customers
and not industry
Satisfaction of customers
Customer at the center
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitoranalysis-200119072009/85/Competitor-analysis-5-320.jpg)

![A] IDENTIFICATION OF STRENGTHS
USP in product
Quality of product
Low cost product
Production capacity
Distribution arrangements
Staff
Effective media of advertisements
Quick response to complaints/feedback
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitoranalysis-200119072009/85/Competitor-analysis-7-320.jpg)
![B] IDENTIFICATION OF WEAKNESSES
Lower production capacity
Limitation of higher production
Lack of training and lack of experts too
Limited monetary instruments
No modern technology [R&D]
Improper logistics
Financial weakness
Marketing of product
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitoranalysis-200119072009/85/Competitor-analysis-8-320.jpg)
![C] IDENTIFICATION OF OPPORTUNITIES
High cost of competitor’s product
High price of competitor’s product
Low quality product of the competitor
Problems in distribution channel of competitor
No awareness of brand of competitor
Loss to competitor
Failure of executed strategy of competitor
Traditional methods of production (no advanced
technological methods used)
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitoranalysis-200119072009/85/Competitor-analysis-9-320.jpg)
![D] IDENTIFICATION OF THREATS
Cost advantages to competitor
Low price of competitor’s product
High or good quality of competitor’s product
Widespread distribution channel
Product or market development
Supplier power
Technological progress by competitor
Success of newly executed strategies
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitoranalysis-200119072009/85/Competitor-analysis-10-320.jpg)
![E] CUSTOMER AND COMPETITOR
BALANCE BETWEEN CUSTOMER AND COMPETITOR
COMPETITORS ORIENTED COMPANY
CUSTOMERS ORIENTED COMPANY
customer
competitor
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitoranalysis-200119072009/85/Competitor-analysis-11-320.jpg)
![F] COMPETITOR’S REACTION
It is important to know about the competitor’s particular
beliefs regarding way of doing business on the basis of a
reaction pattern by such competitor
Different types of competitor :
The laid back competitors
The selected competitors
The tight competitors
The stochastic competitors
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitoranalysis-200119072009/85/Competitor-analysis-12-320.jpg)
![G] COMPETITORS TO ATTACK AND AVOID
An important part in the process of analyzing competitors.
To understand their strengths and their weaknesses on the
basis of types of competitor.
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitoranalysis-200119072009/85/Competitor-analysis-13-320.jpg)
![H] TYPES OF COMPETITORS
STRONG WEAK
BAD
DISTANTCLOSE
GOOD
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitoranalysis-200119072009/85/Competitor-analysis-14-320.jpg)