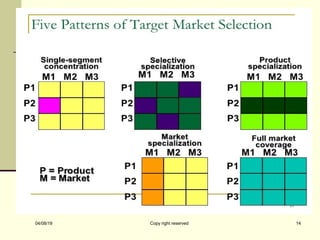
Market segmentation involves dividing a large heterogeneous market into smaller homogeneous segments based on characteristics like geography, demographics, psychographics, and behavior. The key steps are identifying segments, profiling them, selecting target segments, and positioning products to occupy a clear place in customers' minds. Marketers must choose segmentation variables to group customers with similar needs and select the most attractive segments to target based on size, growth, profitability, and organizational fit.