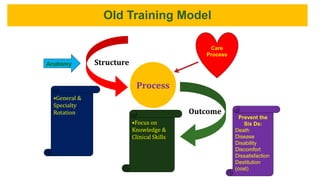
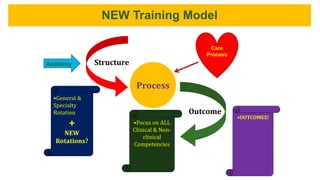
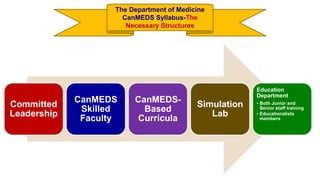
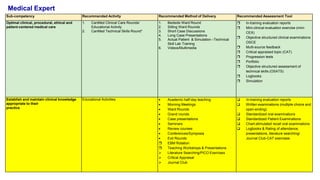
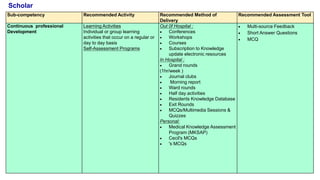
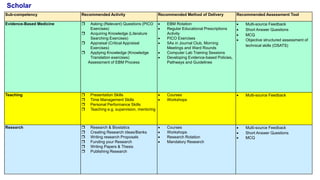
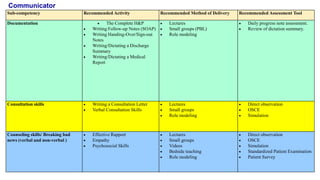
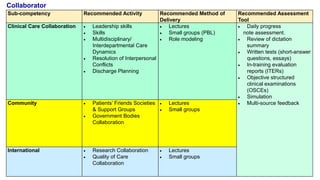
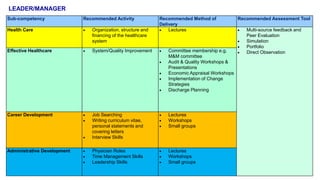
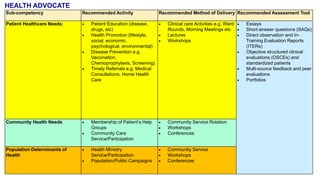
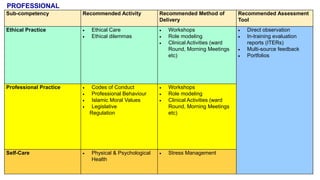
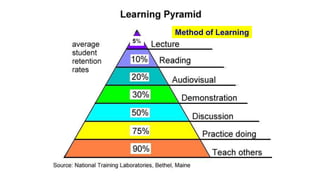
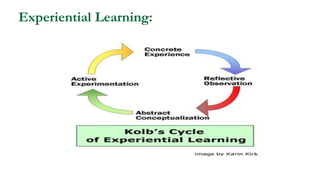
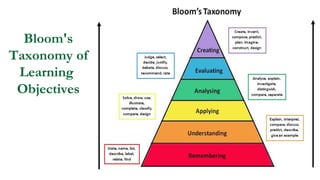
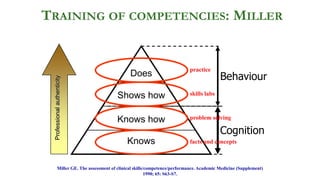
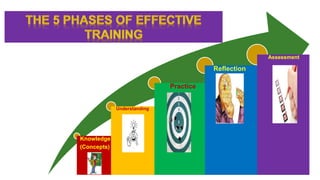
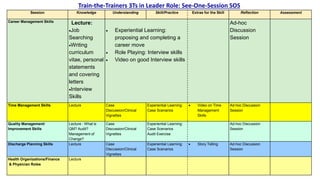
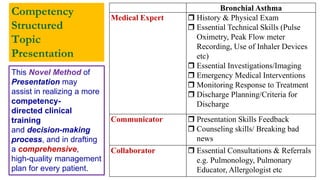
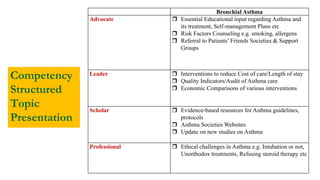
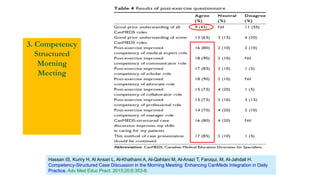
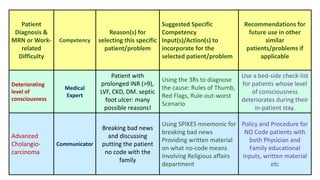
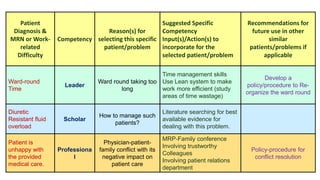
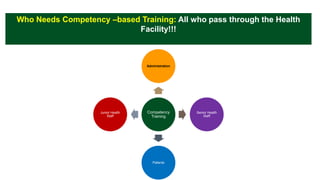
This document outlines plans to restructure medical training at an institution to a competency-based model. It discusses transforming the curriculum, faculty development, assessment tools, and training processes. The plans include establishing competency-focused committees and faculty/resident teams. Training workshops will develop materials for each CanMEDS competency. Assessment tools like online logbooks and end-of-rotation evaluations will evaluate competencies. Educational activities like ward rounds and morning meetings will highlight competencies. The overall goal is to implement a competency-based medical education approach to improve training outcomes.