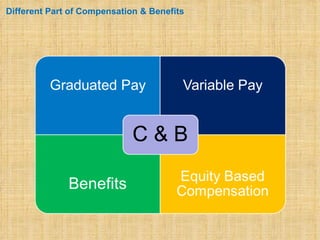
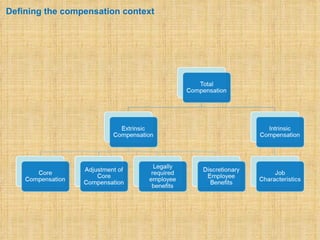
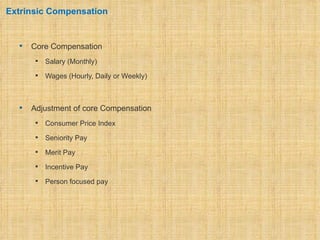
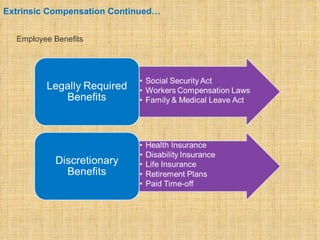
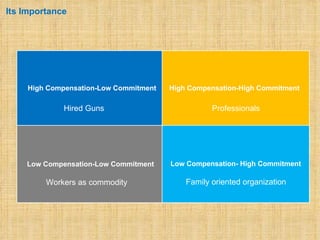
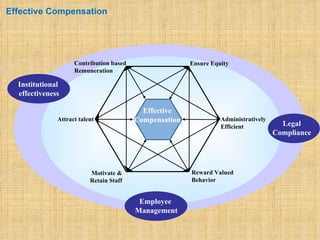
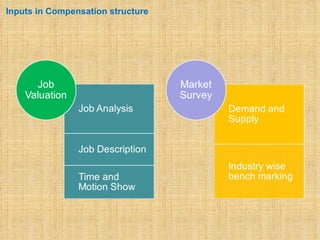
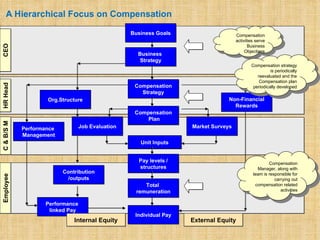
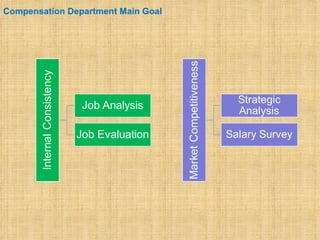
The document discusses compensation and benefits. It defines compensation as payment to employees for their contributions, which usually takes the form of wages and salaries. Benefits are non-payment forms of value provided to employees like healthcare. The document outlines different types of compensation including core compensation, adjustments, incentives and benefits. It discusses the purposes of compensation for both employers and employees. Factors that influence compensation and the constituents and laws around compensation structures are also examined. The goals of compensation professionals and departments are defined as aligning compensation with business objectives and strategy.