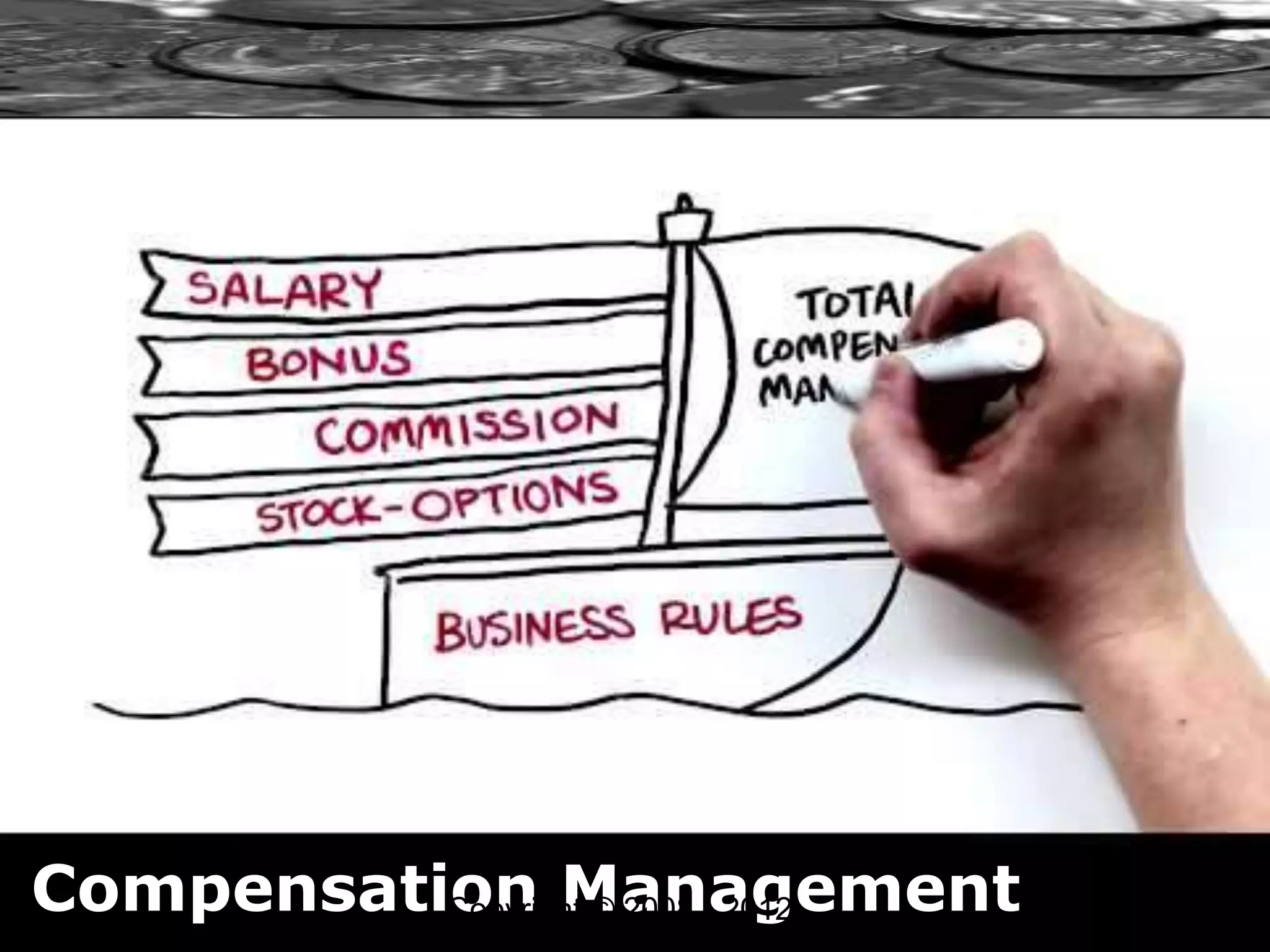
A global pharmaceutical company was losing executives in their mid-thirties to competitors. An investigation found this was due to compensation issues, as the company focused on long-term incentives and post-retirement benefits rather than current pay. It was recommended that the compensation package be redesigned to increase take-home pay for younger employees by reducing deferred benefits. The document then provides an overview of compensation management principles, theories, and practices.