This document provides an overview comparing NetBSD and Linux operating systems for embedded systems. Both systems are highly portable and POSIX compliant, with active development, but they differ in key areas like memory footprint, process scheduling, threading models, debugging support, and availability of drivers. NetBSD emphasizes reduced size and portability while Linux prioritizes functionality and third-party support. The document examines features and tradeoffs to help choose between the two for embedded applications.





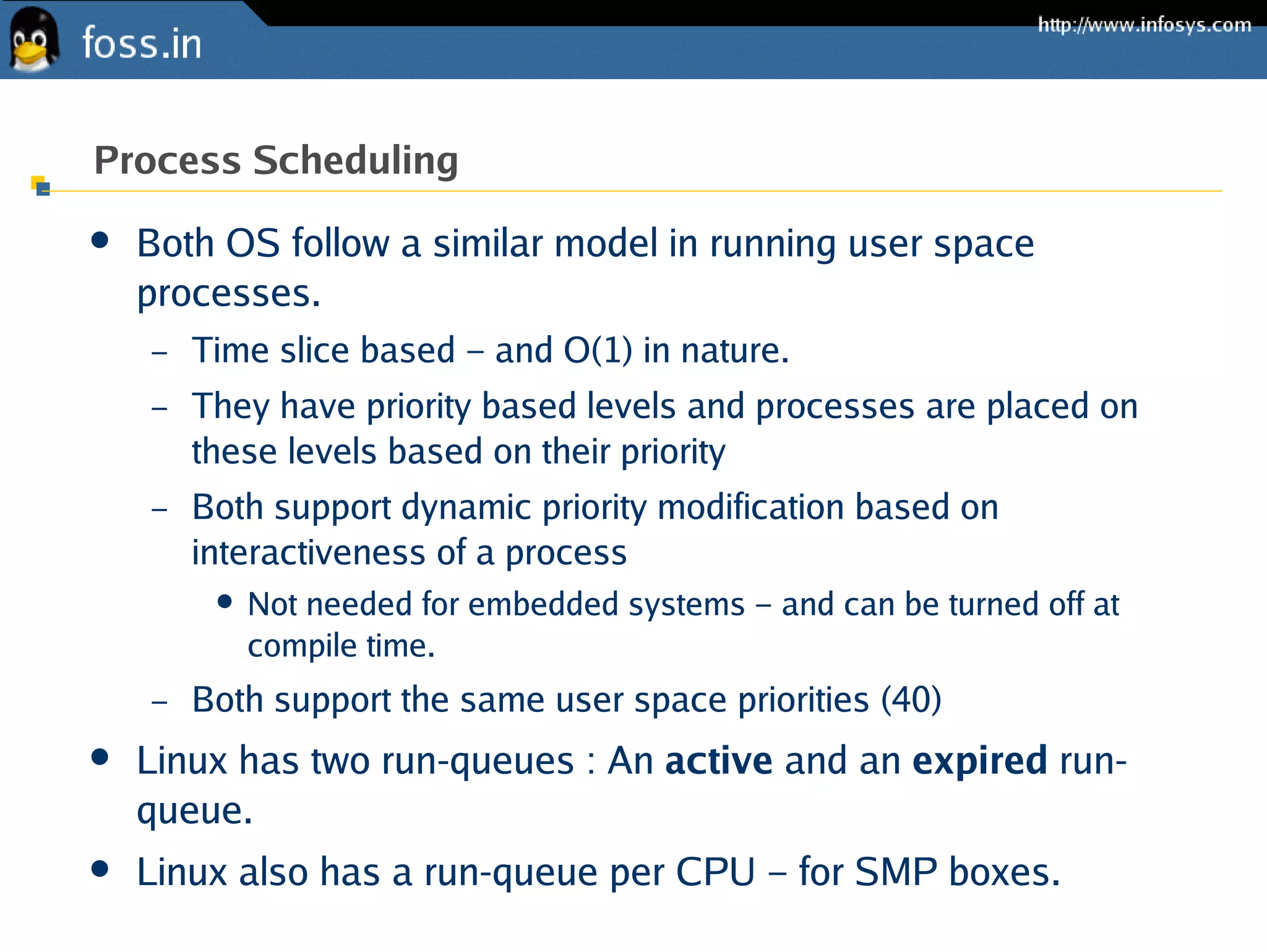
![Process Run-queue
RunQueue
Doubly linked lists of tasks
Active
Task 1 Task 2 ... Task N [Priority: 1]
...
Task 1 Task 2 Task M [Priority:140]
Expired
...
...
Migration Thread
From kernel/sched.c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/netbsd-linux-121102035019-phpapp01/75/NetBSD-and-Linux-for-Embedded-Systems-8-2048.jpg)