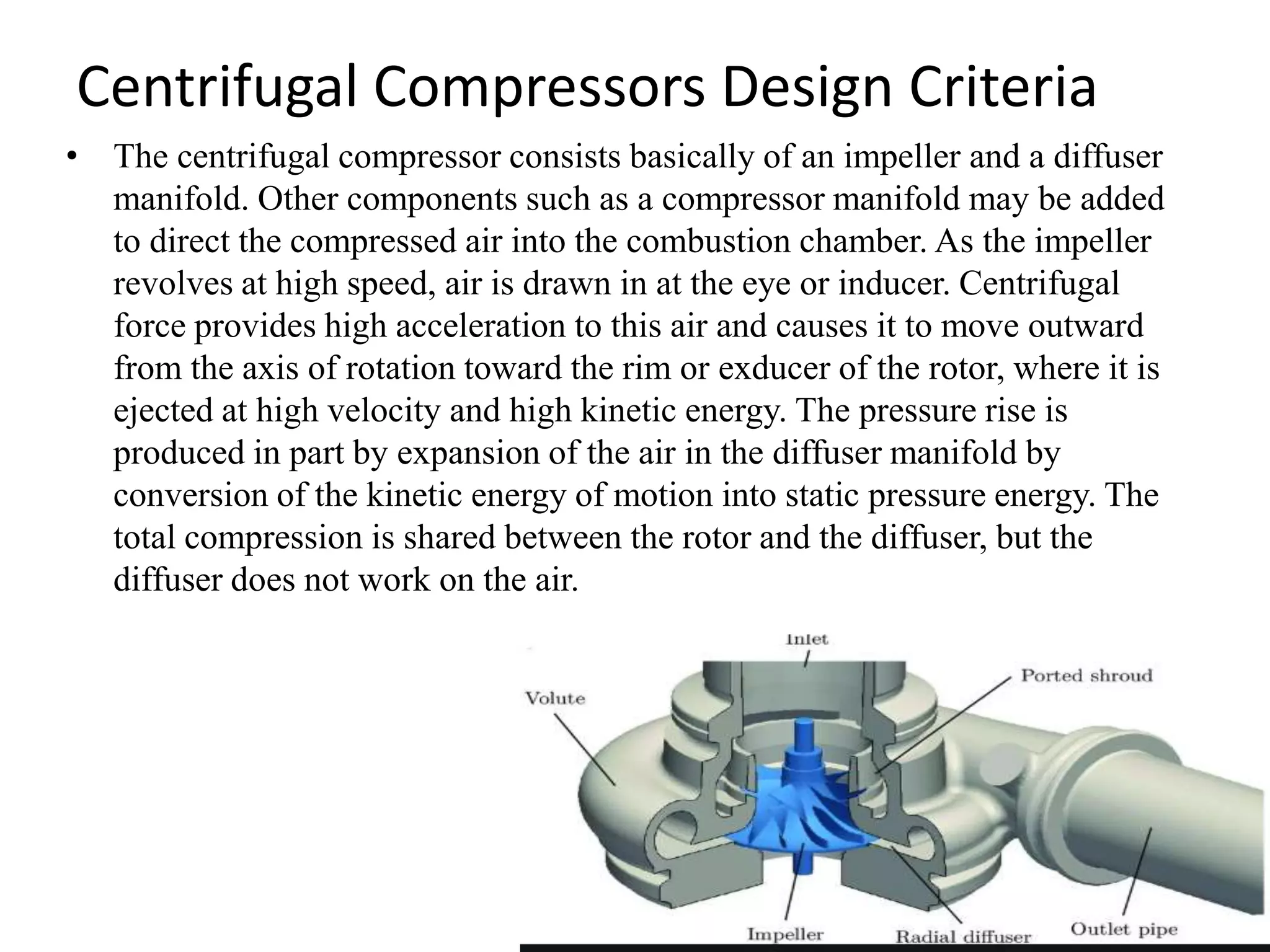
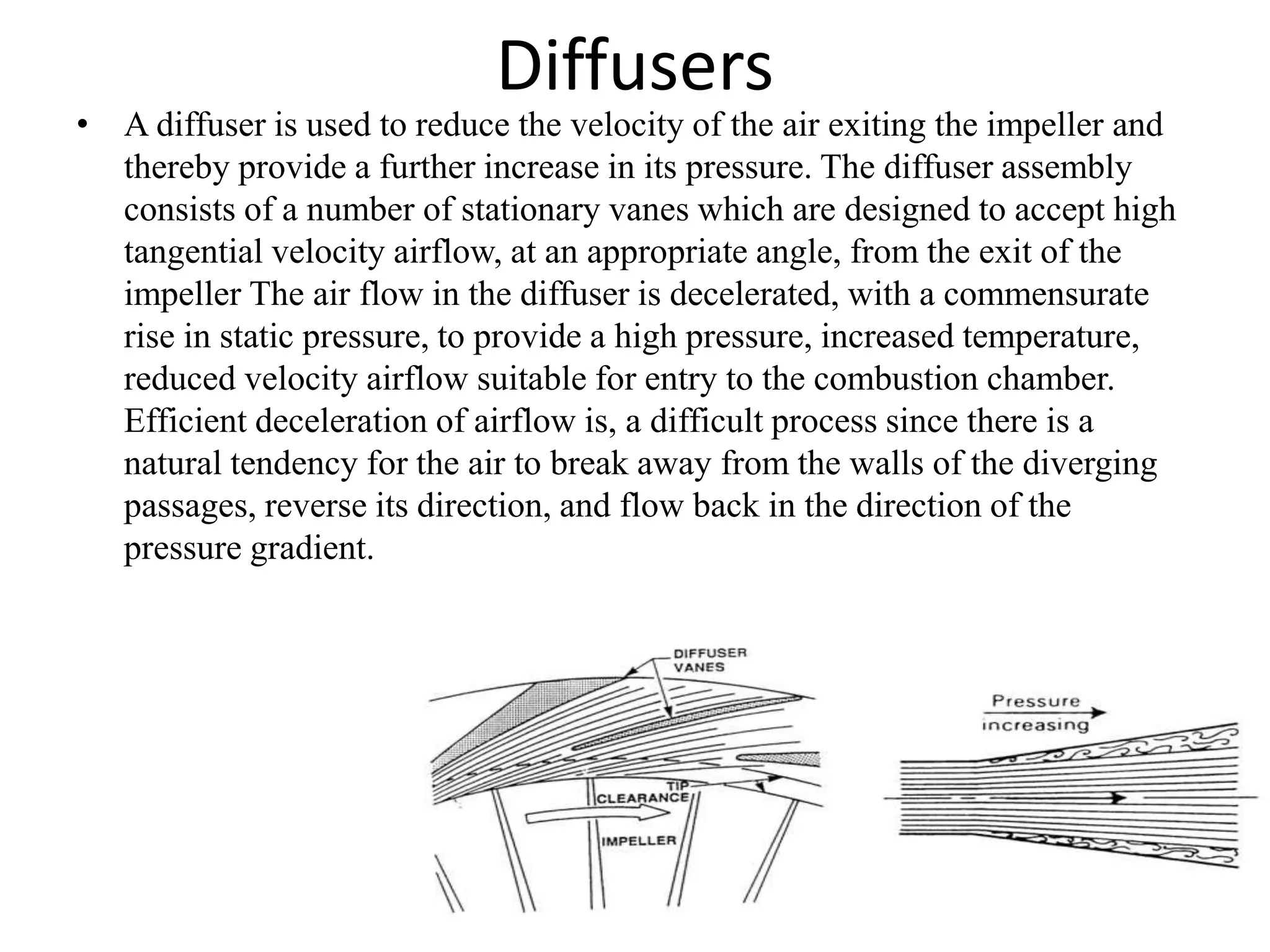
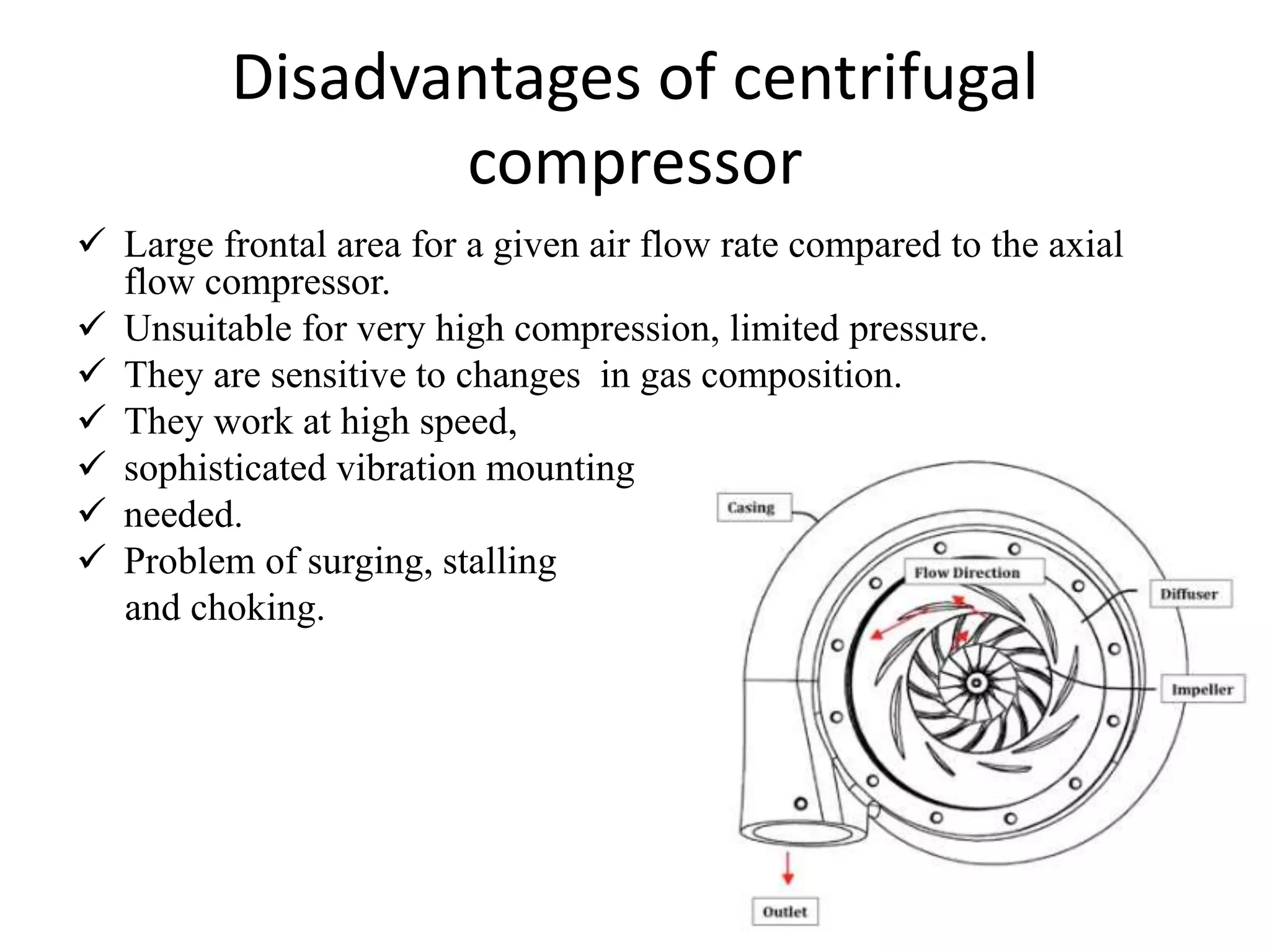
Centrifugal compressors work by accelerating air radially outward between impeller vanes via centrifugal force, increasing pressure. Axial compressors compress air flowing parallel to the axis using multiple rotor and stator stages. Centrifugal compressors are commonly used in industrial applications while axial compressors are used in jet engines due to their high efficiency at large flow rates. The key differences are that centrifugal compressors have higher pressure ratios per stage but are limited to lower pressures overall, while axial compressors can achieve higher pressures through multiple stages but are more complex, heavy, and expensive.