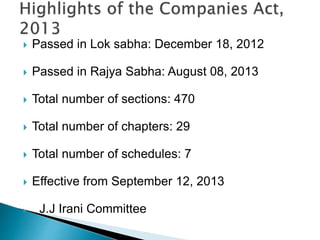
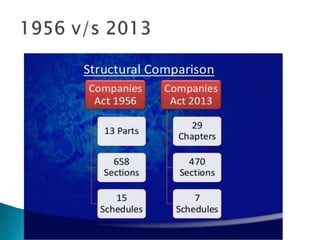
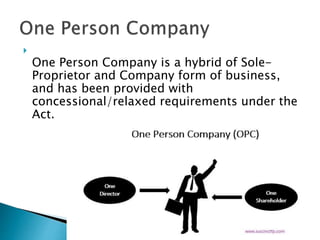
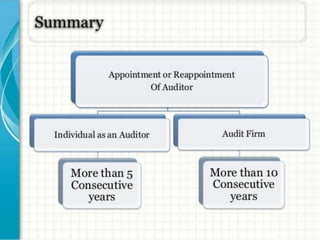
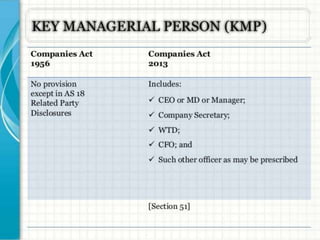
The document discusses key aspects of company law in India. It provides definitions of a company and its characteristics like corporate personality and limited liability. It traces the history of company law in India and summarizes the key aspects of the Companies Act of 2013 like increased transparency, recognition of new business structures like One Person Companies, and mandatory requirements for women directors and auditing rotation.