The Indian Contract Act 1872 establishes the framework for contracts in India. It aims to ensure that rights and obligations from contracts are upheld and legal remedies are available for breaches. The Act applies across India except Jammu and Kashmir. It covers the basic principles of contracts, indemnity, guarantee, bailment, and agency. A contract requires an offer and acceptance, lawful consideration, capacity and consent to contract, a lawful objective, and certainty of terms. The Act defines different types of contracts based on their validity, formation, and performance requirements.





















![Types of Contract – On the basis of
Validity
• Valid contract: An agreement which has all the essential elements of a
contract is called a valid contract. A valid contract can be enforced by
law.
• Void contract[Section 2(g)]: A void contract is a contract which ceases
to be enforceable by law. A contract when originally entered into may
be valid and binding on the parties. It may subsequently become void.
-- There are many judgments which have stated that where any crime
has been converted into a "Source of Profit" or if any act to be done
under any contract is opposed to "Public Policy" under any contract—
than that contract itself cannot be enforced under the law-
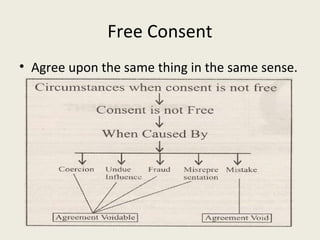
• Voidable contract[Section 2(i)]: An agreement which is enforceable by
law at the option of one or more of the parties thereto, but not at the
option of other or others, is a voidable contract. If the essential element
of free consent is missing in a contract, the law confers right on the
aggrieved party either to reject the contract or to accept it. However,
the contract continues to be good and enforceable unless it is
repudiated by the aggrieved party.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indiancontractact1872-120924222037-phpapp02/85/Indian-contract-act-1872-23-320.jpg)
























