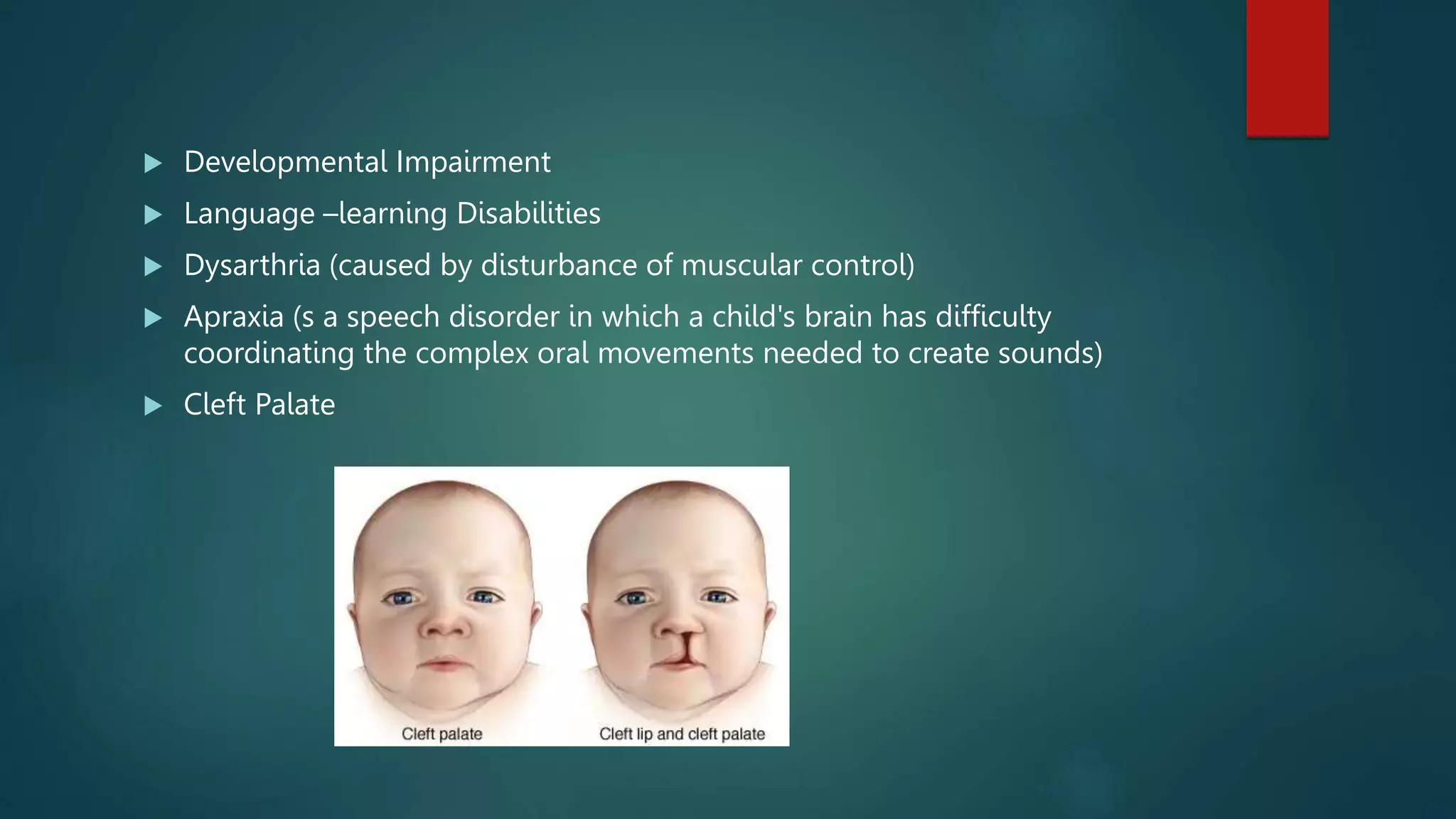
This document provides an overview of communication disorders and delays. It discusses that communication disorders encompass any impairment in receiving, sending, processing or comprehending verbal or non-verbal concepts. Communication delays refer to delays in meeting age-specific communication milestones. It outlines the abilities needed for speech including motor and mental abilities. The document also describes different types of language skills, communication disorders including hearing, language and speech disorders, and provides details on fluency disorders, voice disorders and articulation disorders.