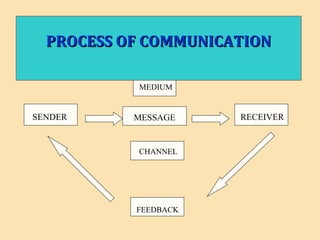
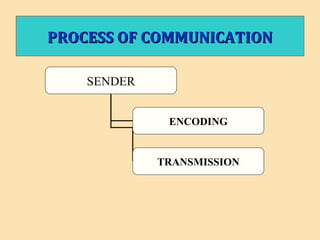
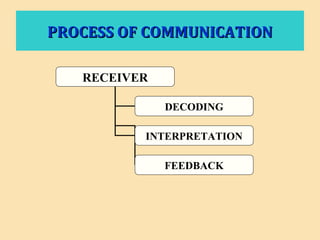
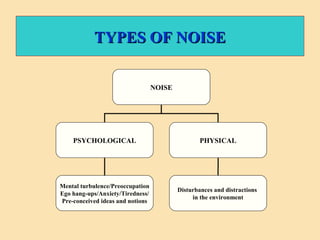
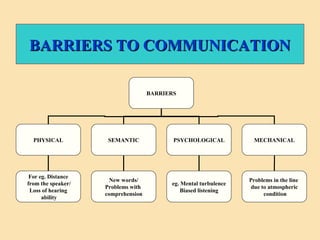
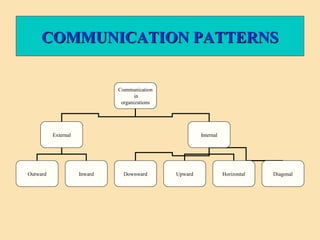
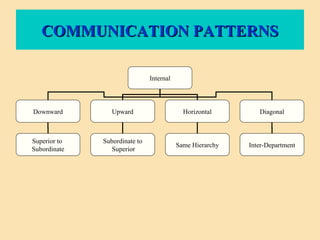
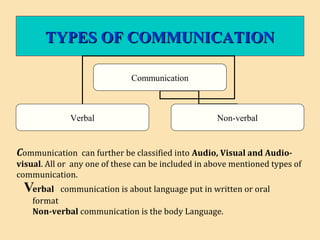
The document discusses the significance of communication skills in personal and professional contexts, highlighting that these skills can be developed and improved. It outlines the communication process, principles, barriers, and effective strategies to enhance communication, including the seven 'C's of communication and the role of feedback. Additionally, it differentiates between verbal and non-verbal communication, emphasizing their importance in conveying messages effectively.