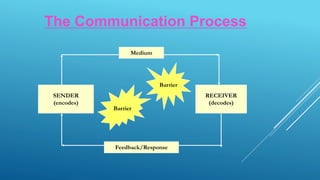
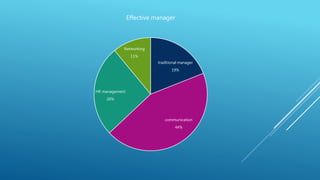
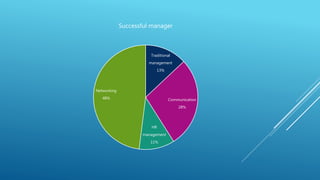
This document discusses communication skills and provides definitions of communication from various authors. It outlines the key components of the communication process, including the context, sender, message, medium, receiver, and feedback. It also discusses the benefits of communication, such as problem solving and decision making. Additionally, it provides tips on improving communication skills and overcoming barriers to effective communication.