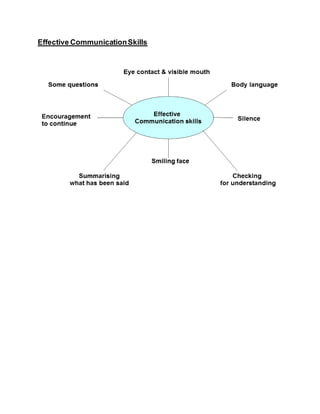
This document discusses communication and effective communication skills. It notes that communication is a dynamic process through which thoughts and feelings are conveyed to others, but how the message is received depends on the experiences and context of the receiver. While words account for only 7% of communication, paralinguistic elements like tone and body language account for 38% and 55% respectively. Barriers to effective communication can come from the communicator, such as a lack of self-awareness or confidence, or from the receiver, like selective perception or prejudice. External barriers like noise or status differences can also interfere with communication. Improving listening skills and understanding different types of body language can help enhance communication.