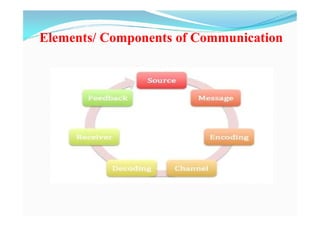
This document discusses communication in a healthcare context. It defines communication as the sharing of information between individuals through speech, signals, writing or behavior. The document outlines the purpose of communication as the flow of information, coordination, learning skills, and accepting change. It discusses the importance of communication for action, planning, coordination, decision-making and motivation. The document also covers the elements, principles, types, levels and barriers of communication.