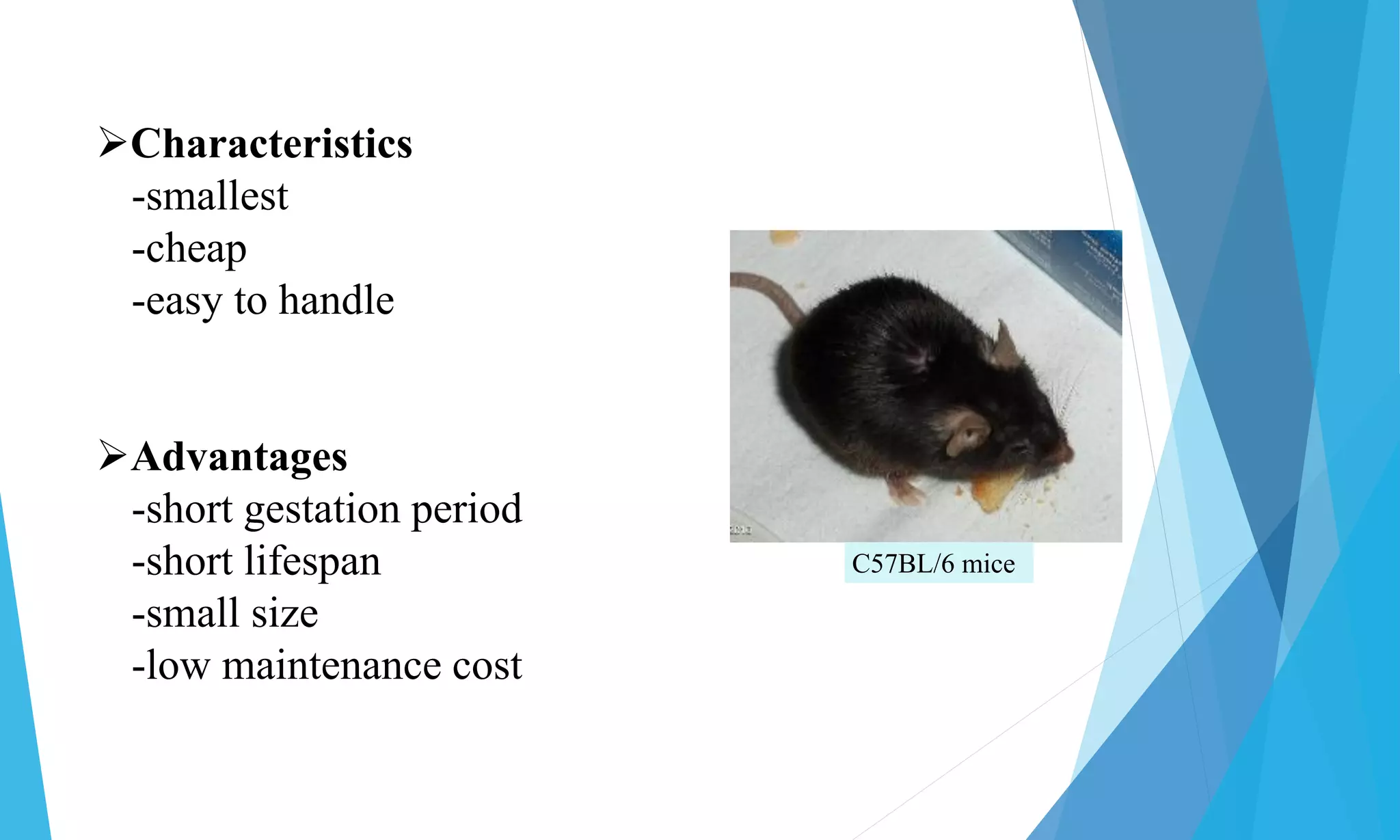
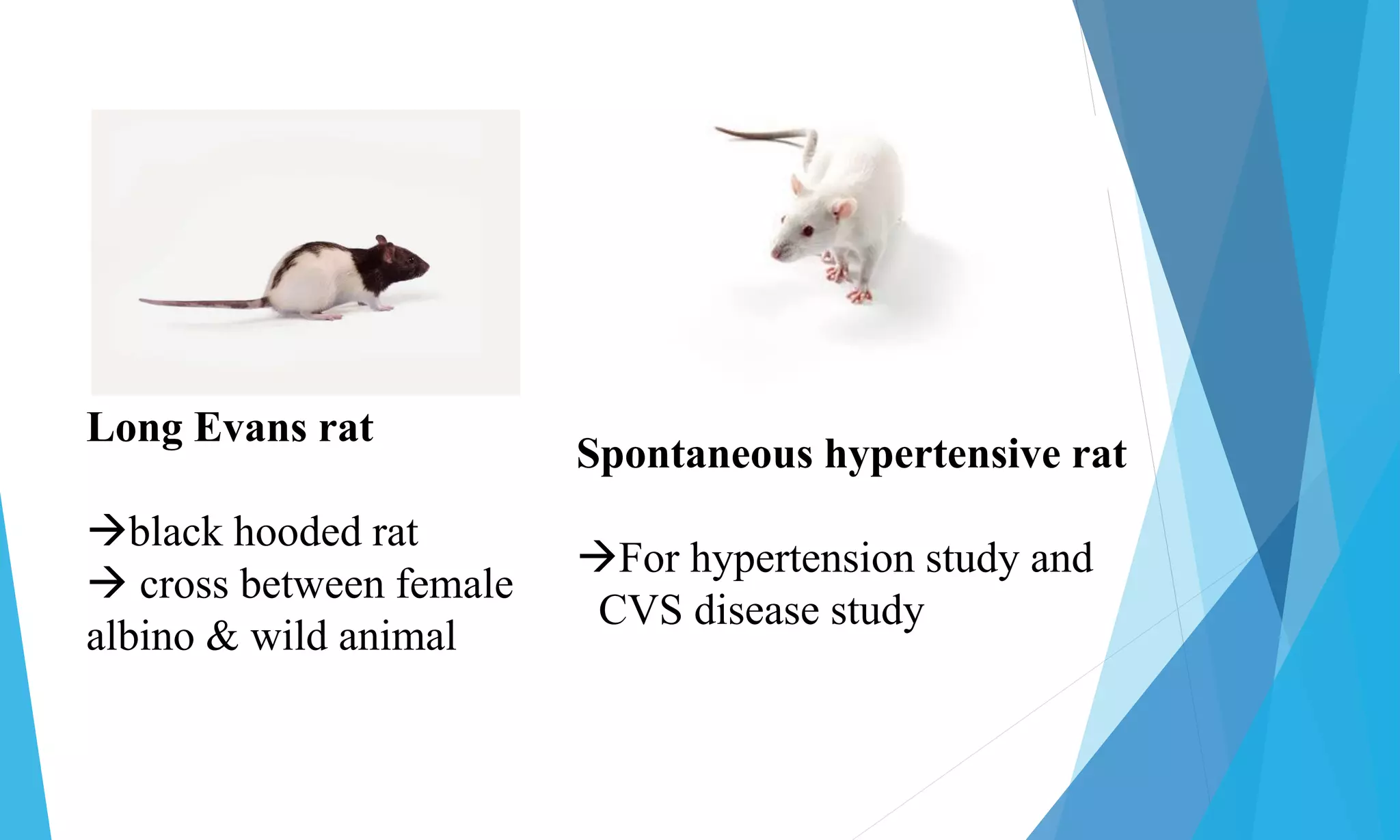
The document outlines common laboratory animals, their characteristics, biological names, and experimental uses. It covers a variety of species including mice, rats, guinea pigs, frogs, rabbits, hamsters, monkeys, cats, gerbils, dogs, pigs, chickens, and pigeons. Each animal's unique qualities facilitate specific types of research and experimentation in areas like pharmacology, toxicology, and genetics.