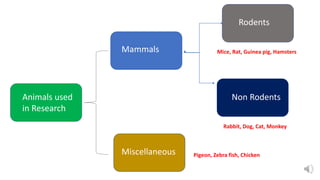
Common laboratory animals used in drug development include rodents like mice and rats as well as non-rodents. Non-rodent models discussed in the document include rabbits, monkeys, cats, dogs, frogs, zebrafish, chickens, and pigeons. Rabbits are used for pyrogen testing due to their resistance to atropine. Monkeys such as rhesus monkeys and squirrel monkeys are used due to their similarity to humans, though squirrel monkeys are smaller making them easier to handle. Cats and dogs are also used for research due to their similarities to humans. Frogs have provided a new class of antibiotic compounds and zebrafish are used for genetic research due to external fertilization. Chick