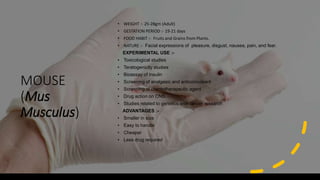
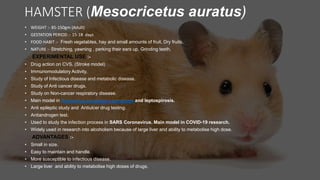
This document summarizes commonly used experimental animals in pharmacology research including mice, rats, guinea pigs, gerbils, hamsters, rabbits, frogs, dogs, pigs, and monkeys. For each animal, it provides details on weight, gestation period, diet, behaviors, and their typical uses in experiments. The aims of experimental pharmacology are to identify safe and effective therapeutic agents, study drug efficacy and toxicity, and understand drug mechanisms and sites of action. Proper handling and care of laboratory animals is important to avoid unnecessary pain or suffering.