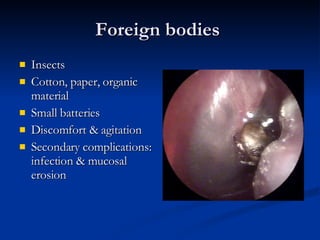
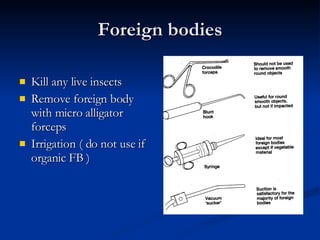
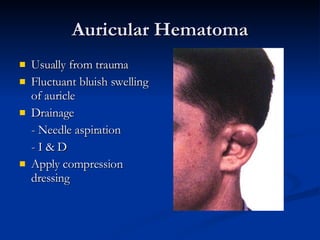
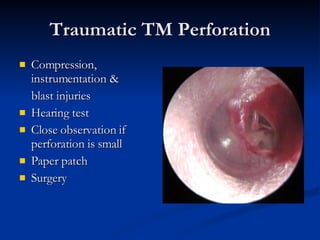
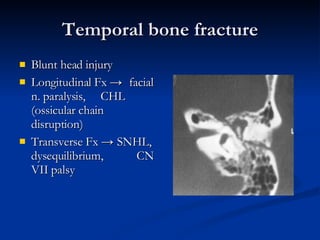
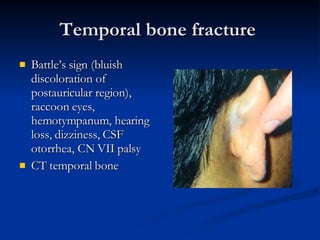
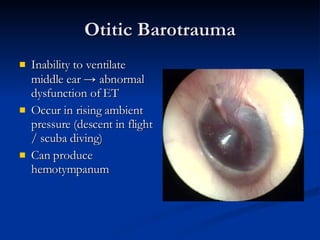
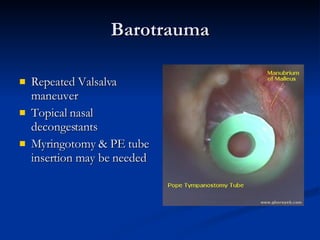
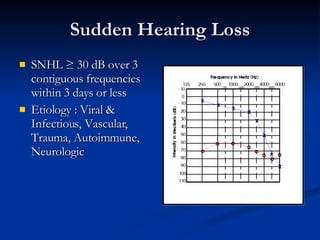
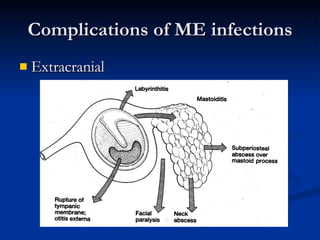
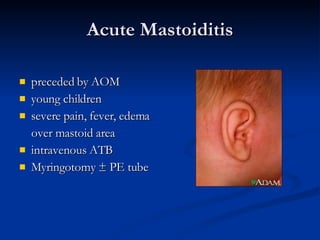
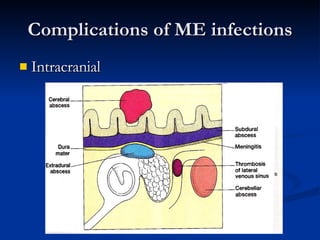
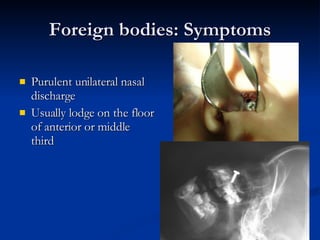
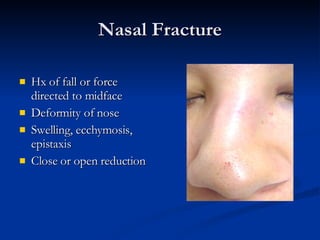
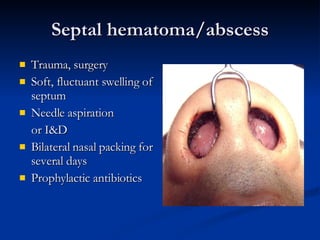
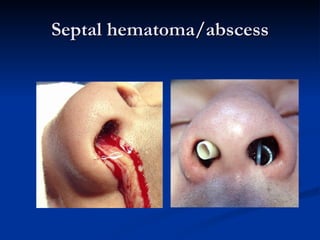
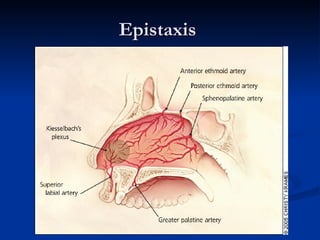
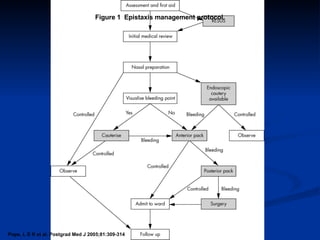
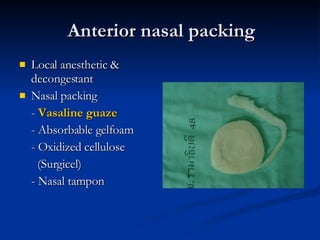
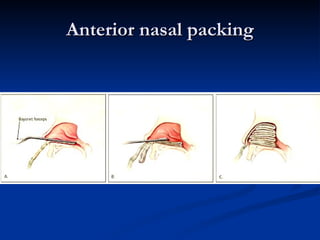
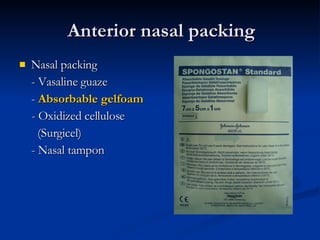
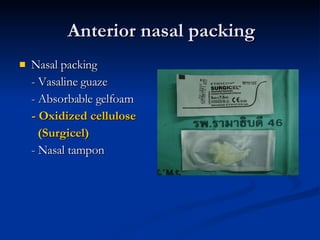
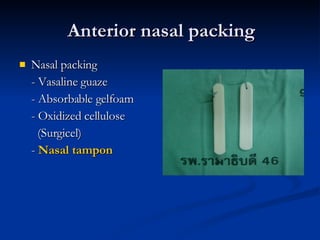
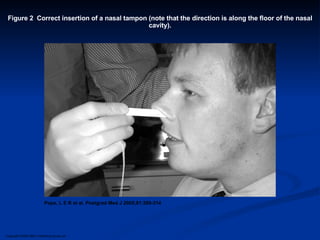
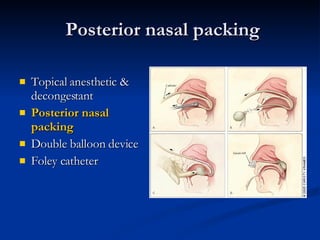
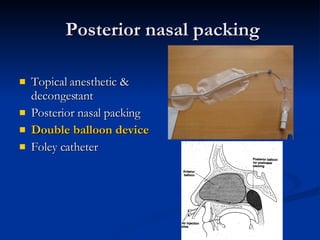
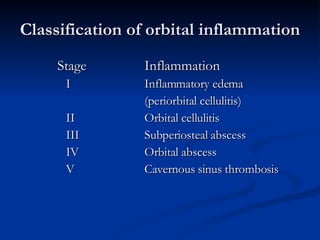
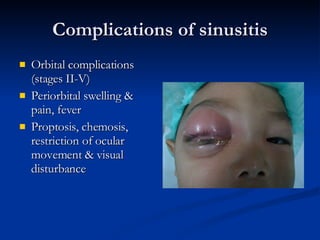
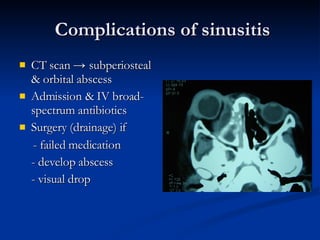
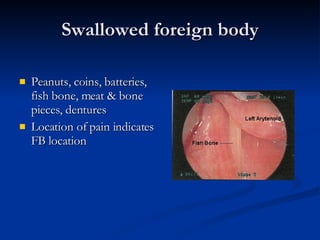
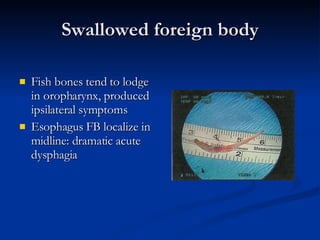
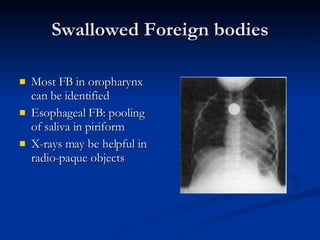
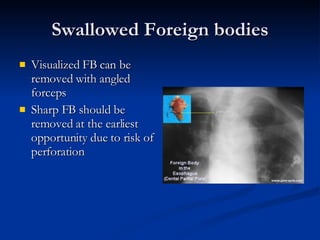
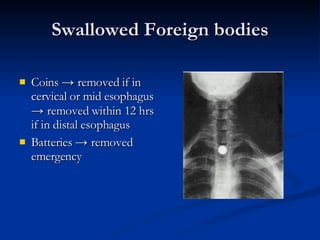
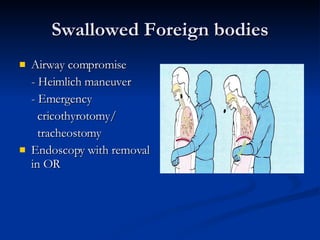
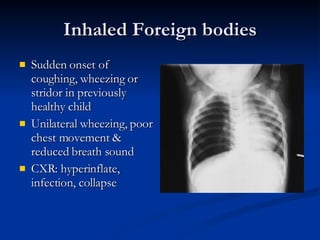
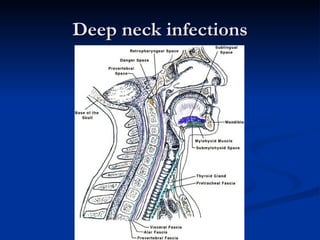
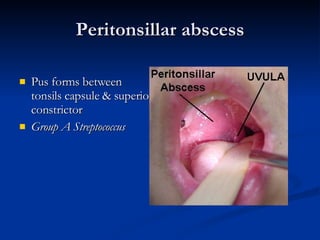
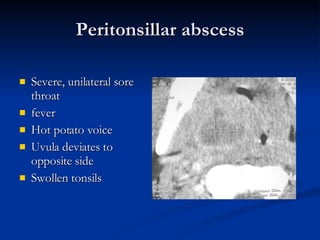
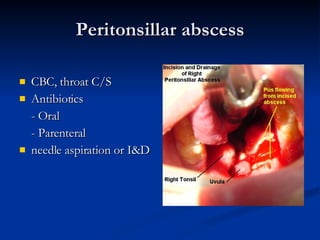
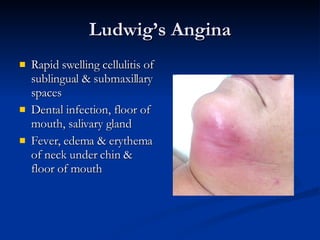
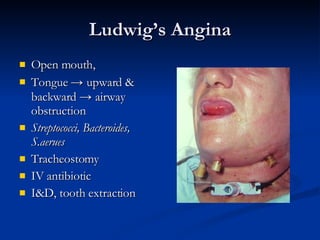
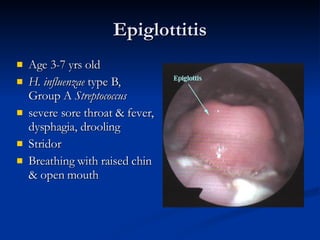
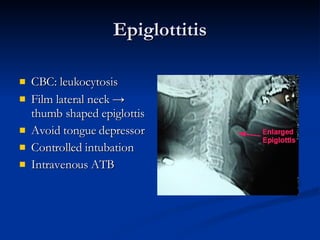
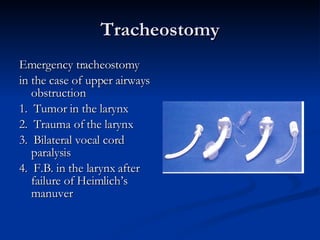
Common ENT emergencies include foreign bodies, trauma, and complications of infections in the ear, nose, and throat. Foreign bodies in the ear can cause discomfort and infection if not removed. Epistaxis (nosebleeds) may be caused by trauma, dry air, or medical issues and are typically managed first by applying pressure and then treatments like cauterization if needed. Infections of the sinuses can lead to orbital or intracranial complications requiring intravenous antibiotics or surgery. Deep neck infections like peritonsillar abscesses or Ludwig's angina require needle aspiration, drainage, or tracheostomy. Airway obstruction emergencies are treated by securing the airway through maneuvers like Heimlich