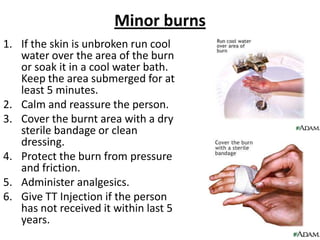
This document outlines common emergency situations and treatments including minor burns, major burns, dog bites, and choking. It provides detailed first aid instructions for each such as running cool water over minor burns, wrapping major burns, cleaning and dressing dog bites, and performing back slaps or abdominal thrusts to treat choking. Key steps are summarized for each emergency like elevating burned areas, preventing infection from dog bites with immunoglobulins, and performing CPR if choking is severe.