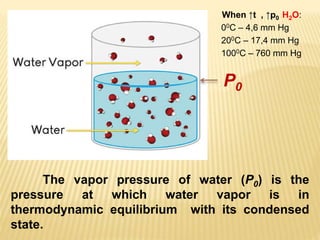
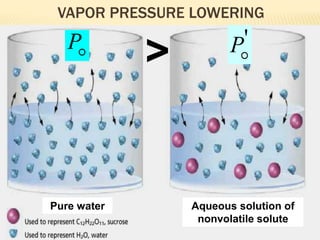
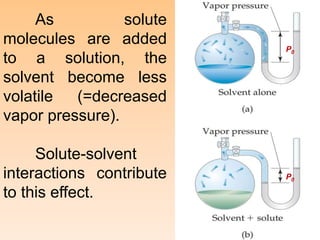
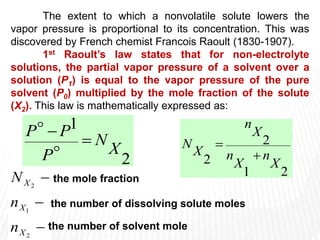
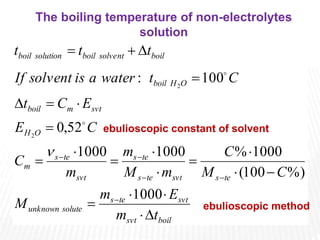
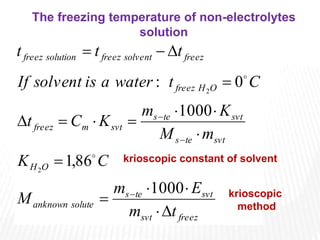
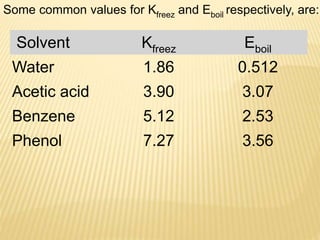
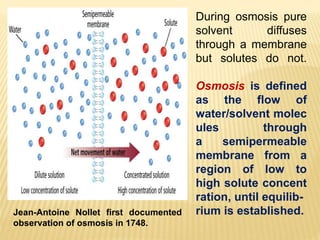
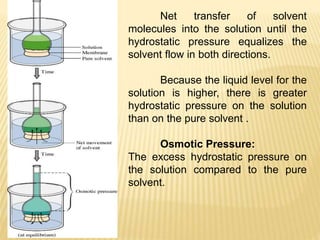
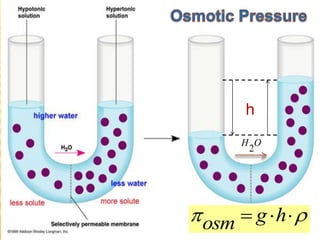
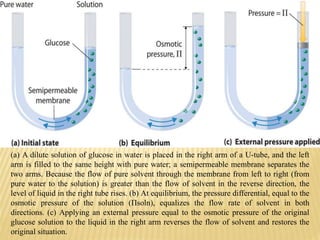
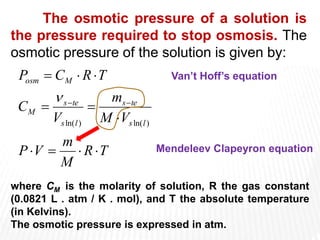
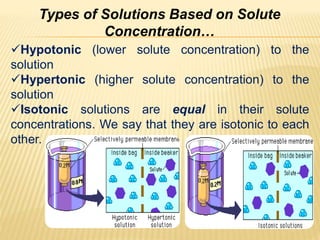
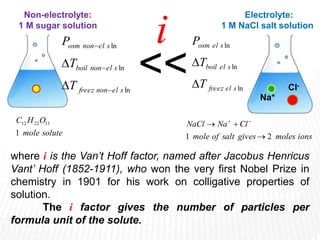
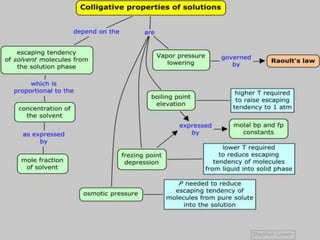
This document provides information about different types of solutions and their properties. It discusses true solutions as homogeneous mixtures containing a solute dissolved in a solvent. Properties like vapor pressure lowering and boiling/freezing point changes depend on solute concentration and are known as colligative properties. Osmotic pressure, the pressure required to stop osmosis across a semipermeable membrane, can be calculated using Van't Hoff's equation and depends on solute molarity. Solutions can also be classified as hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic based on their solute concentrations.