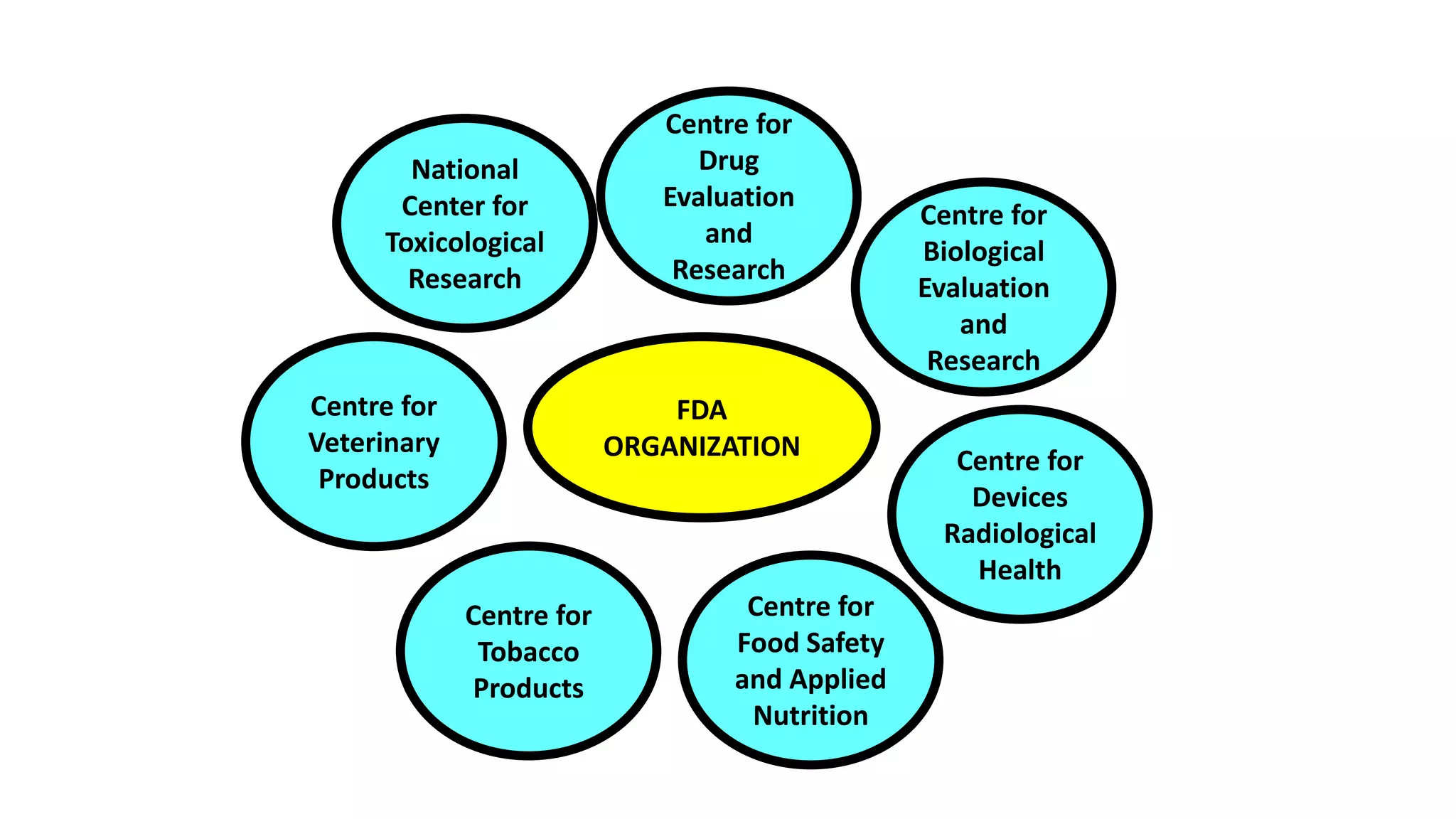
The document provides an overview of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21 Parts 210 and 211, which establish the Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) regulations for the manufacturing, processing, packing, or holding of drugs. It discusses the history and purpose of the FDA and CFR. It also summarizes key aspects of Parts 210 and 211, including definitions, facility requirements, quality control responsibilities, equipment and utensil cleaning procedures, and material receipt and testing standards. The regulations are intended to ensure that drugs are safe for use and have the ingredients and strength claimed.